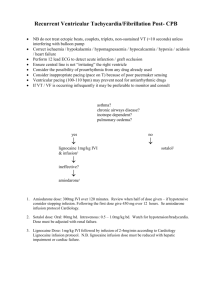
Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Approved For Drug Acetazolamide (Diamox®) Acetylcysteine (Acetadote®) Acyclovir Adenosine (Adenocard®) ICU ED Telemetry Required Acute Care IVP X X X X X Infusion only X X X Bolus + infusion X X X X IV Infusion X See restriction Concentration Usual Dosing and Administration Dilute to MAX of 100 mg/mL 30 gm/1000 mL (30 mg/mL) 5-10 mg/kg/dose MR q 8 or 6 hrs. MAX dose: 25 mg/kg/dose up to 500 mg/dose MAX Rate: IVP over 1 minute. Requires toxicology approval. Bolus: 150mg/kg over 1 hr. Maintenance: 15-7.5mg/kg/hr. See dosing protocol or contact pharmacy for weight-based protocol. Diluted to <5 mg/mL Infusion over 60-90 minutes. Dose: 5-20 mg/kg/dose q 8hrs. 6 mg/2 mL. (3mg/ml) DOSE:0.05-0.1 mg/kg up to 6 mg over 1-2 seconds followed by rapid NS flush. May increase dose by 0.10.2 mg/kg q2 minutes up to 12 mg/dose every 1-2 mins till termination of arrhythmia to a MAX CUM dose of 0.3 mg/kg/dose upto 30 mg. > 50kg: 6mg, 12mg, 12mg 0.5-1 gm/kg/dose (10-20 mLs/kg/dose). Infusion over 3060 minutes. In emergencies, may administer over 15 minutes. Adult MAX: 600mls/hr . Comments Monitor serum electrolytes When used in acetaminophen overdose, monitor serum acetaminophen concentrations; monitor LFTs. Bolus doses, monitor for hypotension, flushing, anaphylaxis Bolus doses must be completed in critical care areas only. Maintenance IV infusions may be continued or initiated in acute care areas. Patient should be well hydrated to prevent nephrotoxicity. Monitor urine output, Scr. Restriction: In acute care areas, doses must be administered by a physician. . Communication with the ICU team prior to adenosine administration is required. An attending Hospitalist, Cardiologist, or ICU physician must be at the bedside. A continuous ECG rhythm strip must be obtained during dosing to monitor and document drug effects Rapid infusion may cause hypertension and pulmonary edema. Monitor vital signs and fluid balance. Use within 4 hours of opening vial. 60 micron filter/tubing supplied by pharmacy Albumin 5% (forhypovolemia, hypoalbuminemia X X X 5% (50 mg/mL) Albumin 25% X X X 25% (250 mg/mL) 0.25-1 gm/kg/dose (1-4 ms/kg/dose) Infusion as tolerated over 30-120 minutes. Adult MAX :180ml/hr Rapid infusion may cause hypertension & pulmonary edema. Monitor vital signs and fluid balance. Use within 4 hrs of opening. 60 micron filter/tubing supplied by pharmacy X Dilute 500 mcg in 50mls NS (10 mcg/ml) Initial: 0.05- 0.1 mcg/kg/min. Range: 0.01 up to MAX 0.4mcg/kg/minute Infuse via large vein. Monitor arterial pressure, RR, HR, oxygen saturation, temp. Diluted to < 5 mg/mL 5-10mg/kg/dose q8hrs with NL renal function. Infusion: Over 30 minutes. Urine output, Serum creatinine, Peak and trough concentrations. (forhypoproteinemia w/ generalized edema) Alprostadil, PGE1 Prostin VR Pediatric®) X Amikacin (Amikin®) X X Continuous infusion X X NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. 1 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Approved For DrugDrD Amiodarone (Cordarone®) Ampicillin ICU ED Telemetry Required X X Acute Care IVP IV Infusion X X X Bolus in code only No infusion X X X X Atropine X X X X Azithromycin (Zithromax®) X X Aztreonam (Azactam®) X X Central line preferred for concentrations exceeding 2 mg/mL. Dedicated filtered (0.22 micron) line required. Infusion 450 mg/ 250 mL in D5W For perfusing VF/VT 5 mg/kg over 20-60 min, MR X 3 Continuous BP/cardiac monitoring, thyroid function, LFTs, and pulmonary function should be monitored frequently. X slow Dilute to <30 mg/mL =(amp 20 mg/ sulb 10 mg) X 0.1 mg/mL; 1 mg/mL MD available X Comments BOLUS: PALS for pulseless VF/VT5 mg/kg (MAX 300 mg/dose) given over 5-10 minutes. - 0.22 micron filter preferred . Flush post dose. Dilute to <20 mg/mL X Usual Dosing and Administration Bolus diluted to 1.5-3 mg/mLin D5W X slow Ampicillin/ Sulbactam (Unasyn®) Concentration X Dilute to 2 mg/mL X Dilute to < 20 mg/mL Infusion: Initial dose of 5 mcg/kg/min, increase to desired effect to a MAX of 15 mcg/kg/min IVP: not to exceed 10 mg/kg/minute. Infusion: over 15-30 minutes Dosing: 100-400 mg/kg/day divided every 6 hrs. MAX 12 gm/day IVP: not to exceed 15 mg/kg/minute (amp/sulb) Infusion: Over 15-30 minutes >1 month: 150-225 mg/kg/day (amp/sulb) divided every 6 hrs Children: 150-300 mg/kg/day (amp/sulb) divided every 6 hrs. (non-meningitic doses) (MAX dose: 12 gm ampisulb/day) IV Push: given over 1 minute Dosing: 0.01-0.2 mg/kg (MIN 0.1 mg) Child: up to 0.5 mg, MRx1 Adolescent: up to 1 mg, MRx 1 Please see reference for dosing for specific indications. Infusion:MAX concentration of 2 mg/mL over 1 hr Dosing: 5-10 mg/kg/day as q 24 h (MAX 500 mg) Single dose regimen: 30mg/kg X 1 (MAX 1500mg) For specific indications, please consult pedi reference for recommendations. IVP: over 3-5 min Infusion: Over 20 minutes Dosing: >1 month-90-120 mg/kg/day div q 8h or q 6 h. CF: 50 mg/kg/dose q 6 hrs MAX 8 gm/day NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. Adjust with renal dysfunction. Unsayn: Each 1.5mg unasyn=1mg apicillin +0.5mg sulbactam. With prolonged therapy, monitor hematologic, renal and hepatic function. Observe for change in bowel frequency. Monitor vital signs and EKG; monitor for side effects including dry mouth, dizziness and palpitations. Monitor for pain at infusion site, LFTs, WBC and infection. Adjust dosing with renal dysfunction. 2 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Approved For Drug ICU ED Telemetry Required Concentration Usual Dosing and Administration Acute Care IVP IV Infusion X X 0.25 mg/mL Dosing:0.015-0.1 mg/kg/dose up to 4 mg q 6-24 hrs (MAX dose is 10 mg/day, 20 mg/day w/ RF)) IV Push: over 1-2 minutes MAX 1mg/min Monitor blood pressure, serum electrolytes and renal function. Clarify if dosing is as citrate salt or caffeine base. Must be specified on medication order. May dilute in D5W Monitor heart rate, number and severity of apnea spells, and serum caffeine levels Not to be administered in neonates(benzoates). Monitor heart rate. Bumetanide (Bumex®) X X Caffeine Citrate (Cafcit) For apnea X X X 20 mg/mL citrate salt (=10 mg/mL caffeine base) Loading: 10-20 mg/kg citrate salt infused over 30 minutes Maintenance: 5 mg/kg/day as citrate salt once daily starting 24 hours after bolus doseinfused over ≥ 10 minutes Caffeine sodium benzoate For spinal headache X X X Dilute to 0.5 mg/mL Adults: 500 mgs as a single dosediluted with 1000 mL NS and infused over 1 hour, followed by 1000 mL NS over 1 hour. X 1 gm/ 10 mL vial Calcium Chloride X X Slow IVP Calcium Gluconate Cefazolin (Kefzol) X X Slow IVP Slow IVP only. X Comments IVP In code only w/MD present. No infusion. Slow IVP in code w/ MD present. Infusion OK X X Slow IVP Recommend use only in symptomatic hypocalcemia Bolus: 10-20 mg/kg/dose up to 1gm over a minimum of 10 minutes. Infusion: Do not exceed 45-90 mg/kg given over 1 hour X X 1 gm/50 mL =20 mg/mL 200-500 mg/kg/DAY as continuous infusion or in 4 divided doses Acute::Usual 100mg/kg or 1gm MAX 3gm over 10 minutes Non-Acute: Usual 50-100mg/kg not to exceed 2gm over no less than 60 minutes. MAX: 200mg/kg up to 3gm X Dilute to < 20mg/ml IVP: Over 3-5 minutes Infusion: Over 10-15 minutes Dosing:Neonates>2 kg, + 7 days-60 mg/kg/day div q 8h. Infants/Children: 50-100 mg/kg/day div q 8h Adolescent/Adult: 1-2 gm IV q 8h MAX ADULT DOSE: 12 gm/day Slow IVP X NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. Central Line preferred unless emergency administration. Do not administer I.M. or S.C. or use scalp, small hand or foot veins for IV administration since severe necrosis may occur. Monitor serum calcium (ionized calcium is recommended), heart rate and EKG. Do not infuse calcium chloride in same IV line as phosphate-containing solutions. Do not infuse calcium gluconate in same IV line as phosphate-containing solutions. Monitor serum calcium (ionized calcium is recommended), heart rate and EKG. See label comments on Pedi IV Calcium Gluconate Bags Adjust dosing with renal dysfunction. 