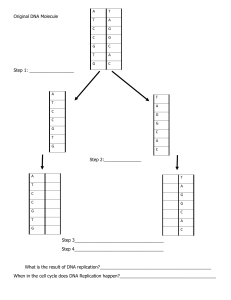
DNA replication models BIOL 141, sp2021 Name: Ethiopia Demisse TA Name: Shandon and Crystal Team, number: Group 1. Shown below are three models that predict the mechanism of DNA replication. Messelson and Stahl designed an experiment that would distinguish between them. They used isotopes of Nitrogen, 14N and 15N, reasoning that DNA would have different densities depending on how much of each isotope was incorporated into each molecule. The first round of replication was done in nutrient broth with only 15N. After that round, the bacterial cells were grown in nutrient broth containing only 14N. The diagram below shows the results they obtained after two rounds of cell division. During the density centrifugation, DNA double helices stay together (their strands DO NOT separate). 14 15 N N 1. Which model(s) can be ruled out after the first round of division? Why? Conservative model because it pairs old strand with nothing but itself and does not pair with the new one. 2. Which model(s) can be ruled out after the second round of division? Why? Dispersive model because the division should be a 50/50 percent do not patch on each strand. The old and new strand should have an even division. 3. What is the correct model of DNA replication? Semiconservative model because the division is even between the two stands. 1 DNA replication models BIOL 141, sp2021 Name: Ethiopia Demisse TA Name: Shandon and Crystal Team, number: Group 1. 4. Draw the expected densities for division 3 for the correct model of replication and indicate the percentages of each isotope at each position between the 15N and 14N lines on the diagram. If you can’t draw on this word doc, scan, and submit, then describe in words where on the diagram above the DNA would be and how much would be there (what %). 14 15 N N There will be more of the original broth N15 and the N14 which is the new strand will have more stands as the original one becomes rare. As the density of the N14 increases the density of the N15 will decrease. 5. What new DNA sequence would DNA polymerase add to the bottom strand below? Write the sequence in 5’ to 3’ orientation. 3'-ATGAGCCTAGCTCAGACTG-5' 5'-UACUCGGATCGAGTCTGAC-3’ 2