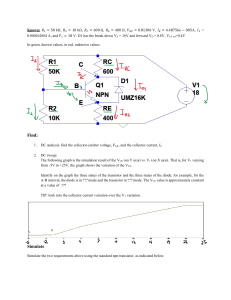
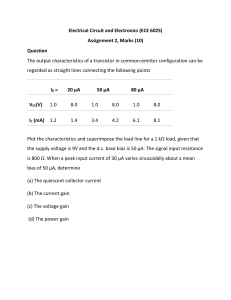
1. 2. 3. 4. Refer to this figure. Determine the minimum value of IB that will produce saturation. A. 0.25 mA B. 5.325 A C. 1.065 A D. 10.425 A A transistor amplifier has a voltage gain of 100. If the input voltage is 75 mV, the output voltage is: A. 1.33 V B. 7.5 V C. 13.3 V D. 15 V Refer to this figure. If VCE = 0.2 V, IC(sat) is: A. 0.05 mA B. 2.085 mA C. 1.065 mA D. 7.4 mA What is the ratio of IC to IB? A. B. DC hFE C. D. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. DC either DC or hFE, but not DC For normal operation of a pnp BJT, the base must be ________ with respect to the emitter and ________ with respect to the collector. A. positive, negative B. positive, positive C. negative, positive D. negative, negative Refer to this figure. The value of VBC is: A. 9.2 V B. 9.9 V C. –9.9 V D. –9.2 V When a transistor is used as a switch, it is stable in which two distinct regions? A. saturation and active B. active and cutoff C. saturation and cutoff D. none of the above The term BJT is short for A. base junction transistor. B. binary junction transistor. C. both junction transistor. D. bipolar junction transistor. For a silicon transistor, when a base-emitter junction is forward-biased, it has a nominal voltage drop of A. 0.7 V. B. 0.3 V. C. 0.2 V. D. VCC. 10. A certain transistor has IC = 15 mA and IB = 167 A. 15 B. 167 C. 0.011 D. 90 11. Refer to this figure. The value of VCE is: 12. 13. A. 9.9 V B. 9.2 V C. 0.7 V D. 19.3 V What does DC vary with? A. IC B. ºC C. both IC and ºC D. IC, but not ºC A BJT has an IB of 50 A. 375 mA B. 37.5 mA C. 3.75 mA D. 0.375 mA A and a DC of 75; IC is: A; DC is: 14. Refer to this figure. The value of VBE is: A. 0.6 V B. 0.7 V C. 1.2 V D. 0.079 V 15. What are the two types of bipolar junction transistors? 16. 17. A. npn and pnp B. pnn and nnp C. ppn and nnp D. pts and stp In this circuit A. 92 k B. 9.1 M C. 100 k D. 150 k The value of DC = 100 and VIN = 8 V. The value of RB that will produce saturation is: DC A. is fixed for any particular transistor. B. varies with temperature. C. varies with IC. D. 18. varies with temperature and IC. A transistor data sheet usually identifies A. hre. B. hFE. C. IC. D. VCE. DC as 19. What is the ratio of IC to IE? A. DC B. DC C. DC D. 20. /( either DC DC + 1) /( DC + 1) or Refer to this figure. The value of A. 18 mA B. 7.92 mA C. 1.8 mA D. 8 DC, but not DC DC = 100 and VIN = 8 V. Determine IC(sat). A 21. Which of the following is true for an npn or pnp transistor? A. IE = IB + IC B. IB = IC+ IE C. IC = IB + IE D. none of the above 22. What is the order of doping, from heavily to lightly doped, for each region? A. base, collector, emitter B. emitter, collector, base C. emitter, base, collector D. collector, emitter, base 23. In what range of voltages is the transistor in the linear region of its operation? A. 0 < VCE B. 0.7 < VCE < VCE(max) C. VCE(max) > VCE D. none of the above 24. The magnitude of dark current in a phototransistor usually falls in what range? A. mA B. μA C. nA D. pA 25. A 35 mV signal is applied to the base of a properly biased transistor with an r' e = 8 voltage at the collector is: A. 3.5 V B. 28.57 V C. 4.375 mV D. 4.375 V and RC = 1 k . The output signal 26. What is (are) general-purpose/small-signal transistors case type(s)? A. TO-18 B. TO-92 C. TO-39 D. TO-52 E. all of the above 27. What is (are) common fault(s) in a BJT-based circuit? A. opens or shorts internal to the transistor B. open bias resistor(s) C. external opens and shorts on the circuit board D. all of the above 28. The dc load line on a family of collector characteristic curves of a transistor shows the A. saturation region. B. cutoff region. C. active region. D. all of the above 29. Refer to this figure. Determine the minimum value of VIN from the following that will saturate this transistor. A. 13.21 V B. 12.51 V C. 0.7 V D. 9.4 V