3 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Approved For Drug ICU ED Telemetry Required Acute Care IVP IV Infusion Concentration Usual Dosing and Administration Cefepime (Maxipime) X X X X Dilute to < 20 mg/mL IVP over 5 minutes. Infusion over 30 minutes Dosing 2 mo-16yo: 100-150 mg/kg/day div q 12 or 8 hrs. CF 50 mg/kg/dose q 8hr MAX 6 gm/day Cefotaxime (Claforan®) X X X X Dilute to < 40 mg/mL IVP over 3-5 minutes Infusion: Over 10-30 minutes <7 days:+>2000 g:100-150 mg/kg/day div every 8-12 hrs > 7 days: >2000 g: 150-200 mg/kg/day divided every 6-8 hrs 1 month- 12 years: <50 kg: 100-200 mg/kg/day divided every 6-8 hoursMeningitis: 200-300 mg/kg/day divided every 4 or 6 hours (MAX 12 gm/day) > 50 kg: Moderate infection 1-2 gms q 6-8hrs, Severe 2 gms every 4 to6 hrs (MAX 12 g/day) Cefoxitin (Mefoxin®) Ceftazidime (Fortaz) X X X X Dilute to < 40mg/ml IVP over 5 minutes Infusion over 10-30 minutes X X X X Dilute to <40 mg/mL Ceftriaxone (Rocephin®) X X X X Dilute to < 20 mg/mL IVP over 3-5 minutes Infusion over 20-60 minutes < 7days >2 kg: 100-150 mg/kg/day div q 8-12 hrs >7 days >2 kg: 150 mg/kg/day div q 8h Infant/child: 100-150 mg/kg/day div q 8h CF: 150-300 mg/kg/day usual MAX 12 gm/day IVP over 5 minutes Infusion over 10-30 minutes Infants and Children: 50-75 mg/kg/day divided every 1224 hours Meningitis: 80-100 mg/kg/day divided every 12-24 hrs (MAX: 4 gm/day) Chlorothiazide (Diuril®) X X X X 500 mg vial diluted with 18 mL SWI for a final concentration of 27.8 mg/mL IVPover 3-5 Infusionover 30 minutes in dextrose or NS <6 months: 2-8 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses up to 20 mg/kg/day >6 months: 4 mg/kg/day in 1-2 divided doses up to 20 mg/kg/day. NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. Comments ID approval required for patients outside the ICU. Pseudomonal infections should be dosed at the higher end of the dosing range. Adjust dosing with renal dysfunction. Indicated in neonate < 2 weeks or in infants with clinically relevant hyperbilirubinemia who may be at risk for kernicturus. With prolonged therapy, monitor renal, hepatic, and hematologic function periodically; number and type of stools/day for diarrhea. Adjust dosing with renal dysfunction. Adjust dosing with renal dysfunction. Monitor INR with prolonged use CO2 is produced with reconstitution. Remove pressure/air by venting vial prior to drawing up dose— Adjust dosing with renal dysfunction.. *Do not use in any child <5kg, unless short-term IV access is unavailable. Avoid concurrent use in all patients requiring IV calcium supplementation. Monitor CBC, platelet count, renal and hepatic function tests periodically, number and type of stools/day for diarrhea. Do not administer I.M. or S.C. since extremely irritating to tissues. May be further diluted. Monitor serum electrolytes and blood pressure. 4 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Approved For Drug ICU ED Ciprofloxacin (Cipro®) X Cisatricurium (Nimbex®) X Telemetry Required Acute Care IVP X X IV Infusion X Dilute to < 2 mg/mL X 40 mg/100 mL 200mg/500ml MAX: 200 mg/100 mL HIGH RISK MED Clindamycin Concentration Usual Dosing and Administration Infusion over 60 minutes Children 20-30 mg/kg/day divided q 12 h CF: 30 mg/kg/day divided q 8 or 12 hrs Bolus:IVP: 0.1-0.2mg/kg over 5-10 seconds Infusion: 1-4 mcg/kg/minMAX 10 mcg/kg/min X X X Dilute to < 18 mg/mL Cyclosporine (Sandimmune®) X X X Dilute in D5W to < 2.5 mg/mL D10W X X X X 100 mg/mL Neonates: 100-200 mg/kg /dose (=1-2 mLs/kg) over 1 minute. D25W X X X X 250 mg/ML Bolus: MAX of 200 mg/kg (=0.8 mLs/kg) over 1 minute not to exceed 6 mLs/minute if undiluted Infants <6 month: 0.25-0.5 gm/kg/dose (=1-2 mLs/kg) MAX of 25 g(50 mLs/dose) Infants >6 months-40 kg: 0.5-1 g/kg/dose (=2-4 mLs/kg); MAX of 25 g(50 mLs)/dose Hyperkalemia<40kg D25W-2mls/kg(0.5gm/kg) over 15-30 minutes + insulin regular 0.1unit/kg IV (MAX 50ml (=25gm) +5 units insulin/dose. Bolus: >40 kg not to exceed 3 mls/minute if undiluted Adolscent/Adult: 25-50 gms (50-100 mLs) over 5-30 minutes Hyperkalemia:adolescent/adult 25-50 gm + 5-10 units insulin (5gm (10ml) per 1 unit insulin) over 5-60 minutes. (Cleocin®) 2.5GM/10ML SYRINGE D50W X X X 500 mg/mL 25gm/50ml syringe Comments May cause venous irritation Monitor muscle twitch response to peripheral nerve stimulation, heart rate and blood pressure Not renally orhepatically metabolized Infusion over 10-30 minutes, not to exceed 0.5 mg/kg/minute Dose: 20-40 mg/kg/day divided q 6 or 8 hrs Usual adult 600-900 mg IV q 8h MAX 4.8 gm/day Initial: 5-6 mg/kg/dose (1/3 of oral dose) administered 4-12 hours prior to transplant Maintenance: 2-10 mg/kg/day in 2 divided doses. May be administered over 2-6 hours or as a continuous infusion. NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. Doses prepared in glass. Use Non PVC tubing( ie// nitro tubing) Patients should be monitored continuously for ≥ the first 30 minutes of the infusion for signs of anaphylaxis. Monitor serum drug levels, serum creatinine and BP Monitor blood and urine sugar, serum electrolytes and I & O. For peripheral venous administration, dilute dextrose to MAX concentration of 12.5%. (1:1 with NS)preferred. Monitor blood and urine sugar, serum electrolytes and I & O. Avoid in infants/ young children. Dextrose 10-25% preferred. Peripheral: Dilution to 12.5% (1:3 D50:NS) preferred. 5 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For ICU ED Dexamethasone (Decadron) X Dexmedetomidine (Precedex) X Diazepam (Valium) X Digoxin (Lanoxin) X Telemetry Required X Concenration Acute Care IV P X X X IV Infusion 4 mg/mL X 200 mcg/50 mL (4mcg/ml) X 5 mg/mL X Dilute to < 100 mcg/mL w/NS Moderate sedation service + moderate sedation RN X MD administration for loading doses only. X X Maintenance doses Digoxin Immune Fab (DigiFAB) X X X X Dilute to 1-10 mg/mL with NS Diltiazem (Cardizem) X X X X 5 mg/mL for IVP Infusion 1 mg/mL Diphenhydramine (Benadryl) X X X Dilute to <50 mg/mL Usual Dosing and Administration Comments Please see reference for dosing for specific indications (usual range 0.3-2 mg/kg/day as a generally up to 40 mg/day) divided q 6-24 hrs. If dose <10 mg, administer IV push over 1-4 minutes. If dose >10 mg, dilute with D5W or NS and infuse over 1530 mins Requires pediatric ICU, moderate sedation service, or anesthesiology attending approval Bolus( attending present) 0.5-1 mcg/kg over 10 minutes Infusion: Usual 0.2-0.7 mcg/kg/hr. Higher doses have been used. Monitor hemoglobin, occult blood loss, serum potassium and glucose. IVP: Peds< 40 kg not to exceed 1-2 mg/min, >40 kg 5 mg/min Dose:0.04-0.3 mg/kg/dose (up to 10 mg/dose) every 2-4 hours to MAX of 0.6 mg/kg within an 8-hour period if needed. Infusion:Slowly administer over 5-10 mins Dosing: See age specific references Loading Dose: range 10-30 mg/kg divided in 3 doses over 16-24 hrs (as 50%/25%/25%) not to exceed total 1 mg dose. Maintenance: approx 1/3 of loading dose divided q 12 or 24 hrs. Rarely exceeds 10 mcg/kg/day up to 0.25 mg/day. Requires toxicology consult! Dosing based on amount of digoxin ingested. Each 40mg vial binds 0.5mg digoxin IVP: If in Cardiac Arrest over3-5 minutes using. Infusion preferred. Infusion:Over 15-30 minutes through 0.22 micron filter. Decrease rate or hold if infusion reaction occurs. Bolus: 0.25 mg/kg over 2- 5 minutes; if inadequate response, 0.35 mg/kg dose may be administered after 15 minutes Infusioncontinuous(start after IV bolus doses) < 50 kg (limited data) 0.05-0.15 mg/kg/hr up to 15 mg/hr Adult: 5-15 mg/hr IVP:0.5 mg/kg/min up to 25 mg/minute Infusion: Over 10-15 minutes Dosing: 0.5-2 mkg/dose(MAX 100 mg) up to 5 mg/kg/day(MAX 300 mg) divided q 6 hrs May cause phlebitis Monitor heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure and mental status NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. Ensure airway and respiratory support measures in place, monitor level of sedation, heart rate, respiration, rhythm. Bolus doses associated with bradycardia and hypotension. c Loading dose requires telemetry. Not for maintenance dose. Monitor heart rate, rhythm, periodic EKGs, serum electrolytes, renal function and serum levels. 