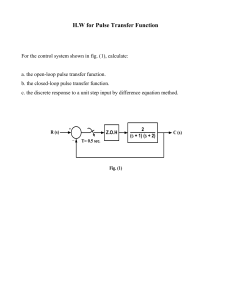
At the end of the lesson, the learners will be able to: Gain factual knowledge on structure, parts and functions of the heart. Objectives Know the circulation of blood to and from the heart. Appreciate the importance of the heart in the human body and its significance on the overall function of the other organ systems of the body. Learn to know how to take care of the heart. The respiratory system consists of conductive airways, paired lungs, and a ventilation mechanism. The REVIEW OF THE PREVIOUS LESSON respiration mechanism, an exchange of gases between inhaled air and the blood of the pulmonary capillaries, takes place in the alveoli. Apart from gas exchange, the respiratory system also filters and temperates inhaled air and contributes to production of speech (larynx), to sense of smell (nasal cavities), and to maintenance of the pH homeostasis (bicarbonate buffer system of the blood). Anatomy of Respiratory System REVIEW OF THE PREVIOUS LESSON FIND YOUR PARTNER in CRIME! 1. Find a partner (preferably girl to girl and boy to boy) 2. Locate your own pulse by placing your fingers on your wrist. Feel and locate your throb then, you have located your pulse. 3. Allow your partner to locate your pulse and vice versa. 4. Record your own pulse rate and your partner’s pulse rate. 5. After recording your pulse rate “at rest”, do jogging in place then record your pulse rate “after exercise”. Guide Questions: 1. What is your pulse rate while “at rest” and “after exercise”? 2. Was your “at rest” pulse rate the same as your partners? 3. Should everyone have the same pulse rate? Why or Why Not? 4. How did exercising affect your pulse rate? LET’S GROUP OURSELVES INTO…… 1. Students will be group into four. 2. Each group will be given cut outs of paper and will write the answer for the different parts of the heart where blood flows. 3. Each group will arrange the given cut outs into the correct sequence of blood flow of the heart. 4. A representative from each group will be asked to present their corresponding output in front of the class. LET’S CHECK IT OUT! • https://fb.watch/aU_zHGhB6v/ LET’S TRY IT OUT NOW • GROUP 1 • GROUP 2 • GROUP 3 • GROUP 4 ANSWER THE FOLLOWING 1. Describe the picture that is assigned in your group and relate it on how does it affect the function of your heart. 2. What are the ways to prevent these hazards of health? (e.g. ways to quit smoking, what should be the proper diet) SUMMARY The human heart is vital in sustaining homeostasis—the stability or equilibrium in a biological system. In fact, the heart has a specific anatomy that aids in this function. The way the heart is designed determines the path that blood must take through it in order to be pumped around the body. The blood flow through the heart were as follows: the unoxygenated blood flow from the systemic circulation to the superior and inferior vena cava to the right atrium to the tricuspid valve down to the right ventricle up to the pulmonary valve then through the left and right pulmonary arteries to the lungs for re-oxygenation; from the lungs the oxygenated blood enters the left and right pulmonary veins to the left atrium to the mitral valve down to the left ventricle to the aortic valve then to the aorta and to the systemic circulation. Since the heart is an important organ in our body, we must make sure to take care of it through healthy lifestyle, healthy eating habits, and stress management. TEST ITEM 1-10 Direction: Multiple Choice. Write the letter that corresponds to the right answer. 1. The pumping organ of the circulatory system. a. Blood pressure b. Heart c. Blood d. Blood vessel 2. The possible cause of heart diseases. a. Vices b. Proper nutrition c. Exercise 3. The function of the heart. a. Delivers food, oxygen and other materials b. Routes blood c. Maintain body temperature d. Carry blood d. Healthy lifestyle 4. Which of the following choices shows the layers of the heart from the innermost layer to the outermost layer? a. Endocardium, myocardium, epicardium b. Pericardium, myocardium, endocardium c. Myocardium, pericardium, endocardium d. Endocardium, pericardium, myocardium 5. How many chambers does the heart have? a. Three b. Four c. Five d. Six 6. The movement of blood through the heart and body is called: a. Circulation b. Locomotion c. Ventriculation d. Heart Pump 7. The beating sound your heart makes comes from: a. Blood going in the wrong direction b. Valves closing c. The heart skipping beats d. Your ears playing tricks on you 8. The atria are the “upstairs” chambers of the heart and these parts are the “downstairs” chambers: a. Valves b. Ventricles c. Pulse d. Candy Hearts 9. What wall separates the left side and right side of the heart? a. Ventricles b. Atrium c. Septum d. The Great Wall 10. What parts act like doors that control blood flow in the heart? a. Valves b. Septum c. Chambers d. Dams ASSIGNMENT / APPLICATION Ask students to write in a ¼ sheet of paper their memorable experience wherein they experienced a fast heartbeat and how did they manage to keep their heartbeat back to its normal rate or how did they kept themselves calm and relax again.