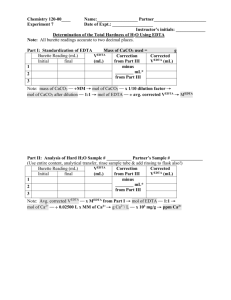
CALCULATIONS Part A molarity 𝑚 𝑚𝑚 2.0046𝑔 100.0869𝑔/𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑛 = 𝑛 = 𝑀 = 𝑀 = 𝑛 = 0. 02002𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑛 𝑉 0.02002𝑚𝑜𝑙 2 𝑀 = 0. 01001𝑀 Part C Average Volume for Blank 1.7 + 0.9 + 0.6 3 = 1. 06𝑚𝐿 molarity of EDTA 𝑛 𝑉 0.02002𝑚𝑜𝑙 11.5𝑚𝐿 𝑀 = 𝑀 = 𝑛 𝑉 0.02002𝑚𝑜𝑙 11.53𝑚𝐿 𝑀 = 𝑀 = 𝑀 = 0. 00174𝑀 𝑀 = 𝑀 = 𝑀 = 0. 00174𝑀 𝑛 𝑉 0.02002𝑚𝑜𝑙 10.6𝑚𝐿 𝑀 = 0. 00189𝑀 average molarity of EDTA 0.00174𝑀 + 0.00174𝑀 + 0.00189𝑀 3 = 0. 00179𝑀 |0. 00174 − 0. 00179| = 0. 00005 |0. 00174 − 0. 00179| = 0. 00005 |0. 00189 − 0. 00179| = 0. 0001 0.00005 + 0.00005 + 0.0001 = 3 0.000067 * 100 = 3. 7 0.00179𝑀 0. 000067 Part D moles 𝑛 = 𝑛 = 𝐶 𝑉 0.00174 25 𝑛 = 𝑛 = −5 𝑛 = 6. 96 × 10 𝑛 = 𝑛 = −5 𝑛 = 6. 96 × 10 weight of CaCO3 per 25mL 𝑚 = 𝑛 × 𝑚𝑚 −5 𝐶 𝑉 0.00174 25 𝑚 = (6. 96 × 10 ) × 100. 0869 𝑚 = 0. 00697𝑔 𝐶 𝑉 0.00189 25 −5 𝑛 = 7. 56 × 10 𝑚 = 𝑛 × 𝑚𝑚 −5 𝑚 = (7. 56 × 10 ) × 100. 0869 𝑚 = 0. 00757𝑔 Weight of CaCO3 per 106mL 6 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 25.00𝑚𝐿 = 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 25.00𝑚𝐿 × 10 0.00697𝑔 25.00𝑚𝐿 6 × 10 = = 278. 8𝑔 6 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 25.00𝑚𝐿 × 10 0.00697𝑔 25.00𝑚𝐿 6 × 10 = 278. 8𝑔 = 6 × 10 0.00757𝑔 25.00𝑚𝐿 6 × 10 = 302. 8𝑔 ppm of CaCO3 −5 = −5 6.96 × 10 2 −5 −5 6.96 × 10 2 = = −5 = 3. 48 × 10 = 3. 48 × 10 average CaCO3 −5 3.48 ×10 |( 3. 48 |( 3. 48 |( 3. 48 −5 1.0×10 −5 + 3.48 ×10 3 −5 −5 + 3.48 ×10 −5 = 3. 58 × 10 −5 | −5 × 10 )| −5 × 10 )| × 10 ) − ( 3. 58 × 10 −5 × 10 ) − ( 3. 58 −5 × 10 ) − ( 3. 78 −5 + 1.0×10 3 −6 + 3.0×10 −5 ) = 1. 0 × 10 −5 = 1. 0 × 10 −6 = 3. 0 × 10 −5 = 2. 3 × 10 7.56 × 10 2 −5 = 3. 78 × 10 WRITTEN ANSWERS 1. Equations and givens 𝑛 = 𝑚 𝑚𝑚 Calculations 𝑀= 𝑛 𝑉 𝑛 = 2.0046𝑔 100.0869𝑔/𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑀 = 𝑛 = 0. 02002𝑚𝑜𝑙 0.02002𝑚𝑜𝑙 2 𝑀 = 0. 01001𝑀 mass = 2.0029g molar mass [CaCO3] = 100.0869g/mol equations and given Calculations Average volume of blank 1.7 + 0.9 + 0.6 3 Molarity of EDTA 𝑀 = 𝑀 = 𝑀 = = 1. 06𝑚𝐿 𝑛 𝑛 𝑀 = 𝑉 𝑀 𝑉 0.02002𝑚𝑜𝑙 0.02002𝑚𝑜𝑙 𝑀 = 11.53𝑚𝐿 11.5𝑚𝐿 0.02002𝑚𝑜𝑙 10.6𝑚𝐿 = 𝑛 𝑉 𝑀 = 0. 00174𝑀 𝑀 = 0. 00174𝑀 𝑀 = 0. 00189𝑀 Average molarity of EDTA 0.00174𝑀 + 0.00174𝑀 + 0.00189𝑀 3 = 0. 00179𝑀 |0. 00174 − 0. 00179| = 0. 00005 |0. 00174 − 0. 00179| = 0. 00005 |0. 00189 − 0. 00179| = 0. 0001 0.00005 + 0.00005 + 0.0001 = 3 0.000067 * 100 = 3. 