0.22 micron filter required Monitor EKG, serum potassium and digoxin serum levels. Check for S/S of an acute allergic reaction. During administration monitor EKG, heart rate, blood pressure and renal function. Monitor symptom relief and sedation 6 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For Acute Care Concentration IV P ICU ED Telemetry Required Dobutamine X X X Dopamine X X X Doxycycline (Vibramycin) X Droperidol (Inapsine) X Enalaprilat (Vasotec) X Enoxaparin (Lovenox) X X X X IV Infusion X X 2.5 mg/mL In pts w/ cardiac history X <10 kg 250 mg /250 mls > 10kg500 mg /250 mls MAX: 1000 mg/250 mL <10 kg 200 mg /250 mL >10kg 400 mg /250 mL MAX: 800 mg/ 250 mL Dilute to <=1 mg/mL MAX: 2.5 mg/mL X X < 1.25 mg/mL SC 100 mg/mL For doses <10 mg, a special dilution of 20mg/ml will be prepared by pharmacy MD available X S C Usual Dosing and Administration Comments Infusion: continuous at 2-20 mcg/kg/minute. MAX 30 mcg/kg/min Monitor EKG, blood pressure, heart rate, CVP, MAP and urine output. Infusion: continuous at 1-20 mcg/kg/min; titrate to desired response; MAX dose 30 mcg/kg/min. Central line preferred. Monitor EKG, blood pressure, heart rate, CVP, MAP and urine output. Infusion: Doses < 100 mg over 1-2 hrs Children: (rarely used) 2-5 mg/kg/day divided q 12 or q 24 hrs not to exceed 100 mg/dose Adolescents/Adults:Rarely exceeds 200 mg/day. IVP: Slowly over 2-5 minutes Postop nausea/vomiting prophylaxis 0.05-0.06 mg/kg/dose; MAX 0.1 mg/kg up to 2.5 mg Postop nausea/vomiting treatment: 0.01-0.03 mg/kg/dose; MAX 0.1 mg/kg up to 2.5 mg Adult: 0.625-2.5 mg/dose May cause phlebitis, dizziness, N/V I5-10 mcg/kg/dose administered every 8-24 hours (as determined by blood pressure readings) over 5-15 minutes. MAX: 60 mcg/kg/day, rarely to exceed 20 mg/day Infants <2 months: Prophylaxis: 0.75 mg/kg every 12 hrs Treatment: 1.5 mg/kg every 12 hours Infants >2 months and <18 years: Prophylaxis: 0.5 mg/kg every 12 hours Treatment: 1 mg/kg every 12 hours NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. Monitor blood pressure, heart rate, respiratory rate, temperature, serum potassium and magnesium. Observe for dystonias and extrapyramadial side effects. EKG monitoring is recommended in patients with a history of QT prolongation or cardiac disease. Clinical response seen within 15 minutes, peak within 4 hrs. Monitor blood pressure, renal function, WBC, serum potassium and serum glucose. Deep SC administration preferred(not im) and allowed in all nursing units. Do not rub injection site after administration. Monitor CBC, platelets, stool occult blood tests. If antifactorXa level are indicated, draw peak levels 4 hrs post dose. 7 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For Concen tration Acute Care IV P IV Infusion X X X ICU ED Telemetry Required Epinephrine (Adrenalin®) X X Ertapenem (Invanz®) X X Erythropoetin (EPO®, Procrit®) X X Esmolol (Brevibloc®) X Esomeprazole (Nexium®) X Etomidate X SC, IVP For anaphylaxis, CPR X X X For IVP 1:10,000 (0.1 mg/mL) For ET/ SC /Drips 1:1,000 (1 mg/mL) Drip Concentrations < 10 kg 8mg / 250mls 10-50kg 16 mg/ 250mls >50 kg 4 mg/ 250 mls MAX: 16 mg/250 mLDilute to < 20 mg/mL in NS only. Various, may be given undiluted or diluted 1:1 with NS X X X X X X X X Per moderate sedation protocol Moderate sedation service + sedation RN <10 mg/mLfor IVP 20 mg/mL drip < 4mg/ml 2mg/ml 20 and 40mg vials Usual Dosing and Administration Comments IV Push: 0.01 mg/kg (=0.1 mL/kg) up to 1 mg (10 mLs) over 1 minute, every 3-5 minsprn. Infusion: 0.1-1 mcg/kg/min; titrate dose to desired effect. Central line preferred. Do not use if pink in color. Monitor EKG, heart rate, blood pressure, pulmonary function and injection site monitoring for extravasation. Infusion: Over 30 minutes. 3 mths-12yrs: 15 mg/kg/dose q 12 h up to 1 gm/24 hrs Adolescent/Adult: 1 gm q 24 hrs. IVPush:Over no less than 1 minute, SC preferred, See pediatric dosing recommendations for disease specific guidelines. Range 10-600units/kg Bolus: 250-500 mcg/kg over 1-2 minutes Infusion: 50-300 mcg/kg/min; titrate up every 20 mins to desired effect. Dosing may be higher with SVT (up to 1000 mcg/kg/min in small children) 1-2 mg/kg/day administered in 1-2 divided doses. Usual adult dose 20-40 mg/day MAX 80 mg IVP: Dilute with 5 mLs NS per vial and push over ≥ 3 minutes. Infusion: Add 40mg to 100ml Moderate Sedation for Short Procedures: -.10.2mg/kg/dose RSI/ induction of Anesthesia: 0.3mg/kg IV (-.20.6mg/kg) IVP: Over 30-60 seconds Do not infuse with dextrose containing solutions. NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. Do not shake vial. Monitor Hgb/Hct, Iron stores, BP EKG, BP, HR, respiratory rate monitoring mandatory during administration. Gastric pH monitoring may be needed in select patients. Has no analgesic properties. Requires moderate sedation monitoring with procedure related use. May result in transient myoclonus. Avoid small vessels on the dorsum of the head or hand. May cause discomfort at injection site. 8 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For ICU ED Famotidine (Pepcid®) X Fentanyl(Sublimaze® ) X Telemetry Required Concen tration Acute Care IV P X X X X IV Infusion Dilute to >=4mg/ml X Filgastim (G-CSF, Neupogen®) X X Fluconazole (Diflucan® X X Flumazenil (Romazicon®) X X X S C Gastric pH monitoring may be needed I select patients X 10 mg/mL vial STD infusion 10mg/250NS (40mcg/ml) MAX Infusion 10 mg/100 mL NS (100 mcg/mL) Dilute with D5W only to a concentration greater than or =15 mcg/mL (ie//300 mcg/ 20-50 mLs). Usual dosing: 0.1-0.8 mcg/kg/minute Recommended MAX 1.6 mcg/kg/min Titrate: 0.05-0.1 mcg/kg/minute q 10-20 minutes Do not bolus or flush line. Monitor HR, BP, EKG, renal function Infusion over 15-30 minutes. Incompatible with NS. Dosing: 5-10 mcg/kg/day Do not administer 12 hrs before or after radiotherapy. Dilute to <2 mg/mL Infusion: <6 mg/kg up to 400 mg over 1 hr > 6 mg/kg over 2 hrs Dosing: 3-12 mg/kg/day 0.01 mg/kg (MAX dose: 0.2 mg) given over 15-30 seconds. May repeat after 45 seconds and then every min to MAX total cumulative dose 0.05 mg/kg or 1 mg, whichever is lower. See dosing table. Monitor level of consciousness and resedation, airway, BP, HR and RR. X X X <3 months: 0.5 mg/kg/dose once daily 3 mths-1 yr: 0.5 mg/kg/dose twice daily 1-12 yrs: 0.5-1 mg/kg/day divided twice daily IVP: Over > 2 minutes. MAX 10 mg/min Infusion: Over 15-30 minutes MAX DOSING: 2mg/kg/day Younger infants: Bolus: 1-2 mcg/kg/dose over 35 mins; may repeat every 2-4 hrs. Doses >5 mcg/kg over 5-10 minutes. Infusion: 1-2 mcg/kg bolus, then 0.5-1 mcg/kg/hr; titrate to desired effect Older infants and children 1-12 years: Bolus: 12 mcg/kg/dose over 3-5 mins; may repeat every 30-60 mins. Doses >5 mcg/kg over 5-10 minutes. Infusion: 1-3 mcg/kg/hr; titrate to desired effect. 