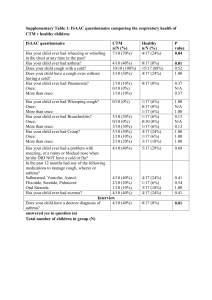
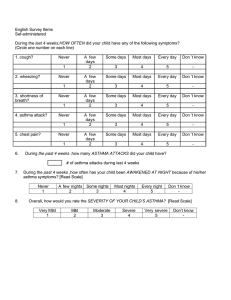
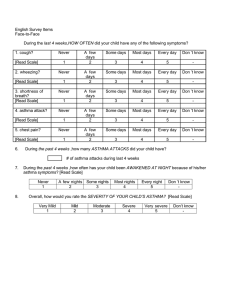
Respiratory Pharmacology Bronchial Asthma الربوالشعبى Bronchial Asthma Inflammation Bronchial Hyper-responsiveness Reversible airway obstruction AIRWAY HYPER-RESPONSIVENESS Bronchi constrict easily to a wide range of specific or nonspecific stimuli (Triggers) that are too weak to affect non- asthmatics Shortness of breath, wheezing يزيق, chest tightness & cough Causes Genetic Environmental النسيج,سمنت4 ا, مصانع الرخام, drugs, cold weather, exercise Home dust, العثmites بد التهوية و الشمس4 mites Chronic obstructive pulmonary diseaseزمنDنسدادي ا4مرض الرئة ا 2 diseases Chronic bronchitis + mucus Emphysema Irreversible Asthma reversible by drugs Drug Therapy of Bronchial Asthma As needed Daily 1. Short-acting b 2-agonists (rapid; 1st 1. Corticosteroids (CS) choice). salbutamol 2. Long acting β2-agonists 2. Antimuscarinics 3-Methyl xanthines (theophylline) . +CS,( not alone). Salbutamol If the patient chronic give oral drugs If the patient acute give IV or inhalation drugs Bronchodilators Relieve acute bronchospasm Antimuscarini c Β2 agonist Muscarinic receptors adenylyl cyclase Ton e Vagus nerve β2receptors cAMP Tone Adenosin e receptors Block Ton e Adenosine Antimuscarinic Drugs (atropine xxx) (Ipratropium Bromide) BLOCK M3 RECEPTORS IN BRONCHIAL MUSCULATURE → BLOCK VAGALLY-MEDIATED BRONCHOSPASM AND MUCUS SECRETION Uses: 1. Bronchodilator of choice when 2- agonists & theophylline are CI (e.g. cardiac & thyrotoxic patients). 2. Adjuvant to 2- agonists or theophylline in A. severe asthma Disadvantages: 3T, H 1. Tolerance: block M2 R 2. Delayed onset of action ↑ ACh release ↓ its own effect. (Ipratropium Bromide) Iتروب4ابن عم ا Quaternary not cross blood brain barrier Atropine…….sedation, dryness,, hotness, constipation SADHc not present More selective to bronchi No systemic action as atropine Ipratropium Bromide With combivent beta 2 agonist مع بعضIثن4ا cAMP Phosphodiesterase Enzyme 3,4 GAMP Antiinflammatory Bronchodilation Relaxation of smooth muscles Blocks adenosine receptors Aminophylline is a drug combination of theophylline and ethylenediamine in a ratio of 2 to 1. it serves to solubilize the active ingredient theophylline. I.V. infusion to avoid tachycardia no inhalation due to irregular absorption Theophylline For Chronic asthma give Quibron T-SR tablet theophylline tablet For acute asthma give aminophylline I.V. infusion 1520 minutes no inhalation due to irregular absorption Uses 1. Bronchial asthma: 2nd line drug to β2-agonists 2. COPD :Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Other uses xanthine's 1. CNS stimulation 2-for migraine •Cafergot for migraine due to vasoconstriction due to synergism ergotamine and caffeine cerebral between Adverse Effects (Limit its use) 1. CNS stimulation Insomnia – Anxiety -Tremors – convulsions headache 2. GIT: ↑HCl ,Gastric irritation Peptic ulcer xxx 3. CVS: Hypotension, arrhythmias and cardiac arrest arrhythmias xxx ↑HC l Precautions 1- If used orally, it is taken with food to avoid gastric ulcer 2- If used IV, it is injected very slowly to avoid cardiac arrest 3- Plasma level should be monitored (narrow therapeutic index) 4- Adjust the dose in age extremes, liver disease, HF, heavy smokers and if used with enzyme inducers or inhibitors Antiinflammatory Long Term Control of Persistent Asthma Corticosteroids Mainstay of Therapy Immunosuppressants Antiinflammatory Potentiate β2 agonists (↓downregulation of β2 R ↓tolerance). CS Preparations Inhalation: acute asthma Beclomethazone (↓ systemic adverse efects) 2. Oral: Prednisolone or dexamethasone. 3. I.V.:hydrocortisone (it is used in emergency). Acute asthma : Hydrocortisone injection for emergency Or inhalation bechlo Beclomethazone Adverse Effects Oropharyngeal candidiasis Due to Cortisone immune suppressant 2. Salt and water retention, hypokalemia ياكل موز و موالح 3. edema. Give diuretic Minimized by: Gargling & spitting Drug Therapy of Cough peripheral cough receptor in bronchi ترسل رسائل الى Cough centers in medulla (central) •الى يعطى اشارة respiratory muscle in alveoli contraction مدة الكحة •Less than 3 weeks……………acute cough •More than 8 weeks …………… chronic cough •More than 3 weeks and less than 8 weeks …………… subacute cough •Dry or wet Drug Therapy of Cough Dry (non-productive cough): Treated by: Antitussives (Cough Suppressants) Productive cough: Treated by: Mucolytics and expectorants Antitussives Central Antitussives 1. Opioid antitussives: inhibits cough center a- Codeine & Hydrocodone : b- Dextromethorphan: Less addictive -no respiratory depression – no constipation. 2. Antihistamines (1st G) (Diphenhydramine) Peripheral Antitussives 1. Volatile oils (menthol and camphor): Protect irritant receptors by a mucin layer (demulcents). 2. Benzonatate: - local anesthetic effect on irritant receptors in respiratory mucosa. Thin film of water steam or volatile oils on bronchi wall Demulcent effect تلطف Tincture benzoin compound صنغ جاوة Expectorants (1st line) liquefy bronchial secretion (↑volume &↓viscosity) Facilitate sputum removal by cough -Guaifensin: guaiac tree gastric irritant; given with a full glass of water. -Aromatic expectorants: volatile oils in water vapor e.g. tolu . -Nauseant: e.g. syrup ipeca. -Alkaline: Na+ acetate or Na+ citrate., - Guaifensin Na+ & K+ Iodides Adverse Effects of iodides: 1. Respiratory irritation (CI: acute bronchitis & asthma). 2. Gastric irritation 3. Hypersensitivity and allergy. 4. Iodism: excessive secretions of exocrine glands (lacrimal, salivary…metallic taste). others Ammonium chloride Guafia Ipeca Mucolytics (2nd Line) They ↓ viscosity of bronchial secretion without affecting the amount; potentiating expectorants e.g.: دوب البلغم ولم يؤثر علي الكمية 1- Bromhexine (Bisolvon) 2- ambroxol 3.Acetylcysteine, carbocysteine Adverse Effects of Mucolytics: Gastric irritation Hypersensitivity Bronchospasm (acetylcysteine). Water vapor inhalation is an excellent expectorant and mucolytic. Questions???