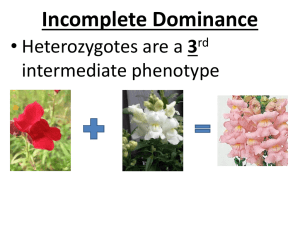
PATTERNS OF INHERITANCE THE MANNER IN WHICH A GENE IS TRANSMITTED 5 PATTERNS OF INHERITANCE • Incomplete Dominance • Codominance • Autosomal Dominant • Autosomal Recessive • Autosomal = On a chromosome that is NOT sex chromosome (X or Y) • Sex-linked BEYOND MENDELIAN GENETICS: INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE Mendel was lucky! Traits he chose in the pea plant showed up very clearly… One allele was dominant over another, so phenotypes were easy to recognize. But sometimes phenotypes are not very obvious… INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE – NEITHER TRAIT EXPRESSED Snapdragon flowers come in many colors. If you cross a red snapdragon (RR) with a white snapdragon (rr) You get PINK flowers (Rr)! Heterozygous genotype results in an Intermediate Phenotype (blended trait) RR Rr rr INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE When F1 generation (all pink flowers) is self pollinated, the F2 generation is 1:2:1 red, pink, white R r R r R R Rr Rr rr Examples What happens if you cross a pink with a white? Rr r r rr R r R r rr Rr rr A pink with a red? RR R R r Rr R R R RR Rr Rr ANOTHER VERSION OF INCOMPLETE DOMINANCE • Both alleles contribute to phenotype • Mixing of parental traits • Ex. A gene for hair texture: Curly hair allele from one parent and Straight hair allele from other = Wavy hair CODOMINANCE • Both alleles expressed, NOT mixed • Each trait is retained CODOMINANCE • Both traits expressed. • Ex. An animal with allele for white hair and an allele for red hair produce a roancolored coat (both white hairs and red hairs, not blended). EXAMPLE OF CODOMINANCE CODOMINANCE WITH MULTIPLE ALLELES: BLOOD TYPE • Multiple alleles control the ABO blood groups in humans. • The A and B alleles are codominant to each other, and the O allele is recessive • A Type x B Type = A and B type • A, B, O alleles A, B, AB, O blood BLOOD TYPE POLYGENIC INHERITANCE (MULTIFACTORIAL INHERITANCE) • More than one gene involved in determining a particular characteristic, e.g. height or skin colour. • Not to be confused with multiple alleles • Example: Human height SEX LINKED INHERITANCE • Genes that are carried by either sex chromosome EXAMPLE: COLOR BLINDNESS EXAMPLE: HEMOPHILIA • Blood-clotting disorder caused by a mutation in a clotting factor • Queen Victoria of England was a carrier of the gene for hemophilia. PEDIGREE ANALYSIS • Used to study trait inheritance in humans and predict how a disease is transmitted in families • The trait must cause a phenotype • Females are circles • Males are squares • A filled in symbol indicates that individual has the trait of interest. • Partially Filled = Carrier (Heterozygote)