50 mcg/mL IVP 2000 mcg/100 mL MAX: 2000 mcg/40 mL 5000 mcg/ 100 mL Epidural OK Fenoldopam (Corlopam®) Comments X Moderate sedation service Only HIGH RISK MED Usual Dosing and Administration 0.1 mg/mL NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. Titrate to patient response using age appropriate pain scale.Peak response 5-10 minutes post dose. Monitor respiratory rate, blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation, and bowel sounds. Rapid IV push may cause apnea/ muscle and chest wall rigidity. 9 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For ICU ED Telemetry Required Concen tration Acute Care IV P IV Infusion X Folic Acid (Folvite®) X X X Fosphenytoin (Cerebyx®) Note:preferred over X X X Furosemide (Lasix®) X X X Gentamicin X X 0.1 mg/mL 25 mg PE/mL phenytoin, write all doses as PE equivalents X 10 mg/mL 100 mg/100 mL X Dilute to 2 mg/mL 40mg/ml for IM use Usual Dosing and Administration Infants: 15 mcg/kg/dose daily or 50 mcg daily 1-10 years: 1 mg/day initial; maintenance 0.1-0.4 mg/day >11 years: Initially 1 mg/day; maintenance 0.5 mg/day MAX rate: 5 mg/min Loading dose: 10-20 mg PE/kg not to exceed 3mg PE/kg/min up to 150 mg PE/.minute Maintenance: 4-8 mg PE/kg/day in 2-3 divided doses IVP: MAX rate: 0.5 mg/kg/min up to 20 mg/minute IVP; 0.5-2 mg/kg/dose every 6-12 hrs (MAX 6 mg/kg/day) Infusion: 0.05-0.4 mg/kg/hr Infusion:Administerover 30 minutes. Peak levels drawn 30 minutes after infusion completed. Trough levels just before dose. Infants > 7 days and children <5yrs: 2.5 mg/kg/dose every 8 hours; once daily dosing: 5-7.5 mg/kg/dose every 24 hrs Children >5 years: 2-2.5 mg/kg/dose every 8 hours; once-daily: 5-7.5 mg/kg/dose every 24 hours. Cystic Fibrosis: 5 mg/kg/dose q 12 hr or based on previous dosing history. For other dosing, please see reference for dosing for specific indications. NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. Comments Monitor CBC with differential Doses of fosphenytoin are expressed in phenytoin equivalents (PEs). Monitor ECG, BP and RR during loading dose q 5 minutes and for ≥ 30 minutes thereafter. Monitor serum phenytoin levels, CBC, platelets, glucose and LFTs. Monitor I & O, electrolytes, renal function, BP; in high doses monitor hearing. Monitor serum levels, urine output, and serum creatinine, drug levels. 10 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For ICU ED Insulin Regular (NovolinR®) Telemetry Required X Concentration Acute Care IVP IV Infusion X X X < 50kg: 25 units/50 mlsMAX: 100 units/ 100 mL X X X X X May give undiluted, or as an infusion of < 2mg/ml 20mg/ml, 50mg/ml Infusion 200 mg/100 mL NS 500mg/250ml In Code HIGH RISK MED Iron Sucrose (Venofer) X Ketamine (Ketalar®) X Ketorolac (Toradol®) X Labetalol (Normodyne®, Trandate®) X X for moderate sedation, MD present X See comments X Critical care areas only X X X MD available X 15 mg/mL 30 mg/mL X Critical care areas only 5 mg/mL 500 mg/250 mL 900 mg/250 mL Usual Dosing and Administration Comments IVP: Over 1 minute Infusion: (regular insulin only) DKA: Initial0.05-0.1 units/kg/hour up to 10 units/hr, titrate to response. > 50 kg: Normoglycemia in ICU..see adult protocol Hyperkalemia: after calcium and bicarb administration, infuse dextrose 0.5-1 gm/kg over 15-30 minutes followed by insulin 0.1units/kg Critical illness hyperglycemia: Review indications with ICU attending. Usual starting dose 0.02-0.05 units/kg/hr titrateto maintain blood glucose 80-140 Dosing: Refer to dosing references. Limited pediatric dosing available. IVP: Give each 100mg over 2-5 minutes (MAX 200mg) Infusion: Each 100mg over 15-30 minutes Monitor urine sugar, blood sugar and electrolytes. Drug may adsorb to IV bag and tubing, when using new tubing, prime, wait 30 mins, then flush tubing prior to starting infusion. IVP: 0.25-2 mg/kg not to exceed 0.5 mg/kg/min. Supplemental doses usually 1/3 to ½ of initial dose. Infusion: Usual for analgesia/sedation or bronchospasm 5-20 mcg/kg/minute Monitor RR, BP,HR, O2 sats. Avoid in patients with increased ICP or hypertension Increases oral secretions. Pretreatment with glycopyrrolate is recommended if used for monitored sedation. Monitor for signs of pain relief, BUN, creatinine, liver enzymes, blood loss and urine output. Stop before surgery due to prolonged bleeding IVP: Over 1-2 minutes Bolus: (optional): > 2yrs. MAX 1 mg/kg up to 60 mg x 1 Maintenance: > 6 months 0.25-0.5 mg/kg/dose (MAX 30 mg given every 6 hours as needed, not to exceed 20 doses/treatment course. Bolus: 0.25-0.5 mg/kg/dose up to 1mg/kg MAX rate: 0.25mg/kg over 3 minutes up to 10mg/minute. Peak effect 5-15 minutes, duration 2-4 hrs. Infusion: 0.4-3 mg/kg/hour > 50kg: 2-6mg/minute NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. No test dose required. May cause hypotension, esp w/ IVP. .Hypotension may be rate related. ECG monitoring ,HR, and BP recommended during administration. Monitor heart rate and blood pressure every 5 mins until stabilized and every 15 mins during hypertensive episode up to 30 minutes post dose. Patient should remain supine up to 3 hrs post dose. Monitor blood pressure and heart rate pre/post doseeInfusion allowed in ICU only. 11 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For ICU ED Telemetry Required Concentration Acute Care IVP IV Infusion X X IVP Dilute to 5 mg/mL. Infusion: 100 mg/250 mL Lepirudin (Refludan®) X X Levetiracetam Keppra® X X X Dilute to < 15mg/ml w/NS Levofloxacin (Levaquin®) X X X Dilute to 5 mg/mL Levothyroxine (Synthroid®) X X X X May dilute w/NS to 40 mcg/mL (5 mLs/200 mcg) Lidocaine X X Code only X X 20 mg/mL IVP 2 grams/250 mL Linezolid (Zyvox®) X X X 2 mg/mL Usual Dosing and Administration Comments Requires hematology/oncology approval! May contact anticoagulation service for dosing recommendations and monitoring. Dosing adjustment with renal impairment required. Bolus: 0.4 mg/kg not to exceed 44 mg over 15-20 seconds. Infusion (continuous): Initially 0.15 mg/kg/hr not to exceed 16.5 mg/hr, titrate based on an aPTT. Dosing:20-60mg/kg/day divided q12hrs MAX 4GM/day Infusion:Over 15 minutes Monitor aPTT, renal function, and for signs and symptoms of bleeding. Infusion: Over 60-90 minutes 6 mths-5 yrs: 10 mg/kg/dose every 12 hours(limited data). Children> 5 yrs: 10 mg/kg/dose every 24 hrs (MAX dose: 500 mg) Adolescents/Adults: 250-750 mg IV q 24 hrs IVP: Dilute vial with 5 mL NS, use immediately, administer over 2-3 minutes. Discard remainder. See age specific initial dosing, or per endocrine; IV form is 50% of PO recommendation. Too rapid infusion may cause hypotension. Monitor renal, hepatic, and hematopoietic function periodically; number and types of stools/day for diarrhea. IV dose usually 50% of oral dose. Monitor T4, TSH, heart rate, clinical signs of hypo- and hyperthyroidism.May be used as a continuous infusion prior to organ donation— Monitor EKG, HR, BP.UO, LFT’s and serum concentrations with continuous infusion & IV site for thrombophlebitis if via peripheral administration. Contraindicated with heart block. Lower dosing may be required with severe CHF or hepatic impairment. Requires ID approval. Avoid foods/beverages high in tyramine to avoid hypertension (consult nutrition) Load: 1-1.5 mg/kg over 2-4 minutes up to MAX 0.7 mg/kg/min up to 50 mg/minute, MR 0.5-1 mg/kg Q 5-10 minutes X 2 Infusion: 20-50 mcg/kg/min MAX up to 6 mg/min in adults (usual 1-4 mg/min). Infusion: Over 30-120 minutes < 12yo: 10 mg/kg/dose q 8-12 hrs up to 600 mg/dose >12yo/adult: 400-600 mg q 12 hrs NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. 