
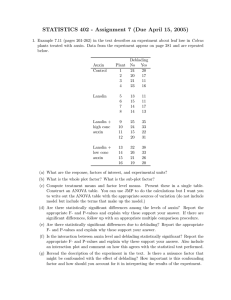
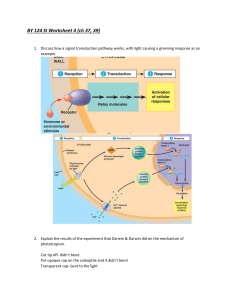
Topic 9.3 Growth in Plants Test Name: ______________________ _____/70 marks 1. What best describes an efflux pump with a correct example? a. Pumps material out of a cell; proton pump involved in cell wall acidification b. pumps material into a cell; proton pump involved in cell wall acidification c. Pumps material into a cell; formation of cellulose cell wall d. Pumps material out of a cell; electron pump involved in thylakoid membrane. 2. The image below (Fig. 1) shows a micrograph of a developing plant. What structures are labeled X and Y? Fig. 1 Developing plant 400x magnification a. X= primordial leaf; Y= shoot apical meristem b. X= primordial leaf; Y= shoot lateral meristem c. X= developing bud; Y= root apical meristem d. X= shoot apical meristem; Y= primordial leaf 3. In Fig. 1, what structure is labeled Z? a. b. c. d. Primordial leaf Axillary bud Primordial bud Axillary shoot 4. What is the name given to areas of undifferentiated cells in the apex of roots and shoots of growing plants? a. b. c. d. Lateral meristems Adventitious root tip Apical meristems Stem cells 5. What is meristematic tissue AND where is it found? a. Undifferentiated tissue; throughout the entire plant. b. Undifferentiated tissue; in apical and lateral meristems. c. Differentiated tissue, throughout plant d. Differentiated tissue; in apical and lateral meristems 6. Cells on which side of the stem will undergo elongation? a. b. c. d. Light side Both sides In the middle Dark side 7. Which of the following are involved in phototropism? I. auxin II. proton pumps III. phototropins IV. sunlight a. b. c. d. I and II only I, II and III only II and III only I, II, III and IV 8. What process can cause cells to elongate? a. b. c. d. The movement of protons into the cell wall; loosening of the cellulose; efflux of water The movement of protons into the cell wall; loosening of the cellulose; influx of water The movement of protons into the cytoplasm; loosening of the cell wall; influx of water The movement of protons into the nucleus; activating genes to loosen the cell wall; influx of water 9. Micropropagation can be used to: I. Produce many clones of new varieties of plants II. Repopulate endangered plant species III. Protect plants from viruses and bacteria found in the natural environment a. b. c. d. I only I and II only II and III only I, II and III 10. Which processes best describe phototropism? a. Plants growing towards light; cells on light side elongating b. Plants growing away from light; cells on light side elongating c. Plants growing toward light; cells on the dark side elongating d. Plants growing towards light, cells on the light and dark side elongating 11. Why is it important for the cell wall to loosen during cell elongation? a. b. c. d. To activate proton pumps To allow active transport of water To allow auxin to be released To allow cell growth via osmosis to occur 12. What best describes a group of undifferentiated plant cells produced by micropropagation? a. b. c. d. embryoid explant/callus plantlet seedling 13. Which of the following DOES NOT require activation of gene expression (transcription and translation)? a. b. c. d. activation of proton pumps production of auxin influx of water production of expansins 14. The microscope image and diagram below show the tip of an onion root. What are the characteristics of the cells in the root tip which form the meristem? a. b. c. d. They are small cells found at the very tip of the root They are small undifferentiated cells They are large undifferentiated cells They are large cells found in straight lines 15. What is the name of the plant hormone which causes this unusual plant growth towards a window? a. b. c. d. Tropism Albumen Troponin Auxin 16. Development of leaves and the growth of the stem in plants requires new cells. Which processes together provide these cells in the meristem? a. b. c. d. Mitosis and cell division Cell division and cell elongation Mitosis and transpiration Meiosis and cell division 17. Which tissue allows plants to develop wider stems and roots? a. b. c. d. phloem xylem lateral meristems apical meristems 18. Which of the following are effects of auxin? I. Increasing the rate of cell elongation in stems II. Changing the pattern of gene expression in shoot cells III. Detecting the direction of light IV. Changing the rate of cell elongation in roots a. b. c. d. I and II only I and III only I, II and III I, II, and IV 19. Which of the following are true of the shoot meristem? I. cells at the edge stop dividing and instead differentiate II. mitosis occurs III. it contains undifferentiated cells a. b. c. d. I and II only I and III only II and III only I, II and III 20. Why is a high concentration of auxin used in micropropagation? a. b. c. d. To stimulate development of roots and shoots To prevent dormancy To stimulate cell division To prevent dehydration 21. Why is cytokinin hormone used in micropropagation? a. b. c. d. To stimulate