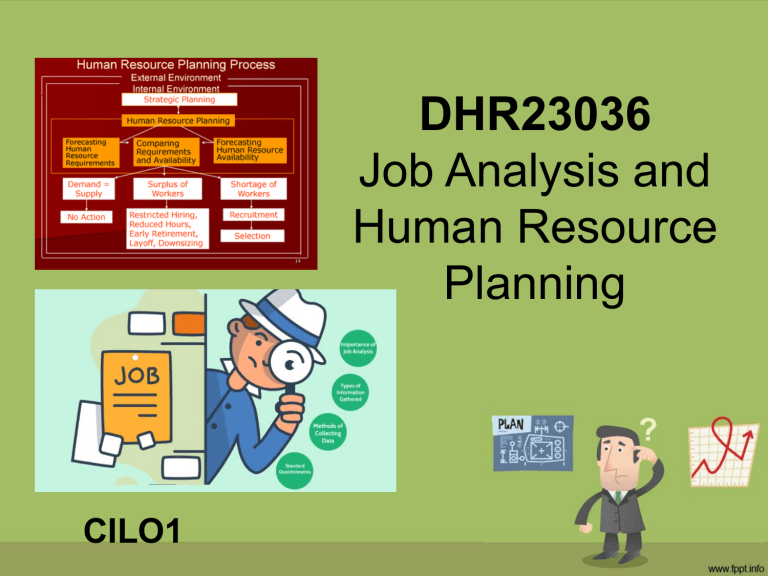
DHR23036 Job Analysis and Human Resource Planning CILO1 Overview of the Unit COURSE INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOMES (CILOs) 1. Evaluate an integrated human resource planning framework. 2. Explore human resource planning. 3. Evaluate the factors influencing job analysis 4. Conduct a job analysis. Overview of the Unit ASSESSMENTS: • Test (25%) - Week 8 CILO1, CILO2 • Practical Assignment (25%) - Week 10-14 CILO3, CILO4 • Final Exam (40%) - Week 18 CILO 1, 2, 3, 4 • Quizzes (10%) - Weeks1-16 CILO 1, 2, 3, 4 STARTER THINGS that GO TOGETHER What goes with the: Shoes Socks THINGS that GO TOGETHER What goes with the: Hammer Nails THINGS that GO TOGETHER What goes with the: Needle Thread THINGS that GO TOGETHER What goes with: Football THINGS that GO TOGETHER What goes with: COURSE INTENDED LEARNING OUTCOME 1 (CILO1) Evaluate an integrated human resource planning framework. Definition of Terms A system is a group of interacting, interrelated, or interdependent elements forming a complex whole. A system is a unit that consists of several sub-systems and is itself part of a larger system. A system can be seen as a regularly interacting or interdependent group of items forming a unified whole. Each system is a part of its environment. Environment includes all those factors that affect it and are so powerful on the functioning of a system that it is almost impossible for a system to exist without taking them into account All parts or components of a system must be closely coordinated and properly integrated, so that the entire system is a unified whole and it can accomplish common objectives as planned. What do you think are the sub-systems of a COMPUTER? Definition of Terms • Integration means: is the act of bringing together smaller components into a single system that functions as one; mixing things or people together that were formerly separated. Definition of Terms • Human resource planning means: the process of systematically reviewing human resource needs to ensure that the required number of employees, with the required competencies, is available when they are needed. • Framework means: the basic structure of something ; a set of ideas or facts that provide support for something. A business enterprise is a system. Framework is a support structure of system that holds parts together. Definition of Terms Strategy can be defined as “a general direction set for the company and its various components to achieve a desired state in the future. It is an action that managers must take to attain one or more of the organization's goals. There are three types of businesslevel strategies to increase in profit and company unity. • Corporate level strategy: This strategy sets out a clear mission and vision for the entire company. Top managers or CEOs are responsible for formulating corporate level strategy, and they generally look ahead for five years or longer. • Business level strategy: This strategy focuses on how the company can compete. • Functional level strategy: This strategy focuses on the individual tasks of departments and employees in working toward corporate goals. Example: Corporate strategy : improve market share Business strategy : improve product quality Functional strategy: • HR: increase hiring of highly-trained employees • Production: reduce rejects and defects Definition of Terms • Strategic planning means: is an organization's process of defining its strategy, or direction, and making decisions on allocating its resources to pursue this strategy. Effective strategic planning articulates not only where an organization is going and the actions needed to make progress, but also how it will know if it is successful. Strategic Planning Process Definition of Terms Human resource planning means: the process of systematically reviewing human resource needs to ensure that the required number of employees, with the required competencies, is available when they are needed. HRP is a sub-system in the total organizational planning. Who are responsible? Strategic Planning vs HR Planning Strategic planning vs Human resource planning Strategic Planning related or NOT? Q U I C K M I N D • • • • • • • • Corporate mission Corporate vision Business opportunities Required number of staff Business strategies Company objectives CEO HR skills needed Dr. Cecilia M. Integrated HRP Framework There is a need for organisations to have an integrated Human Resource Planning Framework in which the external environment, internal environment, the strategic planning and the organisational resources are considered in order to develop various human resource strategies. Each of these areas interrelates with the others and is critical in achieving the overall organisational vision. The integrated Human Resource Planning Framework must attempt to bring all aspects of HR planning together, incorporating the more traditional approach to human resource planning, but going beyond this to include the external and internal environment and the organisational resources. 