7 0.00179𝑀 Equations and given Calculations Moles of EDTA 𝑚 𝑛 = 𝑚𝑚 𝑀= 𝑛 = 𝑛 𝑉 𝑛 = 𝑀 𝑉 0.00174 25 𝑛 = 0.00174 25 −5 0. 000067 𝑛 = 0.00189 25 −5 𝑛 = 6. 96 × 10 𝑛 = 6. 96 × 10 −5 𝑛 = 7. 56 × 10 Weight per 25mL 𝑚 = 𝑛 × 𝑚𝑚 −5 𝑚 = (6. 96 × 10 ) × 100. 0869 −5 𝑚 = (7. 56 × 10 ) × 100. 0869 𝑚 = 0. 00697𝑔 𝑚 = 0. 00757𝑔 Weight per 106mL 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 25.00𝑚𝐿 6 × 10 6 = 0.00697𝑔 25.00𝑚𝐿 × 10 = = 0.00757𝑔 25.00𝑚𝐿 × 10 6 0.00697𝑔 25.00𝑚𝐿 × 10 6 = 278. 8𝑔 Ppm of CaCO3 = 278. 8𝑔 = 302. 8𝑔 −5 = −5 6.96 × 10 2 −5 6.96 × 10 2 = 7.56 × 10 2 = −5 = 3. 48 × 10 −5 = 3. 48 × 10 −5 = 3. 78 × 10 Average CaCO3 −5 3.48 ×10 |( 3. 48 |( 3. 48 |( 3. 48 −5 1.0×10 −5 + 3.48 ×10 3 −5 −5 + 3.48 ×10 −5 = 3. 58 × 10 −5 | −5 × 10 )| −5 × 10 )| × 10 ) − ( 3. 58 × 10 −5 × 10 ) − ( 3. 58 −5 × 10 ) − ( 3. 78 −5 + 1.0×10 3 −6 + 3.0×10 − ) = 1. 0 × 10 − = 1. 0 × 10 − = 3. 0 × 10 −5 = 2. 3 × 10 2. According to the Guidelines for Canadian Drinking Water Quality, the degree of hardness for drinking water can vary from in terms of calcium carbonate by which should be between 80 and 100 mg/L. Based on calculations in part D, the average content of calcium carbonate present in unknown solution #1 is 3.77M. The solution is way lower than the acceptable water hardness which means the solution needs to be diluted with distilled water. 𝑀1𝑉1 = 𝑀2𝑉2 𝑉1 𝑀2 2𝐿 3.77 𝑉2 = = = 2𝐿 3.77 𝑉2 𝑀1 𝑉2 100 × 100 𝑉2 = 52. 06 Therefore, about 52.06L of water should be added to soften up the water to reach about 100ppm. 3. The process of water softening is removing cations from water. Water softeners are ion exchanges that remove mineral salts from hard water. Once these cations are removed, they are placed in sodium ions. These exchanges usually happen within resin tanks. As the water passes through these resin tanks and the minerals are replaced with sodium ions, salt content is increased which results in softening the water. The regeneration process of softening water comes in steps; backwash, brine draw, slow rinse, and fast rinse. During this process, the salt water fills up the tank and the rinse cycle commences and washes the minerals off the beads. It is then flushed out. REFERENCES Canada, H. (2009, February 13). Government of Canada. Canada.ca. Retrieved March 8, 2022, from https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/publications/healthy-living/guidelines-canadia n-drinking-water-quality-guideline-technical-document-hardness.html