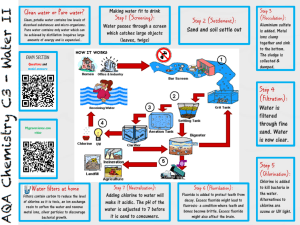
4.0 Cost Estimation A production cost is crucial to estimate its construction, operation and maintenance cost as well as to conduct a financial evaluation. The purpose of conducting a financial analysis is to evaluate a budget and minimize wastage on material and cost during construction, operation and maintenance phase. Table 1: Bill of spring catchment area BILL NO 1: SPRING CATCHMENT AREA Item 1.1 Description Length Qty/Unit Price (RM) Material Supply and erect timber formwork to wall slab Cast reinforced concrete Grade 30 Galvanized Iron Pipe 3”(80mm) (GIP- 50m² 70m³ 3/4in.x10ft 1unit 3.38x 10^4in 2unit RM 3,100 3CAA) PVC expansion joint (826-007X6) Inlet and Outlet Plastering wall 6 bag (kg) Thickness wall applying :5cm River stone Labour Cost RM 2,850 TOTAL RM 5,950 5tons Table 2: Bill of Sand filtration and reservoir BILL NO 2: SAND FILTRATION & RESERVOIR Item Description 2.1 Material Length Qty/Unit Foundation: Reinforced concrete (Rectangular) Thickness of lining wall(m) Gravel small 0.3 to 0.5m 4.0-5.6mm 2 tons Gravel large 16.0-23.0mm 2 tons 9.5mm 1 tons Course aggregate Under drains (Precast concrete slabs on concrete ribs) Gate valve Model: Z41W-16P 2.2 Reservoir Foundation :Reinforced concrete (Rectangular) Thickness of lining wall (m) Galvanized Iron Pipe 3”(80mm) (GIP-3CAA)Inlet and Outlet Metal roofing Width: 762mm Rib Height: 23mm Thickness: 0.23mm to 0.47mm Welded wire mesh (Galvanized steel wire) All wires: 1.24mm thickness Aperture:2mm x 25mm Roll height: 1.2 m Labour Cost 2.3 TOTAL Price 100 m² 50m² 4in 4 unit RM 7,650 (inc. Reservoir) 100m² 3/4in.x10ft 2 Unit 100m² 30m 90m³ RM 6,750 RM 14,400 Table 3: Bill of HDPE Pipeline BILL NO 3: HDPE PIPELINE Item Description 3.1 Material HDPE Pipe (100% Virgin Material PE100) Length Unit Price (RM) 2.5km 50 RM 42,500 Diameter:160mm Specification : DN63mm DN200mm DN315 PN16 SDR11 Pipe Colour: Black With Blue Stripe Supply Ability:100000 Ton/Year Amount: (1Unit/50m : RM850) 3.2 Galvanized Iron & Connection RM 5,000 Installation Cost RM 21,250 TOTAL RM 68,750 Table 4: Bill of Disinfection (Chlorination ring) BILL NO 4: DISINFECTION (CHLORINATION RING) Description 4.1 (RM) Material Y-Strainer Gate Valve Pressure Gauge Ejector TOTAL RM 1,000.00 RM 1,000.00 Table 5: Bill of new water tank & Pump BILL NO 5: NEW WATER TANK & PUMP Item 5.1 Description Length Qty/Unit Price (RM) Material & Installation 15 m² Supply and cast plain concrete B200, 10 cm thick below foundation (base slab) Supply cast fair face reinforced concrete B350 in Raft Foundation Aluminium Extension wall reclining Ladder Height 10’ to 36’ Handrail Balcony (Stainless Steel) Height: 85cm Thickeness:2cm Gate valve 8m HDPE Pipe (100% Virgin Material From PE100) Diameter:160mm 20 m² 15m² RM 24,500 3unit pumping 20m Specification : DN63mm DN200mm DN315 PN16 SDR11 Pipe Colour: Black With Blue Stripe Supply Ability:100000 Ton/Year Install air U-vent (3in) Fitting material :PVC Polyethylene Tank (PE 4000) Dimension: base (118in) 180° 1 Unit U-Bend 3000/4000 gallons Capacity(Gallons): N4000/4400 5.2 Pump RM 6,150 TOTAL RM 30,650 FINAL SUMMARY Item Description Price 1 2 3 4 5 CHAPTER 5 PROCESS FLOWSHEET AND PLANT LAYOUT 5.1 Process Flow Water supply system is the infrastructure for the collection, treatment, storage, and distribution of water for homes, commercial establishments and irrigation. Water supply systems must also meet requirements for public. In all cases, the water must full fill both quality and quantity requirements. Figure 5.1 show the process flow of water supply system. Figure 5.1: Process Flow of water supply system Sources Spring Water Treatment Sand filter, Disinfection Storage Reservoir, Water Tank Distribution Main Line, Sub-Main Line 5.1.1 Water Sources A spring is a place where underground water surface, usually on the side of a hill or mountain. The water filters slowly down through the subsoil until it reaches an impervious layer, usually rock. The big advantage of springs is that the water has been purified and filtered on its journey below ground. Cost are lower and complicated logistic are avoided. 