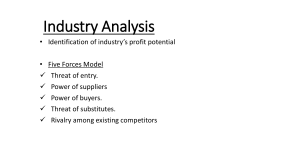
Seminar 6 E-Commerce II What is a Competitive Advantage? - A condition that puts the company above other companies that are in the same industry/market - An attribute of a firm to outperform its competitors in economic value - Economics value= output - input or could be output/input or revenue - cost Strategy and Competitive Advantage - A high-level plan (set of decisions) ⇒help achieve more goals under uncertain ⇒ competitive advantages Example of Apple and China’s Mi (smartphone industry) Apple (Quality focused): - Product Innovation (High Quality) ⇒Expensive but reputation and continuously improved products Shoumi (Strategy⇒cheap price): - Similar products at cheaper price ⇒high quality at half the price A firm can achieve a competitive advantage when it is able to create more economic value than rival firms. Types of Competitive Advantages (use business processes to attract customers): 1. Low-cost leader: producing 2. High quality 3. First-mover status *How to make customers spend more money? What do customers care about? By identifying their strengths not available in their rivals ⇒understand their strengths ⇒ improve competitive advantage Effect of IT on Competitive Advantages Low-cost Leadership (using IS system) - IS ⇒SCM, ERP, CRM - Low-cost leadership: IS⇒lowest price, lowest operational cost Case: Walmart (SCM) - IS ⇒inventory replenishment system sends order to supplier and record purchases automatically when scan (real-time can check supply) - Minimize inventory at warehouse ⇒less storage cost ⇒lower operating cost Strengthen customer and supplier intimacy - IS ⇒stronger connection with customers and suppliers (increase loyalty) - Case: Toyota (ERP) - Direct access from suppliers to production (decide how and when to ship supplies ⇒allow more lead time) - Case: Amazon (CRM) - Keep track of user preference (give real-time recommendation) *Mission Objectives ⇒Internal & External analysis (The Art of War) ⇒Strategic Decision ⇒Comparative advantage ⇒increase economic value (not easy to measure) Internal Analysis (examine economic performance ⇐internal resources) Resources Based View - key performance come from resources and capabilities ⇒ competitive advantage Resources - Tangible (physical ⇒factories, products, inventories) & intangible assets (nonphysical ⇒brand, processes, intellectual properties) ⇒Use for strategies Capabilities - Subset of resources ⇒make use of other resources - Capabilities + resources = conceive and implement strategies (not alone) - ex.) marketing skill ⇒promote, brand image, teamwork VRIO Framework (Value, Rare, difficult to Imitate (Copy), exploited by Organization) Value Does it add value for customers? Are you able to exploit an opportunity or neutralize competition with an internal capability? No ⇒Competitive disadvantage ⇒reassess resources and capabilities to get value Yes ⇒Can move to the next VRIO analysis ⇒rarity Rareness Do you control scarce/limited resources? Is it rare but in demand? No ⇒Hv value but lack rarity ⇒competitive parity ⇒common resources ⇒difficult to compete in marketplace ⇒go back and reassess Yes ⇒Both ⇒move to next analysis ⇒imitability Imitate Easily duplicate your resources/capability? No⇒Hv value, rarity but affordable to copy ⇒temporary competitive advantage (no long term) ⇒need efforts to effort to stay ahead and differentiate service ⇒go back to rareness Yes ⇒Valuable rare hard to imitate ⇒focus on organization Organization Have organized a management system, processes, structure, and culture to capitalize on resources and capabilities? No⇒Internal organization and support are key! Without it ⇒difficult to the max. Potential of valuable, rare resources. Wouldn’t be able to use competitive advantage ⇒reassess to how to attain the needed organization Yes⇒Achieved the ultimate goal of sustained competitive advantage. *Competitive parity: Achieve standard or average results compared to others in same industry Competitive advantage: Achieve above average results ⇒Superior/Industry leader Question resources such as brand, supply chain management, top executive IT resources - data, tech, employee, process ⇒to perform business process and tasks - Tangible or intangible used by firm to create, produce, offer products/services - IT infrastructure - hardware and software - Information repository ⇒allow internal people to share info real-time - Social media, online