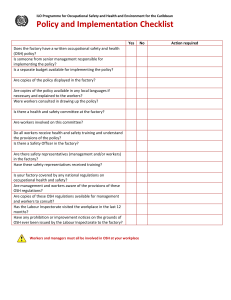
PART 1: OVERVIEW OF OCCUPATIONAL TITLE SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENT. Prepared by: 1.1 Historical Perspective Early Recognition Of Occupational He recognized the dangers of Diseases metal fumes and described symptoms and preventive measures. In 1473 a German physician, Ellenborg, published the first known pamphlets on occupational disease from gold miners. Company should provide a ventilation for miners. In 1556 the German scholar, Agricola, described the diseases of miners. In 1713 Ramazzini, who is regarded as the father of occupational medicine, suggested that in diagnosis doctors should ask patients about their occupations. A book, “The Diseases of Workmen” described the symptoms of mercury and lead poisoning and issues with silica. Emergency Of Industrial Accident Industrial accidents arose out of the Factory System during the Industrial Revolution in Britain in 18th Century (1700s). Women and children worked as heavy labourers under unsafe and unhealthy workplaces. Industrial accidents arose out of the Factory System during the Industrial Revolution in Britain in 18th Century (1700s). Industrial Safety Legislation In 1833 English Factory Act was the first effective industrial safety law. It provide compensation for accidents rather than to control their causes. Insurance companies inspected work places and suggested prevention methods Problem: Safety became injury and insurance oriented. Emergency Of Safety Management Role of Herbert W. Heinrich (1930’s), Developed Domino Theory and promoted control of workers behaviour. Problem: Focused on worker behaviour and not management Caused people to think that safety is about policing worker Frank Bird (1970) developed Loss Control Theory. Suggested that underlying cause of accidents are lack of management controls and poor management decisions. Problem: Not so popular: blames management (responsibility and control). Safety Management Systems In 1980’s, Behavioural Based Safety (BBS) was introduced; Based on Heinrich’s findings. Work by recognizing safe work habits and offering rewards and punishment. Problem: Focuses on workers and not on hazard or management Reward and punishment system have flaws A Self-Regulation Legislation Lord Robens, Chairman of a Royal Safety Commission Report noted that: there was too many OSH legislation, was fragmented, limited in coverage (specific hazards & workplace), out of date and difficult to update, inflexible, people thought that safety was what government inspectors enforced. Lord Robens recommended : Self regulation A Self-Regulation Legislation In principle, self-regulation offers greater speed, flexibility, sensitivity to market circumstances and efficiency than government regulation. Enacted in Malaysia in 1994 after the 1992 Bright Sparkler accident in Sungai Buloh Bright Sparklers Fireworks 1991 Factory caught fire in Sg. Buloh Huge explosion 26 died and over 100 injured BRIGHT SPARKLER, SG BULOH 7th MAY 1991 A Self-Regulation Legislation Legislation follow major accidents and reinforce need for management system ACCIDENT REGULATION/PROGRAMME Flixborough (1974) CIMAH regulations 1996 Bhopal (1984) “Responsible Care” / Process safety Piper Alpha (1988) Risk Assessment / Management system PART 1: OVERVIEW OF OCCUPATIONAL TITLE SAFETY, HEALTH & ENVIRONMENT. Prepared by: 1.2 OSH Programme Creating OSH Policy, Organisation & Arrangements OSHA 1994 requires to have written policy, organisation and arrangements. Purpose of OSH programme is to ensure: Implementing the goals of OSH policy Minimum compliance with national laws and regulations Good operation of the organisation’s OSH management system Continual improvement in OSH performance Planning An OSH Programme Begin with: 1. Goals of the organisation written in the policy 2. Legal and other requirements 3. Identified hazard and risks Prioritise the needs of these requirements and set objectives and target for the organisation to achieve. Set objectives and targets. Create action plans with datelines and responsibilities for completion. Responsibilities For The Implementation of OSH Programmes General responsibility A A.Top Management C Employee C. Overall responsibility Provide resources to implement the policy B B. Line Management and Supervisors To cooperate Obey rules and regulations Reporting Involvement in consultations Day-to-day programme tasks and responsibilities Ensuring that OSH is managed within their area of operations. A B C OSH Programmes Information, instruction, training: OSH promotion Awareness programme Training / induction and other training Signs and labels Tool box meeting Communicating and consultation Safe System of Work A formal procedure to minimise remaining risks: Cleaning and maintenance operations. Working alone. Breakdowns. Emergencies. Should have safe working procedures @ S.O.P for all jobs. IMPLEMENT !! Safe System of Work Permit-To-Work Required Electrical work, especially at higher voltages. Entry into confined spaces e.g. vessels. Excavation work or demolition activities. Presence or possible release of Radiation or flammable gases, liquid or dusts (possible risk of ignition by hot work, electrical or electrostatic sources). Lone working in hazardous environments. Safe System of Work – Lone Working May include the “Buddy System”: (a) Challenge-check system. (e.g. aircraft checklists) (b) Lifeguard system. (e.g. jobs requiring lifelines and special protective gear) (c) Two-person system. (e.g. in electrical substation operations) The Importance Of Human Factors Human factors can lead to accidents: General health and fitness. Complacency (satisfied). Fatigue, Boredom. Rushing (cutting corners). Panic in emergencies. Over eagerness (not following procedures). Build in fail-safe mechanism or remove the risk Assignment: 1. Divide into 6 groups 2. Choose your topic of interest: a) Love Canal – booked b) Itai-Itai Disease -booked c) Minamata Disease -booked d) Triangle ShirtWaist -booked e) Agent Orange -booked f) Chernobyl Tragedy – booked g) Hiroshima & nagasaki atomic bom 3. Present on 09/7/2014 (9.00am – 10.30 am) by using PowerPoint 4. 10 minutes presentation +5 minutes Q&A Session