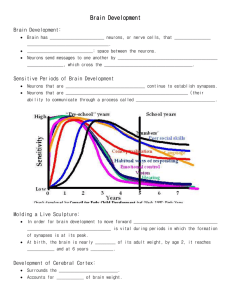
Genesis and Migration I Associated Reading: Chapter 3 Genesis and Migration I • Development of the nervous system requires: • Proliferation and differentiation of progenitor neurons and glia. • Migration of neurons and glia • Histogenesis- differentiation into specialized tissues and groups (e.g. cerebral cortex, basal ganglia) Neurogenesis begins in the neural tube Neurogenesis begins in the neural tube Clonal analysis of progenitor cells • Earlier cells give rise to more clones • Glia and neurons can arise from the same progenitor cell • Ex: In cortex, approximately 5 neurons and 30 glia from each progenitor General Principles of Neurogenesis • Length of cell cycle increases progressively during embryogenesis • Rat cortical progenitor cells: • 11 hrs at E12; • 19 hrs at E19. • Increase in cell cycle period is largely due to lengthening of G1 • Possibly reflects regulation of entry into S phase Numbers of cells generated by progenitors depends on stage and region of development • Early progenitor cells give rise to many more progeny than later cells. • Cells in large regions of brain give rise to more cells. • At early time-points, many more cells undergo symmetric division Neurons are terminally differential Clonal analysis of progenitor cells • Earlier cells give rise to more clones • Glia and neurons can arise from the same progenitor cell • Ex: In cortex, approximately 5 neurons and 30 glia from each progenitor 3H-Thymidine labeling provides information on the cell cycle length 3H-Thymidine Birthdating • Pyramidal cells develop early, granule cells develop late • Cortex develops in an inside-out manner • Phylogenetically older areas develop before newer areas. Cyclins control neuronal proliferation How do cells become differentiated into Neurons and Glia? • Growth Factors • • • • Radial Glia: GGF Neurons: NT3, FGF2 Oligodendrocytes: PDGF, NT3, IGF-1 Astrocytes: EGF, CNTF, • BMP2, BMP4; CTNF and BMP2 activate GFAP. Sonic hedgehog promotes proliferation of neurons Notch Pathway and Neurogenesis Summary • Neurogenesis begins in the neural tube. • Position in neural tube correlates with step in cell cycle. • Length of cycle increases during embryogenesis. • Thymidine birthdating is used to determine the length of the cell cycle and the time of origin of cells in the nervous system. • Cells labeled at mitosis • Cells leaving the cell cycle will have more thymidine than those that continue to divide. • Ontogeny recapitulates phylogeny. • Cortical Neurogenesis occurs late in development. • Growth factors promote differentiation into neurons or glia. • Sonic hedgehog promotes granule cell formation in cerebellum.