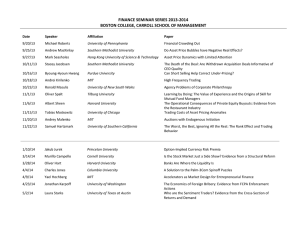
Trading techniques buy first = to be long → Bull sell first = to be short → Bear “STOCKTRAK” at least 20 trades, how to organize the budget, trading strategies, “INVESTOPEDIA” BASIC SECURITIES Trade: → Stocks: a fraction of a company. The → exchange between two counterparts (buyer and seller) perception of the market on the present and the future of the company makes the prices change. Netflix case. Never → Asset: Securities (bonds, etc), Commodities (non financial asset, with a physical character), currencies (FOREX) → Price agreement Trading techniques expire. → Bonds: is a credit from an issuer to a company. Interests (cupon was a piece of paper) - capital gain. bond will be payied in its full amount. 100 means 1 → quantity 100%. 98 means 98% of the cupon. we can pay 103 % returning 100% just for the interest. They usually expire. → Options: derivative of an other assets (options, futures). core option is to buy an option to have a chance to buy an asset. Exercise the option can be easier. QUANTITY liquidity is the chance to sell or buy something, it means that there can be or not enough counterparts in the market. Big amounts can be better for the fees but liquidity can be a problem. PHASES OF A TRADE 1. NEGOTIATION: to find a deal with our counterparts. PROPOSAL of TRADE, is an offer to the counterpart, if someone accepts with it it will deal. 2. AGREEMENT: the two part close the deal. It needs to specify the asset, the quantity/dimension, the price. 3. SETTLEMENT: buyer has to pay, seller has to transfer the asset. The execution of what is been agreed. 4. CUSTODY: stock doesn’t need mantainance activity. The way the asset is kept, useful in investments but less in trade. FINANCIAL MARKETS EXCHANGES The sum of the trades in a certain timeframe. How do they make profit? it is involved in different businesses 1. Exchanges (regulated): everything is settled with certain rules, certain Trading techniques 2 timeframes, certain assets. Index of performance of the market (DOW JONES, NASDAQ) 2. OTC (over the counter): everthing that happens outside the official market. Counter is the desk, means it’s not official. 1. Lisitng companies, that pay to be listed a. why should company want to be listed → find investors 2. Trading → fees 3. Clearing → settle all the contracts. Clear multiple transactions in the simplest way, usually at the end of the day. Services. 4. Settlement no much money involved 5. Custody → Services 6. Information and Data selling, can be up to 30% of the profit. data about prices and similar. NYSE Only admitted trader can join the market, admission requires to be the broker of a recognised company and pass an exam. buyer and seller won’t go to the market directly but they operate using third parties (companies) who can go to the market. a client can ask to a company that talks with another - a client can ask to the broker company that ask the company that talks with another. CLIENT: is not admitted to trade BROKER: represents someone else, receives the order and transmit that order. Its profit come from the fees of the operation. DEALER: Trades in the market on its MARKET MAKER: someone that plays on the market as a central counterpart. i.g. BDP that provides a liquidity service, always buys and sells what people want to. But it buys for lower prices and sells at higher prices. own account. Companies can operate as both dealer and broker. Its profit is the profit of the trade. Trading techniques 3 TRADING DAYS Opening time (9:00 am) - Closing time (5:00 pm) Opening prices are set by rules, after that prices changes following the deal done during the day untile the closing time. Closign prices are the lasts prices of the day. They’re not the opening prices of the day after, it’s just a reference. PRACTICE ORDER TYPE What do I want to trade? MARKET → We’re ok with the market price Amazon, Ineed the international code: Amzn. LIMIT → We declare the price we BUY → I’m buying my stock preferre SELL → I’m selling my stocks STOP LIMIT/STOP LOSS → We fix a price that will stop my loss SHORT → I’m selling not already having the stock, we can do it thank third parties, on the assumption that we’re going to buy the stock later on. We do that to buy then to a lower price. It’s usually not free, it is a service of borrowing from lenders, that wants a fee. RISKY: I can lose both my money and my fee payment. BUY TO COVER → we are short on a position and we buy the stock we sold already. TRAILING STOP → a dinamic stop limit that can change following the market prices DURATION DAY ONLY → my price will be valid the day long, until closing time GOOD UNTIL CANCELLED → if at the end of the day the price hasn’t been acceptes, it will be valid until we cancel it ONE SHOT → It’s valid for a few time REMEMBER TO CALCULATE THE FEES IN THE TRANSACTIONS TRENDS Trading techniques 4 Depend a lot on the time horizon (day, week, month, year, etc. , they can change shapes. DRN → trading something that is not official traded in that exchange. GRAPHS Look at VALUES → Confirmation that something is changing VOLUME → Big changes, something’s up Look as LINES AREAS CANDLES: most common CANDLES They show: if the price in that period decreased (red) or increased (green), the opening price and the closing price with the candles, the maximum and the minimum of the period with the appendix. candles with no appendix are called full body. Trading techniques 5