5 Integration Approaches (Torrington and Hall ) • Approach A - There is no relationship at all between organizational and HR strategies in the organization. This is a typical picture that existed several years ago and still exists today in several small and traditional organizations. • Approach B -There is a growing recognition of the importance of employees, and HR strategy is designed to fit the organization’s strategy. • Approach C- It takes the relationship one step further, as it recognizes the need for an equal relationship between strategy and HRM. Strategy may not always be feasible and alternative possibilities need to be reviewed. • Approach D- It shows a much closer involvement between organizational and HR strategies. It considers HR as the key to competitive advantage. Organizational and HR strategies are developed together in an integrated way. • Approach E- It offers an alternative form, different from integration, which places HR strategy in the prime position. The argument is that if people are the key to competitive advantage, then there is a need to build on people’s strengths. Types of Integration • Vertical fit is concerned with ensuring integration of HRM with the corporate and business strategies. • Horizontal fit is concerned with ensuring integration at the same level. This involves two types of fit Internal fit involves integration between the various HRM sub-functions or sub-systems, such as staffing, compensation, and training. External fit is concerned with the integration between HRM and other functional areas like marketing, finance, and operations. External environment Legislation Economic conditions Technological advancement Demographics Competition Compensation Internal environment: Organisational structure Budget Skills levels Health and safety Organisational culture Employee relation Q U I C K M I N D External or Internal Environment? • • • • • • • • • Health and Safety Compensation Competition Budget Employee relations Legislation Technological advancement Organisation culture Skills level Dr. Cecilia M. Internal External External Internal Internal External External Internal Internal A. Integrating HRP with STRATEGIC PLANNING A. Integrating HRP with STRATEGIC PLANNING HRP must be linked or integrated with strategic planning due to: 1. Work Demand: HR plan as a result of analysing, reviewing and attempting to produce the right numbers and kind of workforce needed by the organization must be according to the approved budget and strategic plan. 2. Work supply: This entails predicting what HR action plan will be necessary to ensure that workforce requirement is available when required for the achievement of the objectives of the business. Benefits of integrating HRP with Strategic Planning HRP must be linked or integrated with strategic planning due to: 3. Organizational change: HR plan must include action plans for changes in skills, job content, surplus or shortage of manpower resulted by changes or enhancement of business strategies due to competition or other external factors. 4. Government influence: As the business strategic plans are aligned with the law and legislation, so as the HR plan especially in staffing, compensation, health and safety and employee relations. B. Integrating HRP with EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT External factors cannot be controlled by the organisation. Factors influencing the HR plan are not fixed, HR practitioners must continually monitor the external environmental factors to be able to adjust the HR plan accordingly. The external factors influencing the development of the Integrated HRP Framework are as follows: • Legislation • • • • • Economic conditions Technological advancements Demographics Competition Compensation B. Integrating HRP with EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT B. Integrating HRP with EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT HRP must be linked or integrated with EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT such as: 1. Legislation: • employment legislation influences every HR process like recruitment and selection, training and development, rewards and compensation, termination, and employee benefits; • organisation can be fined extensively or may close down by not adhering to the law. • new laws can affect HR plan for benefit programs and minimum wage. • safety regulations may be add to HR's training obligations. • new legislation on increased salary can limit company’s ability to hire, enhance employees benefits and keep compensation packages competitive. • In case the law forced the business to freeze salaries, delay contributions to employee savings plans or increase individual workloads, you might lose talented people. B. Integrating HRP with EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT HRP must be linked or integrated with EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT such as: 2. Economic condition: • recession periods and economic downturns can affect HRP leading to workforce reductions and reorganizing the company to adjust workloads, • robust economy often means a tight labor market with a limited pool of candidates. I • interest and tax rates that affect consumer buying and disposable income could trigger the need to hire or lay off employees. • The economic environment in which the business functions influences the supply and demand of workers, • HR plans for recruitment, training and compensation must accommodate talent availability.. B. Integrating HRP with EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT HRP must be linked or integrated with EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT such as: 