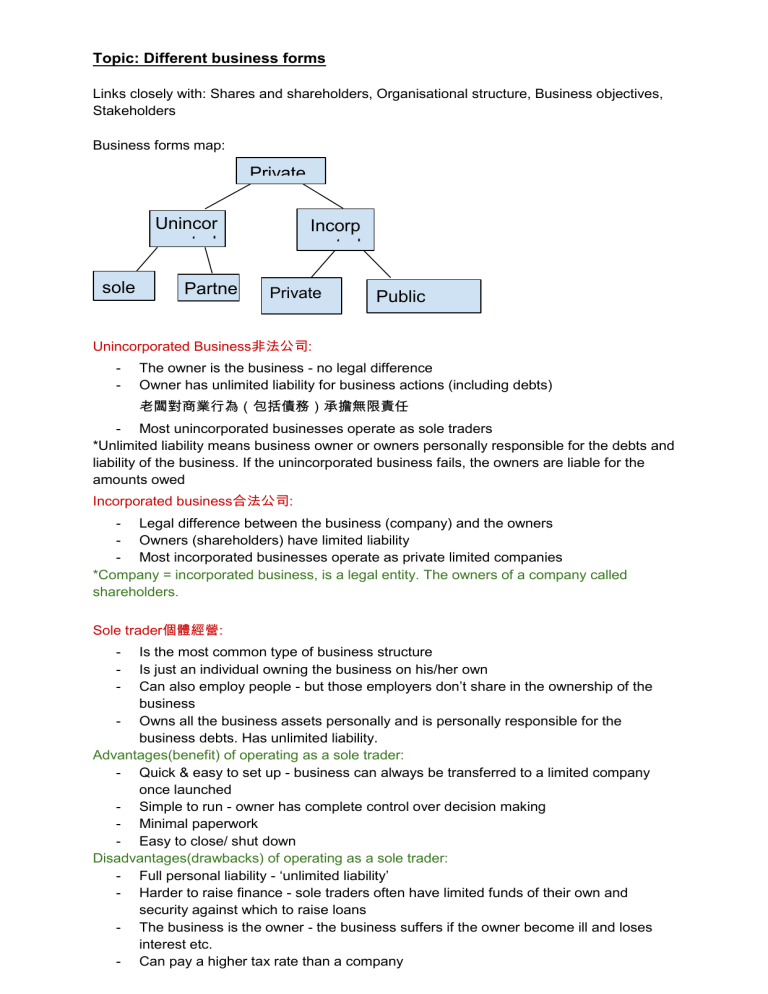
Topic: Different business forms Links closely with: Shares and shareholders, Organisational structure, Business objectives, Stakeholders Business forms map: Private Unincor porated sole trade Partne rship Incorp orated Private Limited Public limited Unincorporated Business非法公司: - The owner is the business - no legal difference Owner has unlimited liability for business actions (including debts) 老闆對商業行為(包括債務)承擔無限責任 - Most unincorporated businesses operate as sole traders *Unlimited liability means business owner or owners personally responsible for the debts and liability of the business. If the unincorporated business fails, the owners are liable for the amounts owed Incorporated business合法公司: - Legal difference between the business (company) and the owners - Owners (shareholders) have limited liability - Most incorporated businesses operate as private limited companies *Company = incorporated business, is a legal entity. The owners of a company called shareholders. Sole trader個體經營: - Is the most common type of business structure Is just an individual owning the business on his/her own Can also employ people - but those employers don’t share in the ownership of the business - Owns all the business assets personally and is personally responsible for the business debts. Has unlimited liability. Advantages(benefit) of operating as a sole trader: - Quick & easy to set up - business can always be transferred to a limited company once launched - Simple to run - owner has complete control over decision making - Minimal paperwork - Easy to close/ shut down Disadvantages(drawbacks) of operating as a sole trader: - Full personal liability - ‘unlimited liability’ - Harder to raise finance - sole traders often have limited funds of their own and security against which to raise loans - The business is the owner - the business suffers if the owner become ill and loses interest etc. - Can pay a higher tax rate than a company Limited company: - Limited companies are separate legal entities to the founders. A legal entity can own things(assets) itself, also can sued or be sued.可被控告/控告別人 - - Companies are owned by their shareholders and run by directors. The shareholders appoint the directors who run the company in the interests of the shareholders. Sometimes directors and shareholders are the same people. Shareholders own a share of the company, but they do not own the assets of the company and they are not liable of the debts of the company. 股東負責股份,不負責資產及債務 - The company owns the assets and pays the debts. If the company becomes insolvent 破產, for example it cannot pay its debts, the company is closed. - *Shareholders are not liable for any debts owed by the company that cannot be settled. - By far目前為止, the most common form is a private limited company. ‘Private’ means that the shares of the company are not traded publicly on a stock exchange. 股票只提供給公司內股東,不上市 - By contrast相比之下, a public limited company(also called by ‘plc’) tends to have a larger value of share capital invested and its shares may be traded publicly. 上市 Importance of limited liability: - An important protection for shareholders in a company - Shareholders can only lose the value of their investment *However, limited liability does not protect against wrongful or fraudulent trading, or when personal guarantees have been given by directors Advantages of operate as limited companies: - Limited company protects the shareholders - Easier to raise finance and debt - both through the sale of shares - Stable form of structure - business continues to exist even when shareholders change Disadvantages of operate as limited companies: - Greater admin costs 更高的管理成本 - Public disclosure of company information公開披露公司信息 - Director’ legal duties 有可能要負上法律責任 Public Limited Companies • A more specialist type of limited company • Shares may be quoted and traded on a public stock market (but don’t have to be) • When traded on a stock market, public companies have substantially more shareholders • Subject to greater regulation in terms of public disclosure of financial and other information 在公開披露財務和其他信息方面受到更嚴格的監管 Public Sector Companies / Businesses: • A relatively small number of companies are owned or controlled by the Government • E.g. RBS (nationalised), Network Rail Public Sector Organisations: • There are many more organisations that provide goods and services which are owned and operated by public bodies • These are funded by central & local government, but may still levy charges for some services • E.g. NHS, Highways Agency, TeachFirst Not for Profit Organisations非牟利組織 • Not-for-profit organisations are businesses that trade in order to benefit the community. These businesses have social aims as well as trying to make money 非營利組織是為了使社區受益而進行交易的企業。 這些企業既有社會目標,也有努力賺錢 • Examples of social aims are job creation and training, providing community services and fair trade with developing countries • There are many different types of social enterprise, including community development trusts, housing associations, worker-owned co-operatives and even sports clubs