12 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For ICU ED Lorazepam (Ativan®) X Telemetry Required Concentration Acute Care IVP X X IV Infusion X ICU only IVP: May be diluted to 1 mg/mL w/ NS MAX 4 mg/mL Infusion 50 mg/50 mL 250 mg/250 mL Magnesium Sulfate X X Mannitol (Osmitrol®) X X X X X Low dose Meperidine (Demerol®) X X X 50 grams /250 mLs (20%) X Dilute to < 10 mg/mL X Dilute to 20 mg/mL slow HIGH RISK MED Meropenem (Merrem®) X X X PEDI STD: 1 GM/25 mLS (40 mg/mL) ADULT: 1 gram/50 mL 2 grams/50 mLs 12.5 grams/ 50 mL (25%) Usual Dosing and Administration Comments IVP: Not to exceed 0.05 mg/kg over 2-5 minutes up to 2 mg/minute Dosing:0.02-0.1 mg/kg/dose (given every 4-8 hours as needed). Initial MAX 2 mg for sedation, 4 mg for seizures. Infusion:0.05-0.15 mg/kg/hr up to 2 mg/kg/day or 100 mg/DAY whichever is less. (see comments) Usual adult initial dosing 0.5-2mg/hr Monitor respiratory rate, blood pressure, heart rate and symptoms of anxiety. Monitor for phlebitis/ infiltration with peripheral access. With normal renal function, doses approaching 3 mg/kg/day( up to 170 mg/24 hrs should be monitored for propylene glycol toxicity (hyperosmolarity, lactic acidosis, renal toxicity) . Other adult studies have recommended doses not to exceed 1mg/kg/day .Patients with renal compromise should switch to oral lorazepam, seek alternative agents, or monitor for toxicity using lower dosing. Infusion ICU only. Can cause hypotension with too rapid infusion.Monitor serum magnesium, deep tendon reflexes, respiratory rate and blood pressure. 1 gm=8.12 mEq=98.6 mg Magnesium Asthma: 25-75 mg/kg over 20 minutes Torsades/PALS: 25-50 mg/kg over 10-20 minutes Repletion(non-acute): 25-50 mg/kg/dose infused over 2-4 hrs IVP: 0.2gm/kg over 3-5 minutes Infusion: 0.25-1 gm/kg over 15 -60 minutes. Requires inline filter. Central line preferred. Monitor for extravasation. IVP slow: 1 mg/kg/dose over 3-5 minutes every 3-4 hours as needed; administer over ≥ 5 mins (do not exceed 25 mg/min) MAX 100 mg/dose, up to 6 mg/kg/day. Avoid repeated doses with renal dysfunction. IVP: Over 3-5 minutes Infusion: Over 15-30 minutes Dosing: 20-40 mg/kg/dose q 8hrs up to 2 Gm/dose NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. Evaluate dose for crystal formation prior to administration. In-line <5 micron filter should always be used with concentrations >20%. . Central line preferred. Extravasation may cause edema and necrosis. Monitor renal function, daily I & Os, serum electrolytes, serum and urine osmolality. Restricted use to post-anesthesia shivering and rigors. Monitor respiratory and cardiovascular status and level of sedation, and pain. Requires ID approval. 13 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For ICU ED Methadone (Dolophine®) Telemetry Required X Acute Care Concentration IVP X IV Infusion X Methylprednisoloneso dium succinate (Solu-Medrol®) X X X 10 mg/mL Dilute w/ NS to volume needed to infuse over 15 minutes Infusion: Over 5-15 minutes Initial Dose in narcotic naïve patients: 0.05-1 mg/kg/dose up to 10 mg/dose q 6-12 hrs(1st 24 hrs) , as drug accumulates over 24-96 hrs, , dosing frequency may need to be reduced to q 12-24 hrs. Monitor RR, HR, BP, sedation and pain levels. Abstinence scoring is used for withdrawal. Monitor for QT prolongation in patients with risk factors. X Dilute with D5W to < 10 mg/mL Initial: 2-10 mg/kg/dose every 6-8 hours. MAXdose 1 gm, Daily dose: 65 mg/kg or 3 grams, whichever is less. Infusion:Administer slowly over 30-60 mins X 40 mg, 125 mg, 500 mg & 1 g vial Dosing: 0.5-2 mg/kg/day as high as 30 mg/kg depending on indication. IVP: <1.8 mg/kg up to 125 mg over 3-15 minutes Infusion:May dilute each 1gm dose in a minimum of 100 mls NS (10mg/ml) (exception: spinal cord injury protocol Onset: 4-6 hrs Duration: 10-16 hrs Monitor blood pressure, CBC with differential, hemoglobin, hematocrit, and liver enzymes. Caution: Methylprednisoloneacetate is for IM use only. Monitor blood pressure, serum glucose and electrolytes. <1.8 mg/ kg Metoclopramide (Reglan®) X Metronidazole (Flagyl® ) X Midazolam (Versed®) X X X X 5 mg/mL X 5 mg/mL X <50kg: 50mg/100ml MAX: 100 mg/100 mL 1 mg/mL, 5 mg/mL Low dose X X X Per monitored sedation protocol for moderate sedation, MD present X Comments X HIGH RISK MED Methyldopa (Aldomet®) Usual Dosing and Administration < 2mg/kg: administer over 1-3 minutes >2 mg/kg: administer over 15-30 mins 15 mg/kg up to 500mg: Administer over >+30 minutes >15 mg/kg up to 1 Gm: Administer over 1 hour Dosing: 0.1-1 mg/kg/dose q 4-6 hrs IVP: Low dose 0.1 mg/kg up to 10 mg over 1-2 minutes Infusion over 15-30 mins (MAX rate: 5 mg/min) Dosing: 20-45 mg/kg/day up to 4 gms/day divided every 6 or 8 hrs Infusion: Over 60minutes 6 months-5 years: Initial 0.05-0.15 mg/kg (MAX total dose: up to 0.6 mg/kg up to 6 mg) 6-12 years: 0.025-0.05 mg/kg (MAX total dose: up to 0.4 mg/kg up to 10 mg in nonintubated patients) IVP: over 2-5 mins, longer for higher doses Infusion: 0.06-0.4 mg/kg/hour MAX 0.4 mg/kg/hr NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. Consider pretreatment with diphenhydramine for doses > 0.25 mg/kg. Monitor for EPS. Too rapid administration may cause anxiety Administer diphenydramine for patients Do not refrigerate. Doses other than 500 mg will be found in the Pyxis drop-off box. Monitor level of sedation, respiratory rate, blood pressure, heart rate and oxygen saturation 14 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For ICU ED Telemetry Required Milrinone lactate (Primacor) X X Morphine Sulfate X Acute Care X Concentration IVP X IV Infusion 1 mg/mL 10 mLs Infusion: 20 mg/100 mL Load: 25-100mcg/kg over 15 mins Infusion: 0.2-1.2 mcg/kg/min Monitor EKG, BP, HR, UO platelet count, potassium, renal function, signs and symptoms of HF X 2, 4, 10 mg/ml PCA 1, 5 mg/mL INF: 1mg/ml 100 or 250ml MAX: 500 mg/ 100 mL Bolus: 0.05-0.1 mg/kg/dose up to initial MAX 10 mg over 5-30 mins Infusion: Initial 0.005-0.15 mg/kg/hr; titrate to patient pain response and tolerance. Monitor HR, RR, BP, oxygen saturation, pain relief and level of sedation. X 20 mg/mL 1-1.5 gm/ 50 mLs 1.6-2 gm/100 mLs Dosing: 50-200 mg/kg/day divided q 4 or q 6 hrs MAX 12 gms/day IVP: Over 5-10 minutes Infusion: Over 30-60 minutes Monitor for burning, extravasation, phlebitis X 10 mg/mL 20 mg/mL Premed: 0.1-0.2 mg/kg MAX 20gm Analgesia: 0.05-0.15 mg/kg every 3-6 hours as needed. Initial MAX 10 mg MAX: 20 mg/dose up to 160 mg/day IVP: Administer over 3-5 mins Infusion:Over 15 mins Monitor relief of pain, respiratory and mental status, and blood pressure. HIGH RISK MED X Nalbuphine (Nubain®) X X X slow X X slow Comments X slow Nafcillin (Nafcil®) Usual Dosing and Administration NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. 