3. Technological advancement • new technology brings new skills requirements, so companies always need to be aware of proficiencies and training needs when planning human resources. • new products and services also may require recruiting highly skilled employees or training existing employees to meet the need. • new equipment or knowledge be needed so they HR may need building the required skills, and most likely salary enhancements, into the plan. B. Integrating HRP with EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT HRP must be linked or integrated with EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT such as: 4. Workforce demographics: • characteristics of the labor market -- age, education, ethnic mix and gender -- can affect HR's ability to provide the manpower needed by the business. • HR plan must accommodate the values and expectations of a younger workforce (Gen Z) through work-life balance, career development and fringe benefits. • wider diversity across the labor pool may lead to the introduction of training to build awareness and cohesive teams. • understanding available skill sets allows HR to recognize the need for partnerships with schools, internships and job-related training, • knowing the geographic areas where those skills can be found allows HR to tailor recruitment efforts. B. Integrating HRP with EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT HRP must be linked or integrated with EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT such as: 5. Competition • extent of competition in the market affects an organisation’s ability to recruit qualified employees. • industry giants can easily find and recruit top-notch talents • spending less in job advertisement as candidates visit the organisational website as first preference in searching for possible vacancies. • small businesses having no the same branding power of big companies need to focus on developing recruitment materials and attending job fairs to promote the organisation and attract applicants. • HR should develop programmes and incentives to retain key employees. B. Integrating HRP with EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT HRP must be linked or integrated with EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT such as: 6. Compensation • Labour supply (i.e. the size of the talent pool) drives the amount of compensation an organisation must pay to attract employees. • In an oversaturated market when unemployment is high and more qualified candidates exist (surplus) than job opportunities, compensation being offered may be low. • when a shortage of candidates exists and the organisation is competing against multiple other companies to recruit employees, compensation being offered is high. • There is a need for continuous evaluation of compensation structure to ensure competitive salary in attracting and retaining key staff members but reasonable to maintain business financial stability and competitiveness • HR must also ensure fair internal compensation structure - for example, experienced workers with specialised qualifications should earn more than recent college graduates performing the same tasks. C. Integrating HRP with INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT C. Integrating HRP with INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT Internal factors are mostly under control within the organisation. HR departments need to keep track of how internal factors influences HR related issues to enable HR practitioners to maintain the most effective staffing levels and maximise productivity. Internal factors include the following: • Organisational structure • Budget • Skill levels • Productivity • Health and Safety • Organisational culture • Employee relations C. Integrating HRP with INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT HRP must be linked or integrated with INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT such as: 1. Organisational structure is a system used to define a hierarchy within an organisation in which it identifies each job, the function and reporting or communication lines. • Structure is developed to establish how an organisation operates and assists the organisation in obtaining its goals to allow for future growth. • Changes in the allocation of responsibilities in each divisions affects the overall HRP . • Job description must be developed according to the organisational structure considering the level of authority and chain of command. • The organisational structure creates salary structures leading to the development of salary ranges for each job in the organisation. • Structure must be designed to attract and retain high-performing people, through the creation of positions that influence their highest skills and provide development and growth. C. Integrating HRP with INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT HRP must be linked or integrated with INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT such as: 2. Budget • • • • • Budgeting involves the systematic collection of information and data so that the finances needed to support an organization's objectives can be projected. HR must align their budget with the organization strategic plan for the achievement of the objectives. HR budget that includes costs for hiring, salaries, benefits, talent management, job advertisements and