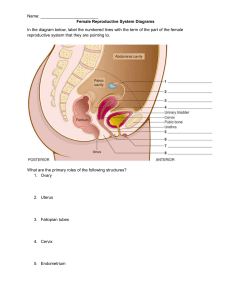
THE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM I. GOALS The primary piece of the men's and women's section of the reproduction system is said to Determines the role of each part of the regenerative system Explaining the stage or phase of the menstrual cycle II. SUBJECT Illustration I: Human Reproduction Fundamental Coexistence Skills: Personal Awareness, Powerful Communication and Creative Thinking Reproductive System alludes to general physical, mental, and social wellbeing connected with the regenerative framework of its technique and interaction. It incorporates the right of individuals to have the information and capacity How the concept of the reproductive system work The female reproductive system is intended to do a few capacities. It creates the female egg cells important for multiplication, called the ova or oocytes. The framework is intended to ship the ova to the site of treatment. Origination, the treatment of an egg by a sperm, ordinarily happens in the fallopian tubes. The subsequent stage for the treated egg is to implant into the dividers or walls of the uterus, starting the underlying phases of pregnancy. If preparation or potentially implantation doesn't happen, the system is intended to bleed (the month to month shedding of the uterine coating). What's more, the female conceptive framework produces female sex chemicals that keep up with the regenerative cycle. The vitally outside constructions of the female regenerative system include: Labia majora: The labia majora ("large lips") that serves as a safeguard to the other outer conceptive organs. During puberty, hair development happens on the skin of the labia majora, which likewise contain sweat and oil-emitting organs. The major internal organs of the female reproductive system incorporate the vagina and uterus which act as the container for semen. And the ovaries, which produce the female's ova. The vagina is affix to the uterus through the cervix, while the fallopian tubes interface the uterus to the ovaries. Because of hormonal changes, one ovum, or egg - or more on account of numerous births - is delivered and sent down the fallopian tube during ovulation. On the off chance that not fertilized, this egg is killed during monthly cycle. Fertilization happens on the off chance that a sperm enters the fallopian cylinder and tunnels into the egg. While the treatment for the most part happens in the oviducts, it can likewise occur in the actual uterus. The egg then, at that point, becomes embedded in the covering of the uterus, where it starts the cycles of embryogenesis (in which the undeveloped organism structures) and morphogenesis (in which the hatchling starts to come to fruition). Whenever the baby is developed to the point of getting by outside of the belly, the cervix enlarges, and compressions of the uterus move it through the birth trench. Organs of Female Reproductive System The organs of the female reproductive system are: Ovaries The ovaries are the essential conceptive organs present in the female regenerative framework. On one or the other side of the uterus, there are matched and almond-shaped ovaries. Oviducts or Fallopian Tubes Oviducts or fallopian tubes are the two cylinders where the treatment interaction happens. These are embellishment conceptive organs of the female reproductive system. The oviduct loosens up from every ovary to the uterus. Uterus (Womb) The uterus is an empty solid organ of the female regenerative system and can be grouped into three sections in particular, body, fundus, and cervix. The uterus is otherwise called the womb and child producer. Vagina (Birth Canal) The vagina is the female copulatory organ of the female conceptive framework. It lies between the cervix to the outside of the body. It is versatile and solid with a delicate adaptable coating. The vagina, otherwise called the birth waterway, joins the cervix to the outside of the body. Cervix The cervix is the lower, restricted piece of the uterus, situated between the bladder and rectum. It frames a trench that opens to the vagina. Regularly called the neck or access to the belly, the cervix lets feminine blood out and semen into the uterus. Developments in the cervix called polyps can at times influence the preparation of the undeveloped organism development process. Vulva The vulva is the outside piece of the female genital organs. The vulva comprises of the accompanying designs: Mons pubis: These are hills of greasy tissue overlying the pubic bone. It is covered with pubic hair after adolescence. Labia majora: These are external folds of skin containing fat, sebaceous organs, bushy and homologous to the scrotum of guys. Labia minora: These are internal folds of skin containing sebaceous organs and are non-shaggy. Clitoris: It is available at the intersection of labia majora and labia minora. It compares to the glans penis in guys. It is the middle for sexual fervor. Vestibule: It is the split between the labia minora that involves the urethral opening, vaginal hole and vestibular organs that produce oils during sex. Hymen: It is a dainty layer that to some extent covers the vaginal opening or vaginal hole. The Bartholin's organs are two pea-sized organs present close to the vaginal opening. These are like the bulbourethral organs in guys. These organs discharge liquid that capacities as an ointment to diminish grinding during intercourse and gives moisturization to the vulva. Now let’s compile the summary and what we learned about the Female Reproductive System Functions: The female regenerative framework fills the accompanying roles: It delivers the female gametes called the eggs or ova. It gives a site to treatment. It mysteries sex chemicals like estrogen and progesterone. It gives a site to the improvement of the hatchling. Male Reproductive System The male reproductive system is a conceptive framework that is present in guys. The human male reproductive system is a gathering of organs that partakes during the time spent multiplication and produces male gametes called sperms. The male reproductive comprises of a couple of the testis, the pipe system, extra organs, and outer genitalia. The male conceptive framework is for the most part situated outside of the body. These outer organs incorporate the penis, scrotum and gonads. Inward organs incorporate the vas deferens, prostate and urethra. It also incorporates a gathering of organs that make up a man's regenerative and urinary framework. The whole male reproductive system is subject to chemicals. These are synthetic compounds that invigorate or control the action of your cells or organs. The essential chemicals engaged with the working of the male regenerative framework are follicle-animating chemical (FSH), luteinizing chemical (LH) and testosterone. FSH and LH are delivered by the pituitary organ. It's situated at the foundation of your cerebrum and it's answerable for some capacities in your body. FSH is important for sperm creation (spermatogenesis). LH animates the development of testosterone, which is important to proceed with the course of spermatogenesis. Testosterone is likewise significant in the advancement of male attributes, including bulk and strength, fat appropriation, bone mass and sex drive. The male regenerative framework fills the accompanying roles: 1. Testis produces regenerative cells by a cycle called spermatogenesis and furthermore secretes the male sex chemical - testosterone. 2. Epididymis stores sperms and development of sperms happens here. 3. Vas deferens help in the transmission of mature sperms. 4. Semen is a discharge of adornment sex organs and bodily fluid. The discharge of the Cowper's organ, being basic, kills the acridity of pee in the urethra. 5. Original vesicles help in the development of a considerable lot of the constituent elements of semen. 6. Prostate organs help in the creation of the liquid that supports and initiates the spermatozoa to swim. 7. Bulbourethral organs emit bodily fluid that serves for oil. REPRODUCTIVE HEALTH Parts of Reproductive Health: There are three fundamental parts of sexual and conceptive medical care like- Family arranging - It fundamentally affects the prosperity of families and particularly ladies. With better family arranging and utilization of contraceptives, one can stay away from undesirable pregnancies, space births and furthermore shield themselves from STDs. Sexual wellbeing - It alludes to an aware and positive methodology towards sexual connections. It is a vital essential for good conceptive wellbeing. Maternal wellbeing - It alludes to the support of a lady's wellbeing during pregnancy and after labor