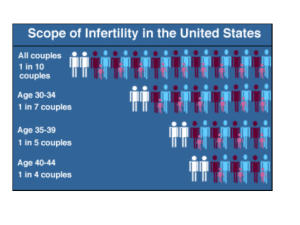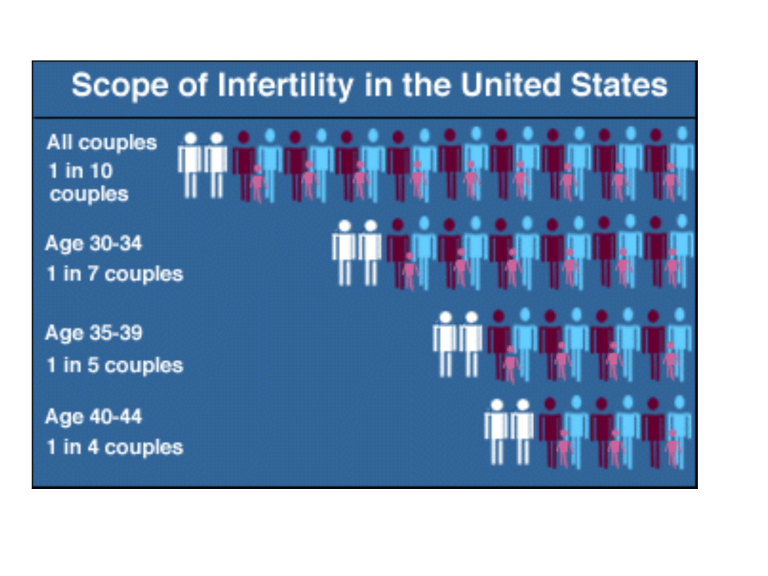
Fertility Facts Definition:unprotected sex for one year, not pregnant Frequency: 1 out of 6 couples in the US Responsibility: 35% female infertility 35% male 20% both 10% unknown Maternal Age USA 20-24 25-29 4.1% 5.5% 30-34 35-39 85% treated successfully 9.4% 19.7% Increase 1970-now-Why? What can cause infertility? Unexplained-18% Female Male • • • • • Ovulation disorders Tube/uterus blockage Cervix Endometriosis Other • Sperm count and defects • Erectile or ejaculation deficiency Intrinsic vs. Extrinsic, Environmental More detail on female infertility • Ovulatory failure-polycystic ovarian syndrome (high androgen/estrogenlevels), resistant ovarian syndrome, gonadal dysgenesis • Impaired gamete/zygote transport-pelvic inflammatory disease, endometriosis • Implantation defects-progesterone low • Spontaneous abortion-chromosome abnormality More detail on male infertility • Cryptorchidism-Why? • Chromosome disorders-gonadal dysgenesis • Obstructions • Gonadotropin deficiency Result in:Low sperm count, sperm of poor quality Female Infertility Tests • For ovulation • Basal body temperature • Ovulation kit (LH surge) • Other hormone tests (steroids) • Post ovulatory block •Laparoscopy-fiber optic look •Hysterosalpingogram-dye •Post-coital /cervical mucous and sperm •Sperm antibodies •Endometrial biopsy Sperm good for 2-3 days, egg for 2 Can find adhesions, structural abnormality, etc Hysterosalpingogram Blocked tubes Male Infertility Tests • Sperm count/motility – > 20 million sperm/ml – Check motility and morphology • >50% motile • >30% structurally normal • If low check LH and androgen levels •Testicular biopsy Sperm Count Older, low tech treatments • Drug treatment for ovulation block • Intrauterine insemination • Tubal surgery High tech Assisted Reproduction Technologies • IVF-in vitro fert and embryo transfer •GIFT-gamete intrafallopian tube transfer •ZIFT-zygote intrafallopian tube transfer •Intracytoplasmic sperm injection frozen eggs/ ovary transplant; cloned human embryo First test-tube baby Assisted Reproductive Technology • Estimate 1/100 births now • Around 40,000/year • Costs between $7,000 to 15,000 per attempt IVF In Vitro Fertilization and Embryo Transfer Basic Steps in IVF •Ovary stimulation •Egg retrieval •Sperm retrieval-wash sperm •Fertilization •Embryo transfer •Progesterone Start with more than 1 egg Drugs used for ovary stimulation •Clomiphene (clomid)-anti-estrogen •hMG (pergonal)-menopausal gonadotropin (FSH and LH) •FSH-(metrodin) •GnRH •GnRH agonists (lupron)-FSH/LH first promoted, then inhibited •hCG-acts like LH In a single cycle, could take clomid, pergonal, hCG shot, then progesterone Why transfer more than one embryo? • Increase the pregnancy rate • Leads to increased risk of multiple pregnancies • In future- Test embryos before transfer sHLA-G measure of embryo health Egg retrieval, vaginal, with ultrasound Modifications if tube not blocked Gametes mixed for GIFT GIFT If fertilization needs help-transfer zygote ZIFT Intracytoplasmic sperm injection ICSI Additional twists • Surrogacy – Gestational – Egg donor plus gestational – Egg donor plus sperm donor plus gestational • • • • Frozen embryos Egg donors Frozen eggs Cloning From CDC IVF Success Rates Stage Number of Women Cycle initiation 100 Ovulation 95 Oocyte retrieval 90 Fertilization 85 Embryo Transfer 70 Pregnancy 24 Birth 18 From The Baby Business by Debora Spar Risks of ART? • To woman – Overstimulation of ovary syndrome – Multiple pregnancies – Risk of ovarian cancer (clomid, pergonal) • To baby – ICSI associated with problems (XYY) Discussion questions-what treatment(s) would you select given the following: • • • • Male with low sperm count 30 year-old female not ovulating 40 year-old female not ovulating Undiagnosed infertility