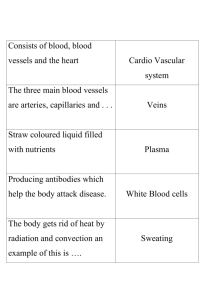
Thermoregulation SI worksheet 1. Normothermia is the balance between heat loss and regulation to maintain an outer core temperature of about 37 degrees Celsius. o The __hypothalamus____ is considered to be the thermostat of the body o The body fluctuates about 1.5 degrees Celsius before compensatory mechanisms are utilized: 2. The four types of compensatory mechanisms include: o ___sweating_____ Evaporation of water off the skins surface o Shivering Involuntary contraction of muscles o Non-shivering Utilization of brown fat. Only found in _infants____ o Vasoconstriction of blood vessels Causes the body to __conserve___ heat through the skin o __vasodilation____________ of blood vessels Causes the body to __lose___ heat. Associated with norepinephrine These cells: ___thermoreceptors____ are responsible for determining if the body temperature is high or low. There are more _warm___ receptors than ___cold__ receptors. 3. Hyperthermia is the significant rise in body temperature (more than 37.6) o Excessive compensatory sweating can lead to dehydration and sodium deficiency o Over time, excessive sweating can lead to Hypotension Tachycardia Decreased perfusion leading to cardiovascular collapse 4. Fever is caused by an increase in core temperature with immunologic benefits o Supportive fluids, calories, and oxygen can be given o Cooling is counterproductive Pyrogens are the substance that causes the hypothalamus to raise the thermostat set point (often times endogenous cytokines released by the inflammatory response) 5. Heat Transfer o Conductive heat loss Warmer skin to colder surface o Conductive heat gain o o o o o Warmer surface to colder skin Convective heat loss Removal of body heat due to air currents Convective heat gain Gain of body heat due to air currents Radiant heat loss Electromagnetic energy loss Radiant heat gain Sunlight to skin/light to skin Evaporative heat loss Loss of heat due to body water evaporating from the skin 6. Heat Production and Loss o Body heat is mainly produced by body metabolism occurring in liver and muscle cells o Body heat is mainly conserved through vasoconstriction of peripheral blood vessels o The main ways in which body heat is lost are Respiration Perspiration EXEMPLARS 1) Hypothermia o Body temperature below 36.2 o Compensatory mechanisms such as vasoconstriction can lead to peripheral ischemia o A body temperature below 28 degrees can cause ice crystals to form in the cell 2) Heat stroke o Due to an overstressed thermoregulatory center Temperatures above 41.2 Caused by: overexertion, over exposure to environmental heat or loss of compensatory mechanisms Signs and symptoms: High core temperature, absence of sweating, rapid pulse, confusion, coma 3.) Newborn thermoregulation o Main heat production occurs through nonshivering utilization of brown fat Ways to manage newborn heat loss include: Drying the infant quickly Utilizing skin to skin Radiant warmer Signs and symptoms: crying/restlessness, cool to the touch, acrocyanosis