development of roots and shoots To prevent dormancy To stimulate cell division To prevent dehydration 22. Why might gibberellin hormone be used in micropropagation? a. b. c. d. To stimulate development of roots and shoots To prevent dormancy To stimulate cell division To prevent dehydration 23. Name the response shown by the plant in the image below which causes it to grow towards the light? a. b. c. d. Phototropism Photperiodism Photoactivation Photosynthesis 24. The graph to the right shows the results of an experiment to evaluate the effect of different concentrations of auxin on the growth of some seedlings. The graph shows the change in length of the seedlings as a percentage of the change in length in a control group which had no auxin added. Which of the following statements is the best description of the change in length of the shoots in concentrations of 10-1 and 10-2 At these values the change in length is negative. a. Something has gone wrong in the experiment at these concentrations. b. The shoots grew less quickly than the control group. c. The shoots became shorter during the experiment. d. The shoots have started to bend showing phototropism. 25. Micropropagation uses plant tissue from the shoot apex to create clones of the original plant. Which of the following suggestions are potential applications of this technique? a. The rapid reproduction of a new variety of bananas. b. The rapid production of a rare flower to increase the genetic variety in that population's gene pool. c. The reduction in the population of insect pests in a field of flowering maize d. The rapid increase in the yield of a field of orange trees during a period of dry weather 26. In micropropagation, which of the following is/are true of an explant? I. it contains genetically identical cells II. it is split apart into separate cells III. it contains unspecialised cells a. b. c. d. I and II only I and III only II and III only I, II and III 27. In micropropagation, where are cells to be cloned usually taken from? a. b. c. d. Leaves Shoot apex Xylem Phloem 28. Which of the following explains why plant shoots bend towards unidirectional light? a. b. c. d. More auxin diffuses to the unshaded side to increase cell elongation More auxin diffuses to the shaded side to decrease cell elongation More auxin diffuses to the unshaded side to decrease cell elongation More auxin diffuses to the shaded side to increase cell elongation 29. Which of the following is not involved in causing a plant shoot to bend towards unidirectional light? a. b. c. d. Cell division The shoot tip Cell elongation Auxin 30. What is the best description of a plan meristem? a. An area of a plant undergoing rapid differentiation so that the plant continues growing b. A new structure growing in a plant, for example, a leaf or a flower. c. An area containing undifferentiated cells which divide by mitosis throughout the life of the plant. d. An area of small cells undergoing meiosis in the apex of a plant. 31. Which of the following is thought to be used inside plants to move auxin within a growing shoot? Fig. 2 a. Auxin efflux pumps b. Auxin channel proteins c. The hydrolysis of auxin in lysosomes of cells d. Auxin binding to a transcription factor The graph to the right (Fig. 2) shows the results of an experiment to test five concentrations of auxin on the growth of some seedlings. The graph shows the change in length of the seedlings as a percentage of the change in length in a control group which had no auxin added. 32. Which of the following statements is the best explanation of the results shown in Fig. 2? a. The low concentrations promote lengthening of the shoots but the higher concentrations inhibit growth. b. As the concentration of auxin increases the length of the shoots decreases. c. The higher concentrations promote lengthening of the shoots but the lower concentrations inhibit growth. d. The auxin action causes 100% growth at low concentration and causes the seedlings to shrink at high concentrations. 33. Which of the following are true of phototropism of plant shoots when exposed to incoming light from one side? I. more auxin diffuses to the side closest to light II. more cells elongate on the shaded side III. receptor cells (phototropins) that detect light are stimulated in the shoot tip a. b. c. d. I and II only I and III only II and III only I, II and III Fig. 3 34. In roots, high auxin concentrations inhibit cell elongation. Where is auxin found? a. b. c. d. At the root tips only The lower side of the root The upper side of the root It is evenly distributed throughout the root 35. What causes some cells in the shoot apex to develop into leaves and others to develop into flowers? a. b. c. d. The cells contain different genes The cells acquire different mutations The cells contain different numbers of chromosomes The cells express different genes





![guide2709.ppt [Compatibility Mode]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/008368905_1-88e9b7f8222ebbb87620800faad10ad9-300x300.png)