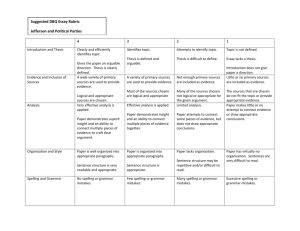
MGT-317 Project Management in Engineering – 3 Credit Hours Course Title (with code) MGT-317 Project Management in Engineering 3 Credit Hours IME-171 Engg. Econ. ; MA-244 Prob. & Stat. Pre-requisite Mechanical Engineering Faculty (Name) faisaltaj636@gmail.com Contact (Ph:& email) Wednesday 10-12, Thursday 10-12 Office Hours Course Description:(Course Aim/Objective and Course Contents Aims/Objectives: 1. Impart knowledge about the fundamentals of project and project management practices in engineering. 2. Identify planning, scheduling and controlling requirements keeping in view nature and type of projects. 3. Analyzing Risk and Response strategies for effective project management. Contents: 1. Introduction to Projects – Classification and PLC Phases. 2. Project Planning – WBS, Activity types and duration estimation 3. Network Models – PERT, CPM, Gantt, Project Crashing, EVA 4. People on Project – Competence, Organization, Motivation 5. Risk Management – Risk assessment and Control techniques Course Learning Outcomes Course Description Learning Outcome (CLO) CLO1 CLO2 CLO3 CLO4 CLO 5 Understand specific terminologies, concepts and techniques related to Project Management. Apply project management approaches, techniques, principles and methods to address project problems. Analyze issues, situations and problems related to projects keeping in view the best practices and standards. Respond actively and effectively sharing learnings and additional valued information. Identify mandatory / recommended certifications / trainings in various fields of maintenance Domain and level of Learning C = Cognitive P = Psychomotor A = Affective Mapping with PLO C2 PLO-1 C3 PLO-5 C4 PLO-2 A2 PLO-10 A3 PLO-11 KEY: Cognitive: Knowledge, Understanding, Applying, Analyzing, Evaluating and Creating Affective (Feelings and Emotions): Receiving, Responding, Valuing, Organizing, Characterizing Psychomotor (Physical which supports above areas): Reflex and Fundamental Movements, Perceptional Abilities, Physical Abilities, Skilled Movements, Body Language Textbooks (include publisher’s details and year of publication) Effective Project Management: Traditional, Agile, Extreme 5th Edition by Robert K. Wysocki Publisher: Wiley (2009) Recommended Books: PMBOK, 5th Edition (Jan 2013) Assessment Tools with Weightage Quiz and Assignment = 15% CEP= 15% Mid Term = 30% Final Exam= 40% Tentative Weekly Lecture Plan Description of topics Week Introduction to the Course Objectives & CLOs - Reference Books - Course 1 Plan – OBE Requirements - Scope of the Subject 2 Project Introduction 3 Classification & Models 4 PLC Phases 5 Presentations 6 Planning & Scheduling – Gantt Chart 7 PERT / CPM 8 Concluding Session before Mids 9 Project Crashing 10 EVA 11 Risk Management; Types; 12 RM Techniques 13 RM Techniques 14 Project Management Organization Levels & Functions 15 PMI & Prince Role in Establishing Project Competence 16 Presentations 17 Presentations 18 Concluding Session before Finals CLOs 1 1-2 1-2-3 1-2 4 2 2 2-3 2-3 1 2 3 2 1-2 4-5 4-5 Assessment Rubrics Dimensions /Levels Knowledge Comprehension Critical Thinking A Defines with complete content including units, schematic diagram and using technical vocabulary with no grammar and spelling mistakes. B Defines with some missing contents of information like units or schematic diagram using technical vocabulary with no or minor grammar and spelling mistakes. Effectively elaborate the concept in an organized manner right from basic definition (if any), working principle, supporting diagram with labeled parts (if apply) and salient features / parameters with proper use of grammar and spellings. Effectively elaborate the concept in an organized manner missing one or more of the followings or with lesser details then desired: basic definition (if any), working principle, supporting diagram with labeled parts (if apply) and salient features / parameters with proper use of grammar and spellings Demonstrates sufficient capability to recognize core differences and barriers in comparing and choosing techniques / methods with reference to the context. Unable to devise / propose solutions to Complex Engineering Problem. Demonstrates capability to recognize core differences and barriers in comparing and choosing techniques / methods with reference to the context. Devise / Propose solutions to Complex Engineering Problem. C Defines with inadequate information lacking units and / or schematic diagram or little use of technical vocabulary with grammar and spelling mistakes. Moderately elaborate the concept missing few of the required aspects like basic definition (if any), working principle, supporting diagram with labeled parts (if apply) and salient features / parameters having grammatical mistakes as well. D Defines with inadequate information lacking units and schematic diagram and no use of technical vocabulary with grammar and spelling mistakes. Poorly elaborate the concept missing many of the required aspects like basic definition (if any), working principle, supporting diagram with labeled parts (if apply) and salient features / parameters with diverging answer. Demonstrates fractional capability to recognize core differences and barriers in comparing and choosing techniques / methods with reference to the context. Unable to devise / propose solutions to Complex Engineering Problem. Demonstrates poor capability to recognize core differences and barriers in comparing and choosing techniques / methods with reference to the context. Unable to devise / propose solutions to Complex Engineering Problem. CLO 1 2 3 4