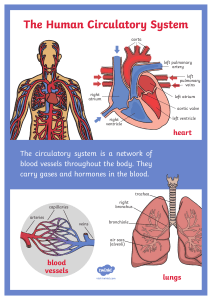
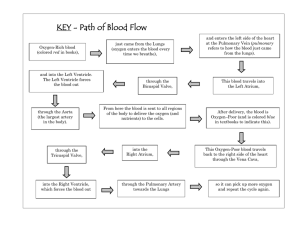
CARDIO VASCULAR SYSTEM Learning Objectives: 1. Describe the major components of the cardiovascular system and their functions. 2. State the flow of blood in the body. 3. Differentiate pulmonary and circulation. 4. Describe the different disorders. systemic The Cardiovascular System Function: The function of the cardiovascular system is to deliver oxygen and nutrients and to remove carbon dioxide and other waste products of the body. Three Major Components 1.Heart 2.Blood Vessels 3.Blood The Heart 1. The Heart - made up of cardiac muscle - pumps blood to all parts of the body (pumping station) - as big as your fist Location of Heart Location: Superior surface of diaphragm Left of the midline Anterior to the vertebral column, posterior to the sternum Pointed apex directed toward left hip Structure of Heart • Three layers of tissue – Epicardium A serous membrane of smooth outer surface of heart – Myocardium Middle layer composed of cardiac muscle cell and responsibility for heart contracting – Endocardium Smooth inner surface of heart chambers Parts of the Heart The Four Chambers Right atrium Right ventricle Left atrium Left ventricle Associated Great Vessels of the Heart Vena cava Enters right atrium Pulmonary arteries Leave right ventricle Pulmonary veins Enter left atrium Aorta Leaves left ventricle The Four Valves of the Heart A heart valve normally allows blood flow in only one direction through the heart. 1.Tricuspid valve -between right atrium and right ventricle 2.Pulmonary valve - between right ventricle and pulmonary artery 3.Bicuspid valve - between left atrium and left ventricle 4.Aortic valve - between left ventricle and aorta The Blood Vessels 2. Blood Vessels -a network of tubes -blood from the heart gets around the body through blood vessels There are 3 types of blood vessels a. b. c. ARTERY CAPILLARY VEIN 1.The ARTERY - Arteries carry blood away from the heart. the elastic fibers allow the artery to stretch under pressure 2. The CAPILLARY Capillaries link Arteries with Veins The exchange of materials between the blood and the body can occur through capillaries. the wall of a capillary is only one cell thick 3. The VEIN Veins carry blood towards to the heart. veins have valves which act to stop the blood from going in the wrong direction. The Blood 3. The Blood Blood is a bodily fluid that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells and transports metabolic waste products away from the cells such as CO2. The Blood Components of Blood a. b. c. d. Plasma Red Blood Cells / Erythrocytes White Blood / Leukocytes Platelets / Thrombocytes The Blood A. Plasma Liquid portion of the blood. Contains clotting factors, hormones, antibodies, dissolved gases, nutrients and waste The Blood B. Erythrocytes - Red Blood Cells Red blood cells are discshaped cells containing hemoglobin, which enables the cells to pick up and deliver oxygen to all parts of the body, then pick up carbon dioxide and remove it from tissues. The Blood C. Leukocytes – White cells Blood –Fight infection and are formed in the bone marrow •Five types 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. neutrophils eosinophils basophils monocytes lymphocytes The Blood D. Thrombocytes – Platelets These are cell fragment that are formed in the bone marrow from magakaryocytes. Clot Blood by sticking together – via protein fibers called fibrin. Blood Types There are four different types of blood A, B, AB, O They are determined by the protein (antigen) found on the RBC Type A, has protein (antigen) A on the RBC Type B, has protein (antigen) B on the RBC Type AB, has both protein (antigen) A and B on the RBC Type O, has neither protein (antigen) on the RBC Blood Types Flow of Blood in the Heart Flow of Blood in the Body Circuits Pulmonary circuit The blood pathway between the right side of the heart, to the lungs, and back to the left side of the heart. R V LUNGS LA Systemic circuit The pathway between the left and right sides of the heart. L V BODY RA Blood Pressure Diastolic pressure is the minimum pressure in the arteries, which occurs when the heart is relaxed. Systolic pressure is highest pressure in the arteries, which occurs when the heart contracts. NORMAL BLOOD PRESSURE : 120/70 Common Circulatory Disorders Anemia - lack of iron in the blood, low RBC count Leukemia - white blood cells proliferate wildly, causing anemia Heart Murmur - abnormal heart beat, caused by valve problems Heart attack - blood vessels around the heart become blocked with plaque, also called myocardial infarction Atherosclerosis- Literally, “hardening of the fatty stuff.” High fat diets can lead to formation of fatty plaques lining blood vessels. Thank You