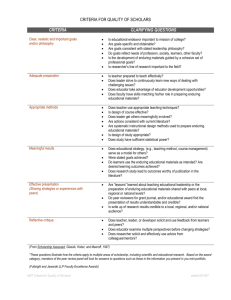
An enduring issue is an important (significant) problem or challenge that has affected many people (in the past and today) that many has competing solutions. Enduring Issues / Themes Conflict is a serious disagreement or argument. Power is the influence or control over the behavior of people and it is a part of every human interaction. Inequality when one person or group of people do not have as much power or opportunity as others. Human Rights are basic rights and freedoms to which all humans are entitled. An innovation is a new method of addressing a problem. Technology Interconnectedness is the state of having connections or relationships with other people. Our ideas and beliefs impact /shape the way we look at the world. Environmental Impact Our environment is the area around us in which we live. We are affected by our environment and we have an effect on it Scarcity is the state of not having enough of something. Everything we use in our daily life comes from the Earth and there is a limited supply of resources on this planet. Population growth occurs when more people are born than die and for most of global history, the number of people on Earth has increased. Cooperation is the process of working together to achieve the same goal. Security is the ability of a government to protect itself from domestic and foreign threats to its way of life Tensions Between Traditional Culture and Modernization Impact of Trade which is the action of buying and selling a good or service Impact of Cultural Diffusion The exchange of ideas between different cultural groups through trade or war. It Nested Issues / Key Ideas War, fighting over resources, religious tension, conquering, invasions, resistance, dispute over boundaries, disputes over power etc. Unfair distribution of power, shifts in power and authority, power struggles, relationship of ruler to ruled, social class tensions, ability of the people to have a voice in government (consent of the governed/social contract), leadership, etc. Division of social classes, lack of access to resources, rights not protected, lack of fairness, unequal participation in government, inequitable treatment, lack of access to jobs, etc. Inventions, new ideas, golden ages, new technology, effects of technology use, faster methods of building/production, etc. Trade, cultural diffusion, different people living/working together, spread of ideas, spread of disease, exploring, trade organizations, etc. Belief systems, new ideas, philosophy, political ideology, beliefs about society, racism, terrorism, ways of looking at the world, etc. Adapting to environment, challenges of the environment, farming, resources, food, trade routes, etc. Not having enough resources, trading for resources, trade networks, exchanges, self-sufficiency, traditional economy, etc. strain on resources, strain on housing, increase in waste and need to address waste disposal, sanitation conditions/strain on sanitation systems, healthcare needs, ability to feed and /or to educate population, need for social services, debate over population policies Trade, cultural diffusion, sharing of ideas, working together, treaties, meeting of leaders, military alliances, working together as a society etc. threats to privacy and property, terrorism, lack of safety, nuclear proliferation, biological, chemical and nuclear weapons of mass destruction, role of technology in protecting and harming security; debates over espionage, protection of sovereignty/ borders/frontiers, debate over formation of alliances/membership in an alliance, protection from disease loss of cultural identity, language, traditional beliefs, traditional gender roles versus modern gender roles, disputes over gender roles, role of ethnic identity and power, ethnic tensions, religious identity, tensions between religious identity and modernization efforts, debate over definition of modernization and/or westernization as modernization, difficulty of maintaining traditions in a time of change integration or rejection of technology, goods and new ideas, economic sanctions, boycotts, embargoes, imposing/levying tariffs, loss of jobs, distribution of/access to new goods, loss of cultural identity, language and traditional beliefs, impact on levels of poverty, the environment, trade agreements and balance of trade; economic costs, political, economic and social benefits and/or cost, attempts to expand trade and restrict trade; ability to participate in global trade, spread of disease loss of/threats to cultural identity, unique language(s), traditional beliefs; spread of disease, impact of introduction of new species (invasive/noninvasive), conflict, debate over change, benefits or challenge of imported technology, transportation and communication; debate over and the (un)intended occurs through the movement of people and goods. Impact of Industrialization transformed of a society from primarily agricultural to one based on the manufacturing of goods using machines and other advanced technology Impact of Urbanization Movement of people from rural/farming areas to cities caused by rapid industrialization Impact of Nationalism A strong feeling of pride in one’s country, nation or ethnic groups Impact of Imperialism /Empire Building – taking over of a weaker nation by a stronger one Impact of Colonization - the action of settling among and establishing control over the indigenous people of an area. Impact of Decolonization – process by which colonies become independent from the colonizers Impact of Globalization - a process of interaction and integration among the people, companies, and governments of different nations, driven by trade and investment and aided by information technology. Impact of Migration – the movement of people from one place to another with the intention on settling permanently or temporarily consequences of accepting a new good, new idea, philosophy, religion and the pace of change of such low wages, poor working conditions, unsafe working conditions, use of child labor, unequal wages for similar work, need for regulations, need for reform, unionization, pollution, carbon emissions, consequence of industrialization, outsourcing jobs, demand for resources, water, energy, transportation and infrastructure; impact of industrialization on agriculture, standard of living, longevity, decline in birthrate, growth of comparative wealth, status of women, rise of socialism, impact of welfare state, sociopolitical reactions/development of sociopolitical philosophies overcrowding, challenge to meet housing/shelter needs, need to address waste disposal/sanitation, ability to keep order, provide protection, clean drinking water and prevent the spread of disease; availability of jobs, increased demand for water, for energy sources, transportation and infrastructure; loss of rural areas, wilderness and forested areas; development/growth of squatter settlements, impact on status of women and family structure; access to/demand for education secession, demand for a shift in the boundaries, reaction to new boundaries, citizenship/what does it mean to belong/what does it mean not to belong, force of unification, force of division, development of national cohesion, dissolution of national cohesion, lack of national cohesion, emergence of separatism, use of terrorism, manipulation of nationalistic