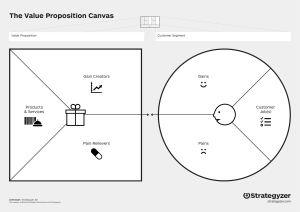
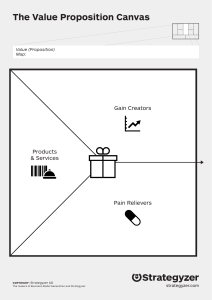
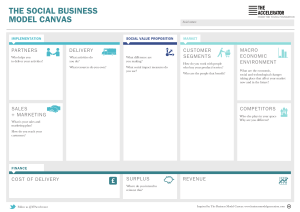
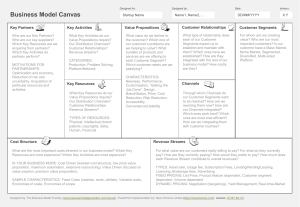
Business Model Canvas https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= QoAOzMTLP5s https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= wwShFsSFb-Y https://www.youtube.com/watch?v= IP0cUBWTgpY business model ? A business model describes the rationale of how an organization creates, delivers and captures value business model canvas ? Simply put… You can: • Create new business models • Analyze and update existing models Business Model Canvas • The Business Model Canvas – as opposed to the traditional, intricate business plan – helps organizations conduct structured, tangible and strategic conversations around new businesses or existing ones • Leading global companies like GE, P&G and Nestle use the canvas to manage strategy or create new growth engines, while startups use it in their search for the right business model Business Model Canvas • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RpFiL1TVLw • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uifGqu3iRE • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=G1lHCP3gT Qc 1. Customer Segments Customer Segments • For whom are you creating value? • Who are your most important users and customers? • Better multiple detailed segments than one generic • Create a detailed portrait of each segment; an archetype / persona(s) Customer Segments • Learn to know your customer: – How do they buy? – How do they learn about new products? – What matters to them? • Look beyond the obvious – – – – Who are the stakeholders? Who is most motivated? Who is most underserved? Who has the most to gain? 2. Value Proposition Value Proposition • NOT a list of features/technologies • How do you create joy or relieve pain? • What are we offering to each customer segment? • Characteristics: Newness, Cost reduction, Design, Quality, Status, Speed, Convenience, Risk reduction, Convenience, Customization, Accessibility etc. • For each customer segment: – What is their pain? – What is the gain for them to solve their pain? – What is their decision trigger? The Decision Trigger • How does your solution change the customer’s life for the better? • What is the “Return on Use”? • Does your offer promise enough added value to motivate your customer to pull out their wallet or credit card? 3. Channels (Distribution) Channels • Through which channels do your customers want to be reached? • How are you reaching them now? • How are your channels integrated? • Which ones work best? • Which ones are most cost efficient? • How are we integrating them with customer routines? Channel Phases How do you deliver this value at every stage of the buying process ? 1. Awareness/Discovery • 2. Evaluation • 3. How do we allow customers to purchase specific products and services? Delivery • 5. How do we help customers evaluate our organization’s Value Proposition? Purchase • 4. How do we raise awareness about our company’s products and services? How do we deliver a value proposition to customers? After sales • How do we provide post-purchase customer support? Physical or Virtual Channel? 4. Customer Relationships Customer Relationships • How do you GET customers? • How do you KEEP them? • How do you GROW your customer base? How do you build a loyal and enthusiastic tribe around your offer? Customer Relationships • What kind of relationship does each of your customer segments expect you to establish and maintain with them? • Which ones have you established? • How costly are they? • Examples: – – – – – Personal Assistance Dedicated Personal Assistance Self-Service Automated Services Community GET customers by PAID demand creation • • • • • • Public relations Advertising Trade shows Webinars Direct (e-)mail Search engine marketing GET customers by EARNED demand creation • • • • Publications in journals Speeches / Conferences Blogging Social Media KEEP customers • • • • • • Loyalty programs Product updates Customer satisfaction Contests / Events Blogs / Newsletters Social media First think about GET, then think about KEEP and GROW 5. Revenue Streams Revenue Streams • NOT ONLY the price people are paying • Revenue Stream = The strategy the company uses to generate cash from each customer segment • Pricing = The tactics you use to set the price in each customer segment Revenue Streams • How do you generate cash from each customer segment? – What VALUE are customers really willing to pay for? (Remember, price on VALUE, not on cost) – For what do