review ⇒to know their position and reputation IT capabilities (learned or developed over time to create, product, offer product/service) - Technical skills: difficult to copy ==. Design, develop, implement IS - IT management skills ⇒put everything together the technical skills - Relationship skills ⇒work with other division ⇒achieve common goals External Analysis (economic performance v.s. rival performance same industry) Five-Forces Model (Micheal Porter) - For analyzing companies’ competitive environment (Threats and opportunities) ⇒ determine whether high/low prices/power ⇒high/low profit ⇒ come up with strategy ⇒increase competitive advantage - If none of the five forces undermine profits ⇒strong profit potential - If all of the five forces work to undermine profit ⇒profit potential weakens 1. Competition in the industry/ Rivalry Among Existing Competitors - Depend on # of competitors/industry concentration - More competitors, less market share, small market growth ⇒cheaper - Less competitors, more market share, high growth, low switching ⇒$$$ 2. Potential of new entrants - Less time and effort to enter ⇒new entry have cost-benefit but weaken current companies - More entrants ⇒low switching costs 3. Bargaining Power of Suppliers - # of suppliers of key inputs in product - Rely only one few ⇒supplier power ↑ ⇒high switching cost ($$$) - ↑suppliers⇒low switching cost/substitute inputs ⇒↑ profit - Threat of forward integration 4. Bargaining Power of Customers - Size of available customers - ↑ buyers ⇒set higher prices ⇒↑ profit - ↓ buyers ⇒↑ power for customer ⇒set lower prices (match customers) 5. Threat of Substitute Products/Services - # of substitution - ↑ substitution ⇒lower price (weaken power of company) - ↓ quantity of substitutes ⇒high prices ⇒high switching cost for customers Case Study of Netflix: - Competitive Rivalry (High) - Many similar services (TV, online platform that sells media content) - Competitors offer additional services (Amazon ⇒music, popular video, - shop) Threat of New entrants (high) - For new entrant of video contents ⇒High/expensive for who don’t have own content ⇒high investment for production - - For established companies ⇒very low since have own content and fan - base Many customers will have many subscriptions for different platforms Power of Suppliers (moderately high) - Suppliers have high bargaining power ⇒Netflix compete with other media distributor - - - Netflix original series ⇒on-trend and popular Power of Buyer (high) - Only rise ⇒increase number of competitor - Depend on quality of content - Low switch cost (similar rates) for customers ⇒easily switch Threat of Substitute Product (moderately high) - Many substitutes (YouTube - 12% of videos watched) - Subscription services on rise ⇒other traditional formats declining Five Forces Model and IT (IT brought more negative effects) - Intensity of Competitive Rivalry (worse) - IT lowers variable cost (lower distributing cost) - Easily search another cost for other competitive rivalries - It reduces differences among competitors since it easily sees other - - - companies’ strategies. ⇒difficult to keep proprietary Threat of New Entries (higher) - Severe competition ⇒so many new entrants - Internet applications are difficult to keep up with new entrants Bargaining Power of Supplier - One supplier give to many companies (access to more customers) - Rise bargaining power - Channel for suppliers to reach user (reduce layers between customers) Bargaining Power of Buyer - Increase transparency (compare prices of same products in internet) - - Reduce information asymmetry btw. buyers and sellers - Increase power reduces switching costs (more similar products) Threats of substitutes - Overall industry more efficient ⇒expand the size of market (new tech, valuable content, niche product/unique products) - Customers can easily switch from traditional ⇒internet/applications on smartphones Short Quiz 1. In the context of the VRIo framework, a resources said to be valuable if it: a. Leads to competitive parity within an industry b. Helps a firm increase its cost c. Allows a firm to take advantage of external opportunity d. Result si na perfectly competitive industry structure 2. Which of Porter's five forces is most closely associated with the concept “Barrier to entry” a. Bargaining Power of Suppliers b. Rivalry Among Existing Firms c. Threat of new Entrants d. Threat of Substitutes