feelings/ultranationalism, manipulation of belief systems to incite conflict challenge of securing resources, controlling land, maintaining control of territory and of exerting power (economic, social and political); ability to supply people and protect citizens in controlled territories; conflicting world views, maintaining and/or loss of cultural identity and/or ethnic identity and traditions; challenges to religious practices, loss of political control, managing change, resistance, response to resistance, resentment, exploitation, segregation, discrimination, disputes, conflict, improvements to healthcare, introduction of new diseases, improvements to infrastructure, loss of jobs, Cost, rate and (un)intended consequences of cultural change; changes in people’s diets/dress/housing/music and traditional culture; threats to traditional culture and language(s), access to information, education, jobs/job opportunities, threats or costs to sustainability, debate over sustainability, ability to maintain unique cultural traits, support for cultural divergence/convergence, use of a common language, displacement of industries/companies and jobs; impact on human capital, consequences of interdependence; economic/political advantages, risks, and challenges; effects of global debt crises, challenges of illegal trade; debate over spread of technology and reduction in barriers and elimination of inefficiencies, hostility and protest against globalization; impact of migration, cooperative economic efforts, cooperative political efforts, the media, blended cultural ideas (music, language, technology, healthcare), power of transnational corporations, importance of international workers, devaluation of diversity, politics of diversity Challenges/efforts to integrate/reaction /acceptance of immigrants, migrants, outsiders/those who are different and refugees; problems faced by refugees, disenfranchisement, strains on housing, impact of squatter settlements, strains on social welfare systems, availability of jobs, access to citizenship, debate over granting citizenship to immigrants, economic costs of accepting migrants, threats to or change to culture as a result of accepting immigrants, economic contributions of immigrants/migrants, debate over economic benefits provided by immigrants/migrants, benefit of cultural contributions of immigrants/migrants, impact of outmigration on homeland Enduring Essay Outline Step # 1: Identify an Enduring Issue in the Documents Look in the documents for evidence of challenges or problems then identify an enduring issue based on what you find. If you see evidence of an enduring issue in the documents that you did not learn in class but you feel confident about then choose that one. Instead of choosing “conflict,” try identifying an enduring issue like “conflict between ethnic groups” or “civil wars” which is really choosing an enduring issue and a nested issue that stresses a key idea that involves the enduring issue. Along with connecting the enduring issue to a related nested issue, you will also want to identify the causes and/or effects of an enduring issue. For example, “conflict caused by competition over resources” or “conflict has led to human rights violations.” Step # 2 – Create Outline Introduction General Statement: Throughout world history they have been many (enduring issue w/o nested issue) ___________________. Specific Statement: (Enduring issue w/o nested issue) __________________________ is defined as______________________ _______________________________________________________________________________________. (Enduring issue with nested issue) __________________________________________ has impacted the lives of many people throughout the world. Thesis Statement: Establish a Claim and Identify Examples (Enduring issue with nested issue) _______________________________________________ is a significant enduring issues because (argument why the issue is significant two effects if has been having on the lives of people from the documents)_________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ as demonstrated by (list of examples that will be discussed in the essay to show the issue has endured and is significant ) _______________________ _______________________________________, ________________________________________________, ___________________________________________________________________________. Body Paragraph # 1 – First Example of the Enduring Issue in History Topic Sentence: Write a sentence that Identifies an example of the enduring issue + nested issue in history which also includes a subordinating (middle or beginning) and/or an appositive. Context / Background: Describe the historical and geographic context of the example by citing and introducing from the document(s) and/or relevant outside information. When and where did the example take place? Who was involved? How did it happen? Explain how the historical and geographic factors you identified help to cause the event? Argument: Describes how people were affected by the enduring issue or how people affected it in the example by citing and introducing evidence from the document(s) and/or relevant outside information. Concluding Sentence: Connect the paragraph to the overall thesis statement. Transition to the topic of the next paragraph. Body Paragraph # 2 – Second Example of the Enduring Issue in History Topic Sentence: Write a sentence that Identifies an example of the enduring issue + nested issue in history which also includes a subordinating (middle or beginning) and/or an appositive. Context / Background: Describe the historical and geographic context of the example by citing and introducing from the document(s) and/or relevant outside information. When and where did the example take place? Who was involved? How did it happen? Explain how the historical and geographic factors you identified help to cause the event? Argument: Describes how people were affected by the enduring issue or how people affected it in the example by citing and introducing evidence from the document(s) and/or relevant outside information. Concluding Sentence: Connect the paragraph to the overall thesis statement. Transition to the topic of the next paragraph. Body Paragraph # 3 – First Example of the Enduring Issue in History Topic Sentence: Write a sentence that Identifies an example of the enduring issue + nested issue in history which also includes a subordinating (middle or beginning) and/or an appositive. Context / Background: Describe the historical and geographic context of the example by citing and introducing from the document(s) and/or relevant outside information. When and where did the example take place? Who was involved? How did it happen? Explain how the historical and geographic factors you identified help to cause the event? Argument: Describes how people were affected by the enduring issue or how people affected it in the example by citing and introducing evidence from the document(s) and/or relevant outside information. Concluding Sentence: Connect the paragraph to the overall thesis statement. Transition to the topic of the next paragraph. Conclusion Restate the thesis: Explains how the issue has continued to be an issue and has changed over time with reference to the examples in the essay and additional modern-day examples. Example # 1: Example # 2: Explain why the issue is significant and has endured