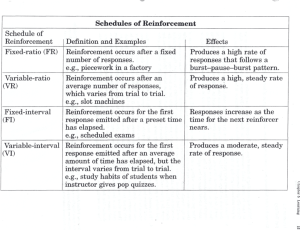
Learning: Theories and Program Design ~ Recognizes that behavior that is reinforced or rewarded tends WHAT IS LEARNING? 10 be repeated. Learning is a relatively permanent change in human capabilities that is not a result of growth processes. These capabilities are related to specific learning outcomes. > The models’ behavior or skill that is rewarded is adopted by the observer. (TBC) Processes of Social Learning Theories Reinforcement Theory Emphasizes that people are motivated to perform or avoid certain behaviors because of past outcomes that have resulted from those behaviors. « Positive reinforcement « Negative Reinforcement « Extinction « Punishment From a training perspective, it suggests that for learners to acquire knowledge, change behavior, of modify skills, the trainer needs to identify what outcomes the learner finds most positive (and negative). Trainers then need to link these outcomes to learners acquiring Knowledge, skills, or changing behaviors. Schedules of Reinforcement - Ratio Schedules Continuous reinforcement Fixed-ratio schedule Variable-ratio schedule Interval Schedules Fixed-interval schedule Variable-interval schedule Social Learning Theory > Emphasizes that people learn by observing other persons (models) whom they believe are credible and knowledgeable. Goal Theories