15 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For ICU ED Naloxone (Narcan®) Telemetry Required X Concent ration Acute Care IVP X X IV X 0.4 mg/ mL Infusion: 4 mg/100 mLs NS (0.04 mg =40 mcg/ mL) X X Comments Infusion IVP dilution: < 40 kg 0.1 mg in 9.75 mLs NS =(0.01mg/mL) > 40 kg 0.4 mg in 9 mLs NS= (0.04mg/mL) Neostigmine (Prostigmin®) Usual Dosing and Administration X 0.5 mg/ml slow 1 mg/mL Nicardipine (Cardene) X X X Standard/Periph eral- Add 25 mg to 250 mLs NS (0.1mg/mL) MAX/Central: Add 100 mg to 60 mLs NS (1 mg/mL) Nitroglycerin X X X 100 mg/250 mLs Post anesthesia narcotic reversal: Narcotic naïve: 0.005-0.01 mg/kgIVP q 2-3 mins as needed Opiate dependent: 0.001-0.002 mg/kg IVP q 2-3 mins as needed(1/10th-1/5th usual dose to prevent acute withdrawal) IVP: Over 30 seconds Narcotic-induced pruritis: 0.25-2 mcg/kg/hr; increase by0.25- 0.5 mcg/kg/hr every few hours as needed Monitor respiratory rate, heart rate, and blood pressure. The duration of action of naloxone is shorter than most opiates (20-30 minutes). Patients who receive naloxone should be monitored for reoccurance of respiratory depression. Patients with acute pain will require careful titration to maintain analgesia while reversing respiratory depression. Opiate intoxication: (narcotic naïve) <20 kg: 0.1 mg/kg every 2-3 minsprn >20 kg: 2 mg/dose every 2-3 minsprn Opiate dependent: (1/10th-1/5th usual dose to prevent acute withdrawal) Infusion: calculate initial dose/hour based on effective intermittent dose used and titrate; range: 2.5-160 mcg/kg/hour Non-depolarizing NMB reversal: with atropine or glycopyrrolate Infants: 0.025-0.1 mg/kg/dose Children: 0.025-0.08 mg/kg/doseMAX/DOSE (see adult) Myasthenia gravis treatment: 0.01-0.04 mg/kg every 2-4 hoursMAX/DOSE (see adult) Adult: 0.5-2.5 mg, MAX 5 mg IVP: Administer over several minutes up to 0.5mg/min Infusion: IF< 50 kg Initial 0.5-5 mcg/kg/minute If >50 kg: 2.5-15 mg MAX: 15 mg/HOUR. Titrate q 5-30 minutes Infusion: If < 50 kg 0.25-1 mcg/kg/min titrate by 0.5-1 mcg/kg/min every 3-5 mins as needed. MAX 20 mcg/kg/min >50 kg:5 mcg/min, titrate by 5-10 mcg/minq 3-5 mins up to 300 mcg/min NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. Atropine or glycopyrrolate recommended prior to neostigmine. Epinephrine should be available. Monitor HR, BP,RR, muscle strength. Monitor blood pressure and heart rate Monitor blood pressure and heart rate. Protect the drugfrom light. 16 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For Acute Care Concentrati on IVP ICU ED Telemetry Required Nitroprusside (Nipride) X X IV Infusio n X Norepinephrine (Levophed) X X X Usual Dosing and Administration Comments 100 mg/ 250 mL Infusion: 0.3-5 mcg/kg/min Titrate by 0.1 mcg/kg/min q 2-3 minutes MAX 10 mcg/kg/min <10 kg 8 mg/250 mL Infusion:Initial 0.05-0.1 mcg/kg/min. Titrate by 0.1-0.2 mcg/kg/minute every 5 minutes till desired effect or toxicity Recommended MAX 2 mcg/kg/min Protect the drugfrom light. Do not use if blue-green in color. Monitor blood pressure, heart rate, cyanide and thiocyanate toxicity; monitor acid-base status as acidosis can be early sign of cyanide toxicity; monitor thiocyanate levels if infusion needed for >3 days or dose >4 mcg/kg/min or in renal dysfunction; monitor cyanide levels in hepatic dysfunction. Monitor blood pressure, heat rate, urine output, and peripheral perfusion. Central line preferred. 10-50 kg + MAX 16 mg/250 mL Octreotide Acetate (Somatostatin) X X X X Note: not to be confused with Sandostatin LAR Depot IM injection >50 kg4 mg/250 mL 50, 100, 500 mcg vial for SC/IV admin Standard infusion: 500 mcg in 100 mLs NS/D5W (5 mcg/mL) REFRIGERAT ED Ondansetron (Zofran) X X X X 2 mg/mL Hypoglycemia/Antisecretory: 2-10 mcg/kg/day divided q 8 or 12 hours or as continuous infusion: titrate to patient response by increasing dose or interval; Monitor baseline and periodic ultrasound evaluations for cholelithiasis, blood sugar, thyroid function tests, fluid and electrolyte balance. GI bleed/esophageal varices:0.5-1 mcg/kg bolus, then 1 mcg/kg/hour continuous infusion; titrate to response(usual adult 25-50 mCG/HR) MAX DOSE: 1500 mcg/day SC: usual bolus route IV: infuse over 15-30 mins in NS IVP: over 3 minutes Chemo induced N/V: Children: 0.15 mg/kg/dose MAX 0.45 mg/kg/day up to 32 mg Nausea/Vomiting: Children >2 yrs <40 kg: 0.1 mg/kg Children >40 kg: 4 mg IVP: undiluted over 1-5 minutes Infusion: over 15 minutes in NS/ D5W NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. Monitor blood pressure and heart rate. May cause headache. 17 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For ICU ED Pamidronate (Aredia) X Pentobarbital (Nembutal) X Phenobarbital (Luminal) X Phenylephrine (Neo-synephrine) X Telemetry Required Acute Care Concentr ation IVP X X X X Continuous Infusion Or per moderate sedation protocol for moderate sedation, MD present slow X Prepared by pharmacy. Volume varies by dose. Hypercalcemia/osteopenia:0.5-1 mg/kg (MAX dose of 90 mg). Do not redose within 7 days. Infusion: Over 2-24 hrs. (Longer infusion times ↓ the risk of nephrotoxicity.) Infuse in dedicated line. X 50 mg/mL Sedation: Children >6–18 mths: 1-3 mg/kg Children >18 mths: 2 mg/kg, then 1-2 mg/kg every 5-10 minsuntil adequate sedation MAX: 100 mg/dose *IVP: slowly (<1 mg/kg/min up to 50 mg/min) Used only with conscious sedation monitoring or in ICU/ER. IV: Over 10-30 minutes. May be further diluted to no less than 5 mg/mL with NS. Do not use unless solution is clear. Pentobarbital Coma: Load: 15-35 mg/kg over 1-2 hrs Infusion: 1-5 mg/kg/hr viadedicated central line preferred. MAX: 10 mg/kg/hr Anticonvulsant: Load: 15-18 mg/kg at 1-2 mg/kg/minute (MAX 60 mg/minute). Maintenance: IV: < 1 mg/kg/min up to 30 mg/minute Infants: ≤ 5 mg/kg/day in 1-2 doses 1-5 yrs: 6-8 mg/kg/day in 1-2 doses 5-12 yrs: 4-6 mg/kg/day in 1-2 doses >12 yrs: 1-3 mg/kg/day in 1-2 doses Hypotension/Shock: Usual 0.1-0.5 mcg/kg/min; titrate to desired effect Infusion: 2500 mg/ 50 mls (50 mg/ml) X X IV Infusion X ICU/ ER only Usual Dosing and Administration X 65 mg/mL 130mg/ml X (for<10 kg) 5 mg/250 mL (10-+kg) 10 mg/250 mL MAX CONCENTR ATION 60 mg/250 mL Comments Thrombophlebitis. Monitor serum creatinine prior to each dose, urine output, serum electrolytes, phosphate, magnesium, hemoglobin, hematocrit, CBC with differential. Monitor vital signs, blood pressure, respiratory status, cardiovascular states, CNS status. Monitor for thrombophlebitis/extravasation. Central linr preferred and particulate filter required with continuous infusions. Check infusion regularly to monitor for precipitation. For pentobarbital coma, also monitor EEG bursts.. Monitor CNS status, seizure activity, LFTs, CBC, renal function, serum concentrations, respiratory rate, heart rate, blood pressure, Monitor heart rate, BP/MAP, CVP. Central line preferred PSVT: 5-10 mcg/kg over 20-30 seconds (Adult: 0.25-0.5 mg) NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. 18 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For ICU ED Phenytoin sodium (Dilantin®) Note:Fosphenytoin should Telemetry Required X Acute Care X Concent ration IVP IV Infusion X be used in children instead phenytoin Phosphate as Sodium Phosphate X X X Each 1 Meq Na+ = 0.75mM Phos, 1mMPhos = 1.33Meq Na+ Potassium Phosphate Each mMPhos= 1..47 meq K+ 1 meq K+ = 0.68mM Phos Phytonadione (Vitamin K, Mephyton®) X Piperacillin/Tazobactm (Zosyn®) X Potassium Chloride X HIGH RISK MED SC/IM only X For IV doses exceeding 0.3meq/kg/hr up to 10meq/hr X (ICU/ OR/ER only) X X X X Usual Dosing and Administration 50 mg/mL (mustdilute to 1-5 mg/mL in NS) Acute Seizures Load: 15-20 mg/kg in a single or divided doses MAXinfusion rate: Neonates: 0.5 mg/kg/min Children: 1-3 mg/kg/min not to exceed 50 mg/min All IV doses prepared by pharmacy. Volume depends on dose and whether via central or peripheral adminis tration. Dosing in MMols: Hypophosphatemia: Phos> 2: 0.05-0.1 Mm/kg up to 15mM Phos 1-2 mM/dl- 0.16-0.25mM/kg up to 30Mm 10 mg/mL 1 mg/mL 60 mg piperacillin and7.5 mg tazobactam/ mL 2.25 g/50 ml 3.375 g/50 mL 4.5 g/50 mL Pedi: 0.4 mEq/mL-25 mL vials for central bolus doses (10 mEq) Maintenance: 4-8 mg/kg/day in 2-3 divided doses Phos< 1mM/dl: 0.25-0.4mM/kg up to 0.6mM/kg to MAX 30mM/dose or 45mM/day IV infusion: Doses < 0.5mM/kg or 30mM over 4 hrs. Doses >=0.5mM/kg or 30Mm over 6 hrs *SC, IM, or PO preferred. Dose: 1-10 mg, Usual 1-2.5 mg IV(restricted) : Dilute w/ NS to volume needed to administer over 15-30 minutes. (see comments) Infants <6 mths: 150-300 mg of piperacillin component/kg/day in divided doses every 6-8 hours >6 mths: 200-350 mg of piperacillin component/kg/day in divided doses every 6-8 hours. CF: 350-450 mg/kg/day divided q4h or q6 hrs MAX 4.5gm/dose IV:Over ≥ 30 minutes Maintenance: Usual daily dose 2-5mEq/kg/day (Adult usual: 40-80 mEq/day.) Hypokalemia: Dosing depends on severity, etiology, and renal function. See comments on individual dosing limitations. 