5.1.2 Sand Filter Sand filters are used as a step in the water treatment process of water purification. Sand filtration is used for the removal of suspended matter, as well as floating and sinkable particles. The wastewater flows vertically through a fine bed of sand and/or gravel. Particles are removed by way of absorption or physical encapsulation. If there is excessive pressure loss on the filter, it must be rinsed. Table 5.1 show the Characteristics of rapid and slow sand filters. Table 5.1 :Characteristics of rapid and slow sand filters Characteristics Rapid sand filter Slow sand filter Filtration rate [m/h] 5–15 0.08–0.25 Media effective size [mm] 0.5–1.2 0.15–0.30 Bed depth [m] 0.6–1.9 0.9–1.5 Run length 1–4 days 1–6 months Ripening period 15 min – 2 h Several days Regeneration method Backwashing Scraping Maximum raw-water turbidity Unlimited with proper pretreatment 10 NTU 5.1.3 Reservoir All water reservoirs should be covered to protect the stored water against contamination. Overflow pipes should be brought down near the ground surface and discharged to minimize erosion. The storage structure should be designed so that there is water circulates. There should be a convenient access to the interior for cleaning, maintenance, and sampling. Rigid storage reservoirs should be vented. By design a reservoir should do no harm to the water. The contamination can come from a variety of origins including piping, tank construction materials, animal and bird feces, mineral and gas intrusion. A correctly designed water tank works to address and mitigate these negative effects. A service reservoir stores the water and supplies it at the required pressure to the farthest point in the area. 5.1.4 Disinfection (Chlorination Ring) Chlorination is one of many methods that can be used to disinfect water. This method was first used over a century ago, and is still used today. It is a chemical disinfection method that uses various types of chlorine or chlorine-containing substances for the oxidation and disinfection of what will be the potable water source. Chlorination can be done at any time/point throughout the water treatment process - there is not one specific time when chlorine must be added. Each point of chlorine application will subsequently control a different water contaminant concern, thus offering a complete spectrum of treatment from the time the water enters the treatment facility to the time it leaves. Chlorination may also be done as the final step in the treatment process, which is when it is usually done in most treatment plants. The main objective of this chlorine addition is to disinfect the water and maintain chlorine residuals that will remain in the water as it travels through the distribution system. The amount of chlorine that is required to disinfect water is dependent on the impurities in the water that needs to be treated. Many impurities in the water require a large amount of chlorine to react with all the impurities present. The chlorine added must first react with all the impurities in the water before chlorine residual is present. 5.1.5 Water Tank A water tank is a container for storing water. Function water tank is providing a reserve of treated water that will minimize interruptions of supply due to failures of mains, pumps, or other plant equipment. Help maintain uniform pressure; provide a reserve of water for fire fighting and other emergencies, act as a relief valve on a system of mains supplied by pumping permit a reduction in the size of distribution mains below that which would be required in the absence of a reservoir and allow pumping at the average rather than peak flow rate. The design depends on the location of tanks, example overhead, on ground or underground water tanks. The tanks can be made in different shapes usually circular and rectangular shapes are mostly used. The tanks can be made of reinforced concrete or even of steel. The overhead tanks elevated tanks are usually elevated from the rooftop through column. In the other hand the underground tanks are rested on the foundation. Water tank design should be based on sufficient resistance to cracking to avoid leakage and adequate strength. 5.2 Plant Layout Figure 5.2 : Plan Layout of reconstruction gravity fed water supply system 5.2.1 Plant Layout Facilities a) Catchment Area TOP VIEW BACK VIEW LEFT SIDE VIEW RIGHT SIDE VIEW b) Sand Filter SIDE VIEW TOP VIEW FRONT VIEW BACK VIEW c) Reservoir TOP VIEW FRONT VIEW SIDE VIEW d) Disinfection (Chlorination Ring) SIDE VIEW TOP VIEW e) Water Tank SIDE VIEW TOP VIEW 5.3 Distribution System Layout Figure 5.3 : Distribution system Layout