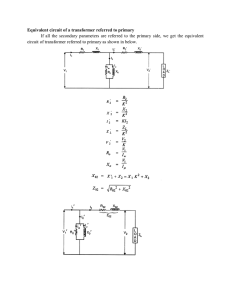
Experiment (10) Electrosurgical unit objective Electro surgery is the application of a high-frequency electric current to biological tissue as a means to cut, coagulate, desiccate, or fulgurate tissue. Theory Electro surgery is the application of a high-frequency electric current to biological tissue as a means to cut, coagulate, desiccate, or fulgurate tissue. Electrosurgical devices are frequently used during surgical operations helping to prevent blood loss in hospital operating rooms or in outpatient procedures. Different levels can be set on the ETU, depending on the depth of the cut and the point of operation. • “Cut” is used for cutting tissue. • “Blend” uses a mixture of blending and coagulation. It is used to both cut as well as stem the resulting bleeding, • “Coagulation” is used for the maximum Homeostasis. • “Dissection” is used chiefly for destroying tissue. Mono-polar modes are used for cutting and coagulation, while the bipolar mode that has forceps like an electrode is usually used for dissecting and destroying tissue. Fig (27) Electrosurgical unit The configuration and parts of the system Types of electrosurgical unit: • Mono-Polar Technique (flow of current) Active Electrode tip Patient Neural Electrode Generator Fig (28) Mono-Polar Technique • Bipolar Technique Generator Active Electrode Fig (29) Bipolar Technique Block diagram Fig (30) Electrosurgical unit block diagram ESU Waveforms Fig (31) Electrosurgical unit waveforms The principle of work of the system Electrosurgical units (ESU) use a high-frequency electrical current to cut tissue and control bleeding by causing coagulation. Tissue resistance to the high-density current causes a heating effect which results in tissue destruction. Electrical current is delivered and received through cables and electrodes. The electrodes may be activated by either a hand piece switch or a footswitch. The ESU may use a monopolar or a bipolar mode. The procedure of operation A circuit for discharging stored energy in an electrosurgical generator. The circuit includes a pulse width modulator for controlling a high voltage power supply, an error signal generating circuit configured for delivering an error signal as a difference between an output signal voltages with a feedback voltage generated by the high voltage power supply. The error signal is transmitted to the pulse width modulator. The circuit further includes a switching circuit configured to switch in a load in parallel with an output of the high voltage power supply when the error signal is lesser than a first predetermined threshold to discharge the output. Fig (32 ) Electrosurgical unit circuit