AC Circuits: Fundamentals and Analysis
advertisement

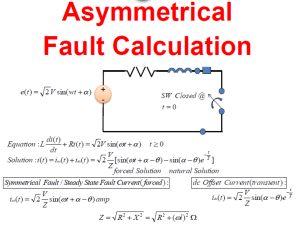
ENGR. REGINALDO N. MARINAY A flow of electricity which reaches maximum in one direction, decreases to zero, then reverses itself and reaches maximum in the opposite direction. The magnitude of a waveform from the peak of the positive alternation to the peak of the negative alternation. The maximum value of a waveform of one alternation either negative or positive alternation. The instantaneous value of voltage or current is the value or current at one particular instant. The average value of voltage or current is the average of the ALL the Instantaneous value during ONE Alternation. Effective Value of Alternating Current of Voltage will have the same heating effect on a resistance as a comparable value of direct current or voltage will have on the same resistance. Ieff = Imax 2 It is the property of an inductor to oppose the alternating current. The property of the capacitor to oppose the alternating current. The total opposition to the flow of the alternating current. It is the combination of resistance and reactance. The AC Voltage will be In-phase with Current. The AC voltage is only supplying a circuit with only an inductor. The voltage leads the current by 90 degrees. The AC voltage is supplying a circuit with only a capacitor as its load. The current leads the voltage by 90 degrees. The AC voltage is supplying the series connection of resistor and inductor. The AC voltage is supplying the series connection of resistor and capacitor. True or Real Power Reactive Power Apparent Power The power consumed by the resistive component. The power consumed by the reactive component, either inductor or capacitor. The vector sum of the true and reactive powers. Conductance Susceptance Admittance Reciprocal of Resistance Symbolized by capital letter “G” G= 1/R Reciprocal of reactance Symbolized by “B” Bc = 1/Xc Bl= 1/ Xl Reciprocal of impedance Complex composite of conductance and susceptance Y = G + jB A circuit phenomenon or condition wherein: ◦ The current is in-phase with the voltage ◦ The circuit power factor becomes unity ◦ The inductive reactance is equal to the capacitive reactance At At At At At At fr, XL = XC fr, Z is minimum (Z=R) fr, I is maximum (I=E/R) fr, Z is resistive (I is in-phase with E) f < fr, Z is capacitive f > fr, Z is inductive At At At At At At fr, IL = IC fr, Z is maximum (Z=RP) fr, I is minimum (I=E/RP) fr, Z is resistive (IT is in-phase with E) f < fr, Z is inductive f > fr, Z is capacitive Quality factor is a measure of the “goodness” or quality of a resonant circuit higher value for this figure of merit corresponds to a more narrow bandwidth, which is desirable in many applications. Q = X/R The width of the resonant band of frequencies centered around the resonant frequency The range of frequencies included between the two frequencies at which the current drops to 70 percent of its maximum value of resonance is called the Bandwidth BW = FR/Q A temporary phenomenon occurring in a network prior to reaching a steady-state condition. Transient period is the period required for the currents and voltages to adjust themselves to the steady-state after it is switched-on. Is the time for a change of 63.2% in the current through inductor or the voltage across the capacitor T = L/R T= RC Long RC Time Constant At least five times longer than the pulse width, in time for the applied voltage Short RC Time Constant ◦ No more than one-fifth the pulse width, in time, for the applied voltage