20 mEq/50 ml bags NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. Comments Loading doses: Monitor HR/ BP and RR during loading dose q 5 minutes and for ≥ 30 minutes thereafter. Telemetry monitoring recommended if patient has significant underlying cardiac disease. Particulate filter required. Check for extravasation. Monitor serum levels, CBC, LFTs, and blood pressure. Maximum Concentration: Peripheral 30mM Phos/L (1.5mM per 50mls Central: 30mM Phos/250 mls= 6mM per 50 mls INFUSION: Intermittent doses over 4-6 hrs. MAX: 0.06mM/kg/hr **in pediatrics, order doses in 50, 100, 150, 250, 500, OR 1000 ml volumes. **caution: for Kphos orders written in mM be aware of K+ dose pt will also be recieving Monitor for potential hypersensitivity reactions, flushing. Monitor BP, HR, RR.@ baseline then q 5 min during infusion . Monitor serum electrolytes, bleeding time especially high dose or w/ renal impairment. periodic tests of renal, hepatic, and hematologic function. MAX: Peripheral 0.06 mEq/mL (60 mEq/L) Central 0.4mEq/mL RATE: non-telemetry <0.3 mEq/kg/hr up to 10 mEq/hr Telemetry-0.6 mEq/kg/hr up to 20 mEq/hr Monitor serum potassium, glucose, chloride, pH, urine output if indicated 19 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For ICU ED Prochlorperazine (Compazine®) Promethazine (Phenergan®) Propofol (Diprivan®) Telemetry Required X X X Acute Care IVP IV Infusion X X X X X Concen tration X Moderate sedation service + moderate sedation RN X X 5 mg/mL 25 mg/mL X 10 mg/mL 200 mg/20 mLs 500 mg/50 mLs 1000 mg/100 mLs Do not dilute to less than 2 mg/mL with D5W (even via y-site) due to emulsion instability. Usual Dosing and Administration Comments Antiemetic: Children >10 kg: Dose IV/IM: 0.1-0.15 mg/kg/dose every 6-12 hours (MAX: 10mg/dose) IV: May be further diluted in a sufficient volume with NS and administered over 15-30 minutes IVP: Administer at MAX rate of 0.1 mg/kg/minute(MAX 5 mg/min) In children < 5yo, reserve this agent for patients who are unresponsive to other alternatives due to the higher risk of extrapyramidal effects. Alternative routes to IV preferred. Not recommended in patients < 2yrs of age due to significant respiratory depression. For use in children >2 years. Oral/rectal routes preferred. Antiemetic: 0.25-1 mg/kg (MAX dose: 25 mg in children, 50 mg in adolescents) 4-6 times/day as needed. Begin with lowest dose. Usual Adult Dose: 12.5-25 mg Monitor for extrapyramidal reactions, respiratory depression, hypotension, and signs of pain and extravasation. IV: Further diluted 1:10 (v/v) or greater in NS to minimize extravasation injuryand administered over 1020 minutes. ICU SEDATION: (> 24 hrs) Infusion 5-50 mcg/kg/minute. Titrate upward by 5-10 mcg/kg/min q 5-10 minutes to desired level of sedation and as hemodynamically tolerated. PRN boluses w/ infusion: 0.25-1 mg/kg up to 50 mg/dose MAX MAINTENANCE ICU sedation rate not to exceed 50 mcg/kg/minute. MONITORED PROCEDURAL SEDATIONInitiation: IVP: 0.5-3 mg/kg over 20-30 seconds OR 0.25-0.5 mg/kg/dose MAX 40 mg/dose q 10 seconds OR 100-300 mcg/kg/min x 3-5 minutes, then titrate to desired effect Maintenance infusion: usual 50-300 mcg/kg/min Monitor for extrapyramidal reactions, hypotension, and signs of extravasation. Avoid in patients with significant peanut/ soy/ or egg allergies. Monitor respiratory rate, blood pressure, heart rate, oxygen saturation, ABGs, depth of sedation, serum lipids or triglycerides if use is >24 hours. To minimize pain at injection site, administer through central line or large peripheral veins. Use filter with pore size > 5 microns. Insure strict aseptic technique. Unused drug and tubing must be discarded every 12 hrs to minimize risk of infection. Drug transferred to syringes must be discarded within 6 hrs. In patients receiving parenteral nutrition, consider amount of fat provided by propofolemulsion in nutrition goal. NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. 20 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For ICU ED Telemetry Required Propranolol (Inderal®) X X Protamine Sulfate X Acute Care IVP IV Infusion X 1 mg/mL May dilute each MG in 10-50 mLs NS X Rasburicase (Elitek®) X X Rho(D) Immune Globulin (WinRho®) X X Rocuronium X HIGH RISK MED Concen tration X X X X X 10 mg/mL* * After vial reconstitutio n with 5 mLSWI. May be further diluted with NS or D5W. 1.5 mg/mL Requires oncology attending approval. Prepared by chemo pharmacy in 10-50 mLs NS. Approx 230240 units/mL, as 0.5, 1.3, 2.2, 4.4, 13 mL vials Does not require further dilution. 1 mg/mL Usual Dosing and Administration Comments 0.01-0.025 mg/kg slow IV over 10 mins (MAX dose: 0.5 mg/dose for infants and 1 mg/dose for children) Usual adult dose: 1-3 mg slow over 10 minutes, not to exceed 1 mg/minute Conversion from PO to IV unpredictable due to first pass metabolism. Recommend alternative IV hypertensive’s (labetolol or metoprolol for BP control) Monitor blood pressure, CVP, and EKG Dose determined by the most recent time and dosage of heparin or low molecular weight heparin, (please see dosing references) MAX dose: 50 mg MAX rate: IVP < 5 mg/minute Use cautiously in pts with fish or protamine allergies. 0.15-0.2 mg/kg/dose MAX: 0.4 mg/kg/day for up to 5-7 days. Infuse over 30 minutes. Flush with NS pre- and post infusion. Monitor for potential anaphylaxis. Dedicated line preferred. Do not shake or filter. Recommended as a single course of therapy. Dose for ITP: 25-75mcg/kg slow IV over 3-5 minutes Hgb should be >8 gm/dl prior to administration. May be further diluted with NS. Infants: 0.5 mg/kg/dose, repeat every 20-30 minutes as needed Children: Initial: 0.6 mg/kg/dose with repeat doses of 0.075-0.125 mg/kg every 20-30 mins to desired effect Infusion: 10-12 mcg/kg/min Monitor peripheral nerve stimulator measuring twitch response, heart rate, blood pressure and assisted ventilator status. NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. Hypotension, bradycardia and flushing may be infusion rate related reactions. Continue to monitor coagulation, blood pressure, and cardiac status. 21 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For ICU ED Sodium Bicarbonate X Sodium Chloride 3% (hypertonic) 0.513meq Na+/ml X Sodium Chloride 23.4%(hypertonic) 4 meq Na+/ml Succinylcholine X X HIGH RISK MED Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim (Bactrim, Septra®) Telemetry Required X Concen tration Acute Care IVP IV Infusion X X X X X Preferred Emergency intubation only X X 5 mEq/10 mL(4.2%) (=0.5 mEq/mL)* *Preferred in infants and small children 50 mEq/50 mL(8.4%) (=1 mEq/mL) Please see reference for dosing for specific indications. Code: 1 mEq/kgdose over 3-5 minutes Concentrated electrolyte Symptomatic IsovolemicHyponatremia: uptp4mls/kg/dose over 15 minutes. (equivalent to ~ 1215mls/kg NS). HypovolemicHyponatremia:Use NS fluid bolus ICP Management: 1-4 mls/kg undiluted over 15 minutes May not be stored at bedside or in pyxis. Available for STAT Call pharmacy. 