they currently pay? – How much do they currently pay? – How do they currently pay? – How would they prefer to pay? • How much does each revenue stream contribute to overall revenues? Where can you generate revenue that others leave on the table? Revenue Streams • Asset Sale: ownership of physical product • Usage fee: proportional fee to usage of service • Subscription fee: continuous access to service • Renting: temporary access to goods/service • Licensing: fee for use of some IP • Intermediation fee: bringing two parties together • Advertising: fee paid by brands and companies for ads 6. Key Resources Key Resources • What infrastructure and resources do you need to deliver what you promise? • Examples: – Physical: • tools, space, locations • equipment (lease or buy) • supplies (component, assemblies) – Intellectual • licenses, intellectual property (patents, copyrights, data) – Human • personnel (qualified, in-house or sub) • Mentors, coaches, teachers – Financial 7. Key Activities Key Activities • What major activities (deliverables) must be produced to deliver your value proposition, when and by who? – Dependencies – Responsibilities • Categories: Production, Problem-solving, etc 8. Key Partners Key Partners • Partners – – – – – – Suppliers Developers Distributors Investors Collaborators Affiliates • Competitors • Alternatives How does each partner help or hinder the business model? • Motivations for partnerships: – Optimization and economy (shared economics) – Reduction of risk and uncertainty (mutual success and failure) – Acquisition of particular resources and activities (coinvention, co-development, common customers) • Risks with partnerships: – – – – – – Timing mismatch No clear ownership of customer Product vision problems Different underlying objectives Churn in partners strategy/personnel IP issues 9. Cost Structure Cost Structure • What are the critical elements of the costs in your business model? – – – – – – Fixed costs Variable costs Resource, activity, partner costs Infrastructure, operational, cost of sales Payroll costs, benefits, bonus structure, taxes What are the costs of each element of the business model? – Where are the economies of scale? – What are the risks, the unknowns? Cost Structure • What are the most expensive Key Resources? • What are the most expensive Key Activities? • Is your business more: – Cost-driven (lean cost structure, low pricing value proposition, maximum automation, extensive outsourcing) – Value-driven (focused on value-creation; premium value proposition) Business Model Canvas Additionally… • Profit – Are the revenue streams superseding the costs? – Does the nature of cost structure match the revenue types? – Can initial investment be paid back within acceptable time frame? • Growth – – – – – Is there growth potential in the business mode? How shall growth be achieved? (organic; mergers and acquisitions) What are the capital requirements for growth? How shall capital be raised? What’s the exit strategy? Business Model Canvas visually shows the following… You sell your value proposition… To a customer segment… Who you reach through some channel… You have an ongoing relationship to create retention and lock-in (and growth)… = That’s how you make money! Business Model Canvas visually shows the following… To create the value proposition, you do certain key activities… Using your key resources… Which costs you money Anything you don’t do or have yourself, you get from a partner The 4 Disrupts • Offer (What) – New products/services that did not exist up to now (invention) • Process (How) – New products or methods hat allow the offer to be produced faster, cheaper, more durable, better quality (production) • Market (Who) – Opening a new market segment poorly served up till now, by making minor modifications to one’s product or service (marketing) • Value (Why) – Meeting a need that is valued by an existing market, but not satisfactorily met by competing offers, and doing it better than the competition (positioning) Validating the Canvas • Everything you put on your canvas is a hypothesis • You must validate every element through – Discovery (your own data) – Research (other people’s data) – Testing (simulation, MVP) To summarize… • The Business Model Canvas is a visual representation of the various elements of your Business Model. • It allows you to: – – – – – See the relationship among the parts of your model Identify hypothesis, assumptions and risks Plan validation testing (market, channels, pricing) Find ways to add value and reduce cost Brainstorm market disruption strategies