promotion, employee training, or employer branding activities must not severely affect profitability. When an organisation wants to increase sales or production, there is a demand for additional staff which may affect the HR budget. A well-planned and thoughtful budget ensures that HR receives the necessary funding to support employee programs and training for new technology and trends critical to attracting and retaining skilled workforce. C. Integrating HRP with INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT HRP must be linked or integrated with INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT such as: 3. Skills level • • • • Forecasting human resource needs as part of HRP should be supported with effective recruitment and selection, replacement and retention policy framework. An organization may find it difficult to fill vacant positions with the same skills level as stated in the HR plan due to pressure of more demand in the job market but less available talent. Being unable to fill positions and train employees for required skills necessary to achieve the operational goals leaves an organization in a weak business position. Organisation may consider offering staff training opportunities which should be reflected within the integrated HRP Framework, including onsite training, coaching and mentoring, and sending workers to seminars and workshops. C. Integrating HRP with INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT HRP must be linked or integrated with INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT such as: 4. Health and safety • • • • • HRP must be complying to the health and safety law and company’s health and safety policies as well. New health and safety legislation may lead to a new planning for employees training and development. HRP must consider effective health and safety environment as it promotes organisational efficiency. HR plan must ensure that the workplace is free from recognized hazards that are causing or likely to cause death or serious physical harm to employees which can lead to talent retention and employee perceptions of fair treatment by the organization. HR professionals should have a sound and working knowledge of health and safety principles, program administration, legislation, and amendments. C. Integrating HRP with INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT HRP must be linked or integrated with INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT such as: 5. Organisational culture is “a system of shared assumptions, values, and beliefs, which governs how people behave in organisations.” These shared values have a strong effect on employees within the organisation and prescribe how they dress, act, and perform their jobs. • • • • Organisational culture can be influenced by the recruitment process, compensation and reward, or employees’ training and development. HRP must develop and maintain unique culture of the organisation which provides guidelines and boundaries for the behaviour of every employee in support to the achievement of the company’s overall strategic plan. HR must create practices that support the business set values. HR leaders should work with the executive team and stakeholders across the business to evaluate their current company culture, assess potential gaps or opportunities, and create a strategic plan to align the organisation’s culture with its values and goals. C. Integrating HRP with INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT HRP must be linked or integrated with INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT such as: 6. Employee relation refers to an organization's • • • • efforts to create and maintain a positive relationship with its employees. HR practices relating to employee rights and discipline must be according to the company’s policies and procedures. HR must understand the importance and impact of labour union in planning for compensation and incentives, promotion, grievance guidelines or health and safety practices. HR should conduct activities like regular meeting or events that allow employees to develop peer relationships and encourage effective communication among team members. Employee relation policies must be for the achievement of the corporate strategic plan. D. Business areas of importance for effective integration of corporate and human resource planning D. Business areas of importance for integration 1. Staffing refers to the continuous process of finding, selecting evaluating and developing a working relationship with current or future employees. • HR should align the recruitment and selection practices with the organisation’s core values not compromising the skills, abilities, and personal characteristics of employees that should match with the demand of jobs in order to stay competitive in the changing marketplace. 2. Compensation Management • Compensation as a human resource planning tool to achieve corporate goals must be carefully formulated and implemented to reward employees fairly, equitably and consistently while maintaining good relationships between labour and management and high profitability. 3. Training and Development • To be able to keep the leading edge in the competition, HR must encourage professional learning across every area of the organisation according to new market trends and technology but within the strategic plan.