20 mg/mL Does not require futher dilution. REFRIGER ATE X Usual Dosing and Administration 16 mg/mL TMP 80 mg/mL SMZ Note:dosin g based on TMP component Non-Code:Not to exceed 1 mEq/kg/hr up to 50 meq/hr Prevention of tumor lysis: 120-200 mEq/m2/day Comments Monitor serum electrolytes, urinary pH and arterial blood gases if indicated, pain and phlebitis with peripheral administration. Hyperosmolar: Central line preferred, or dilute 1 mEq to 2 or 3 mLs for peripheral administration Verify compatability before Y-site administration with other drugs. ICP Management Adults: 15-30mls undiluted over 15 minutes Initial: 1-2 mg/kg (MAXtotal dose: 150 mg) Administer over 30 seconds. Maintenance: Avoid repeated dosing. 0.3-0.6 mg/kg every 5-10 mins as needed. For short-term administration due to risk of hyperkalemia. Evaluate risk-benefit in infants<2 months:. Avoid use if infant has hyperbilirubinemia or in patients with renal failure. Mild-Mod infections: 6-12 mg TMP/kg/day divided every 12 hours Serious infections: 15-20 mg TMP/kg/day divided every 6-8 hours. Administer MAX concentration of 1:10 dilution (each 5 mL of drug added to no less than 50 mLsof D5W) over 60-90 minutes. Complete infusion within 2 hrs of dilution due to limited stability. NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. Central line preferred. For correction of acute hyponatremia, avoid rapid increases in serum sodium. In symptomatic patients or is serum sodium < 120meq/L, target for an initial increase of 4-6meq/L, not to correct beyond 1215meq/L per 24hrs Central line required. Monitor serum Na+ and osmolar gap. Avoid in any patients with neuromuscular disorder/acute burns secondary to risk of hyperkalemia. Avoid with increased ICP. Because of the risk of malignant hyperthermia, use of continuous infusions is not recommended. Monitor heart rate and rhythm, serum potassium, assisted ventilator status, muscle twitching. Use a particulate filter. Monitor for precipitates, especially in maximally concentrated dilutions. Monitor for rash, phlebitis, urine output, CBC, renal function tests. 22 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For ICU ED Telemetry Required Terbutaline (Brethine®) X X Tobramycin (Nebcin®) X Tromethamine (THAM®) X Vancomycin (Vancocin®, Vancoled®) X Acute Care X X X Concentration Usual Dosing and Administration Comments IVP IV Infusion X X 1 mg/mLvials Infusion: 20 mg/100 mLs NS (200 mcg/mL) Prepared by pharmacy unless emergent. See infusion chart Bolus: 2-10 mcg/kg (administer from infusion bag0.010.05 mls/kg over 5-10 mins bag) Infusion:0.1-6mcg/kg/minute (MAX 10 mcg/kg/minute).Titrate by increments of 0.1-0.2 mcg/kg/min every 30 mins to desired effect. Monitor heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, serum potassium, CPK, EKG, and blood gases if applicable. X Dilute to < 5 mg/mL Monitor serum levels, urine output, and serum creatinine X 18 gm/500 mLs (0.3 mM/mL) 1 mEq=1 mm= 120 mg per 3.3 mLs Infusion:Administerover 30 minutes. Peak levels drawn 30 minutes after infusion completed. Trough levels just before dose. Infants > 7 days and children <5yrs: 2.5 mg/kg/dose every 8 hours; once daily dosing: 5-7.5 mg/kg/dose every 24 hrs Children >5 years: 2-2.5 mg/kg/dose every 8 hours; once-daily: 5-7.5 mg/kg/dose every 24 hours. Cystic Fibrosis: 5 mg/kg/dose q 12 hr or based on previous dosing history. For other dosing, please see reference for dosing for specific indications. Neonates: 1 mL/kg for each pH unit below 7.4. Infants/Children/Adults: Dose (in mLs)= kg X base deficit (mEq/L) X 1.1 up to 13.9 mLs/kg/dose Infusion:Over≥ 1 hr. 0.7-1 mL/kg/hr MAX 23 mls/kg/day. Acute Acidosis: 25% of dose over 5-10 minutes followed by remainder over 1 hr. X Dilute to <5 mg/mL Central: < 10mg/ml per request if fluid restricted Infusion:Over 60-90 minutes, slower if pt experiencing red-man syndrome (histamine-like reaction). < 7 days: 10-15 mg/kg every 12 hours > 7 days: 10-15 mg/kg every 6-8 hrs Infants> 1 month, children: 40-60 mg/kg/day divided every 6-8 hours up to initial MAX 1.5 gm/dose up to 4 gm/day. Adjust for renal dysfunction. NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard medication resources or consult the pharmacist. Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D. Intended for short-term use. Central line or large peripheral vein (pH10.5) preferred. Monitor for extravasation, tissue injury, thrombosis. Monitor for respiratory depression, hypoglycemia, hyperkalemia, renal functiom, serum pH, ABG’s, hyperosmolarity Monitor periodic renal function tests, urinalysis, serum vancomycintrough levels, and WBC. Use caution with concurrent NSAID use and/or dehydration + high dose vancomycin secondary to risk of induced acute renal failure 23 Pediatric Guidelines for IV Medication Administration Drug Approved For ICU ED Telemetry Required Acute Care Concen tration IVP IV Infusion Vasopressin X X X Vecuronium (Norcuron®) X X X X X HIGH RISK MED Verapamil (Isoptin®, Calan®) Voriconazole (VFend®) References X X X X X Usual Dosing and Administration Comments PTS <50 kg: DI: 5 units/ 500 mlsNS SHOCK: 50 units/ 250 mLs NS PTS>50 kg/adults DI: 10 units/250 mls NS SH0CK: 40units/ 100 mLNS IVP: Dilute to 1 mg/mL Continuous Infusion: 50 mg/100 mL D5W IVP: ACLS 40 units over 15-30 seconds PTS <50 kg: DI :0.0005 unit/kg/hr; double dose as needed every 30 mins to MAX 0.01 units/kg/hr SHOCK:0.02-0.12 units/kg/hr up to 2.4 units total/hr PTS>50 kg/adults: DI :0.0005 unit/kg/hr; double dose as needed every 30 mins to MAX 0.01 units/kg/hr Hypotension/Shock: 0.04-0.1 units/MINUTE Central Vein Preferred. Monitor fluid intake and output, urine specific gravity, urine and serum osmolality, serum and urine sodium. Monitor BP, S/S ischemia( digital, gut, coronary) IVP: Over seconds Pedi Dosing: Neonates: 0.05-0.2mg/kg/dose IV q1=2 hrs or per hr as continuous infusion. Monitor assisted ventilator status, heart rate, blood pressure, peripheral nerve stimulator measuring twitch response. Patients must be intubated and properly sedated. IVP: 1-2.5 mg/mL Infusion: IVP: Over 2-5 minutes Not recommended in infants. Monitor EKG, blood pressure and heart rate. IV calcium should be readily available. 50 mg/100 mL D5W Diluted by pharmacy to 0.5-5 mg/mL Lexi-Comp’s Pediatric Dosage Handbook- 14th Edition Pediatric Injectable Drugs-8th Edition 2008 Intravenous Medications-24th Edition Micromedex UMMMC Adult Guidelines for IV Medication Administration 2007 VUMC IV Medication Administration Chart revised 09/21/04 University of Kentucky Chandler Medical Center Pediatric IVP/Infusion Drug Lists 2005 Children’s Hospital and Clinics of Minnesotta Pediatric IV Administration Guidelines Revised 09/05 Children 1-16 years: 0.1-0.3 mg/kg/doseMAX initial dose 5 mg, MR in 15-30 minutes x 1 with MAX of 0.3 mg/kg to 10 mg/dose Infusion: Over 1-2 hrs not to exceed 3 mg/kg/hr Dose:3-6 mg/kg/dose q 12 hr, esophageal candidiasis doses may be lower Patients may commonly experience reversible visual changes. Monitor electrolytes. Use cautiously in patients with proarrythmic conditions. Infectious disease approval required. Do not use IV form in renal failure Editor: Barbara Maas Pharm. D. Primary Reviewers/Co-editors: Angela Gilchrist Pharm. D., Amy Hellinger Pharm. D., CharlesTurck Pharm. D. Primary Nursing Reviewers: Carol Kronopolis, Charles Wheeler, Lynn D’Angelo, Rosemary Cerquiera Primary Physician Reviewers: Hospitalist- Tom Guggina ICU Attending- Scott Bateman ER Attending-Mariann Manno Appoved by Pharmacy and Therapeutics 09/14/08 Add formedication future: Cosyntropin, lopressor, gancyclovir, immune globulin, sodium 24 NOTE: This is not a comprehensive medication list. For items not listed, review standard resources oralteplase, consult the pharmacist. chloride 3%, etomidate Version 9/28/2008 Barb Maas Pharm. D.