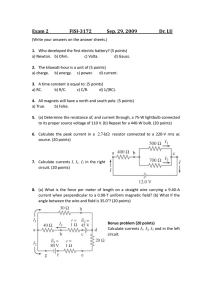
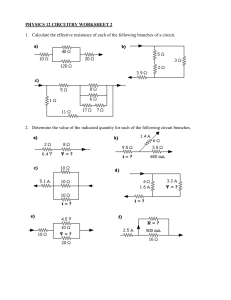
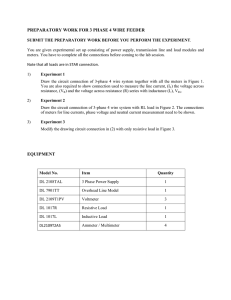
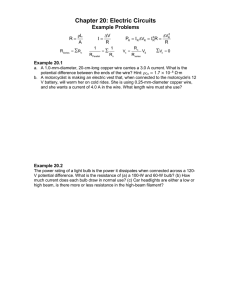
Lesson plan Long-term plan unit: Electrostatics School:Almaty High School for girls st Date: 1 March Teacher name: Zharylkassyn Uldana Grade: 10 Number present: 19 absent:1 Work and power of electric current. Joule–Lenz law. Efficiency of source of Theme of the lesson current To use the formulae of work, power and efficiency of current source Learning objectives in problem solving; that are achieved at this lesson(Subject Programme reference) Lesson By the end of this section, students will be able to: objectives explain the concept of work and power of a current; calculate the work and power of a current; describe the work done by electric current; explain the concept of the power and efficiency of an electrical device; describe energy transformation in an electrical circuit. Understanding Assessment Understand Joule-Lenz's law as the amount of heat generated in a wire; criteria Application Solve problems involving Joule-Lenz's law; Language Subject-specific vocabulary & terminology Electromotive force (EMF) objectives Kirchhoff’s first law sum of p.d.s across the resistors sum of the e.m.f.s loop’ in this circuit Useful set(s) of phrases for dialogue/writing The sum of the currents entering any point in a circuit is equal to the sum of the currents leaving that same point. The sum of the e.m.f.s around any loop in a circuit is equal to the sum of the p.d.s around the loop. Appreciation for the unique abilities of each learner. Values Respect for other’s opinion while working in a group. instilled at the Lifelong learning that theories learned from our discussion could be applied lesson also to practical life. Internationalism – the students must recognize that the discovery of capacitors is made by physicists who came from different countries. Visual Literacy Instruction – the students must understand, appreciate and Crosscomprehend what they have seen in the presentation and other video curricular materials. links *Utilization of IT in teaching and learning process. Mathematics-knowledge on algebra, fundamentals and higher mathematics are pre-requisites to this lesson Presentation, Interactive Board ICT skills The concepts of mechanical work and power; Previous The concepts of voltage and current; Ohm's Law. learning Course of the lesson Planned stages of the lesson Beginning 7min Middle 8-17 min Planned activities at the lesson Resources Teacher: -Introduces the topic of day and spelling out the learning outcome they will possess after the study. 1. Organizational moment to acquaint students with the The theme of the lesson The objectives of the lesson The criteria of success for the lesson The plan of events for the lesson 2.Start. Energy transformations Presentation Teacher shows a picture of electrical devices which transform electric energy into another one. Matching (W) Whole class discussion. Energy transformation in electric circuits. In an electric circuit, electrical energy is converted into other forms of energy. Almost always, a greater or smaller part of the energy is Presentation converted into heat (internal) energy. In heating devices, this conversion is welcomed, whereas in other devices, the resultant heat energy is usually regarded as an unwanted side effect. Electric energy The work done by electric current: The work done by current flowing through a given element of an electrical circuit is equal to the product of the voltage across the element and the charge that has flowed through the circuit. How to calculate work: The work done by electric current in a given element of a circuit is equal to the product of the voltage across this element, the current flowing through the element and the time of flow. 18-25 min (T) Teacher explanation. Joule-Lenz's law Joule-Lenz's law shows the relationship that exists among: The current that flows through a wire. The heat generated by the current that flows through a wire. The resistance of the wire and … The time the current passes through the wire. Joule’s law formula: Q = I2 × R × t where: Q is the amount of heat, in Joules (J) I is the electric current that flows through the wire, in amperes (A) Presentation R is the value of the electrical resistance of the wire, in ohms (R) t is the amount of time that current passes through the wire, in seconds (s). Heating effect Joule’s law can be established as the amount of heat (Q) generated in a wire with resistance (R), when a current (I) passes through it for a period of time (t). This heat is directly proportional to: The square of the current. The resistance of wire. The time the current flows through the wire. (I) Individual work. What are the heating effects caused by electric current? 26-30 min Worked example Calculate the amount of energy supplied by a 4.5 V battery when: (a) a charge of 20 C passes through it (b) a current of 25 mA flows through is for 3 minutes Solution: Energy = potential difference x Q = 4.5 x 20 = 90 J (b) Energy = potential difference x Q = p.d x current x time Therefore: Energy = 4.5 x 25x10-3 x 180 = 20.25 J 31-38 min End 37-40 min (f) Formative assessment. Set of calculations for electrical energy Appendix At the end of the lesson, learners reflect on their learning: - What has been learned - What remained unclear - What is necessary to work on Where possible the learners could evaluate their own work as well as the work of their classmates using certain assess criteria. Differentiation – Assessment – how are you planning Health and safety regulations how do you plan to to check students’ learning? give more support? How do you plan to challenge the more able learners? Differentiation can Use this section to record the methods Health promoting techniques be by task, by you will use to assess what students Breaks and physical activities used. outcome, by have learned during the lesson. Points from Safety rules used at this individual support, lesson. by selection of teaching materials and resources taking into account individual abilities of learners (Theory of Multiple Intelligences by Gardner). Differentiation can be used at any stage of the lesson keeping time management in mind. Reflection Use the space below to reflect on your lesson. Answer the most Were the lesson relevant questions from the box on the left about your lesson. objectives/learning objectives realistic? Did all learners achieve the LO? If not, why? Did my planned differentiation work well? Did I stick to timings? What changes did I make from my plan and why? Summary evaluation What two things went really well (consider both teaching and learning)? 1: 2: What two things would have improved the lesson (consider both teaching and learning)? 1: 2: What have I learned from this lesson about the class orachievements/difficulties of individuals that will inform my next lesson?