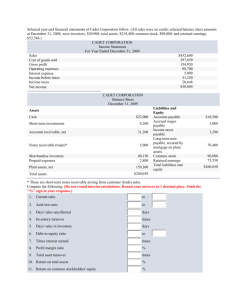
Periodic System (Normal Balance) DEBIT Purchases Accounts Receivable Transportation – In/Out Sales Discount Sales Returns and Allowances CREDIT Accounts Payable Sales Cash Purchase Discount Purchases Returns and Allowances Buyer’s Point of View (Journal Entry of Accounts) 1. Purchase (D) [Less trade discount/volume discount if there are any] Accounts Payable (C) 2. Accounts Payable (D) Purchase Returns and Allowances (C) 3. Accounts Payable (D) [Less Purchase Returns and Allowances if there are any] Purchase Discount (C) [If there are any / if it is still applicable] Cash (C) 4. Transportation In (D) Cash (C) Seller’s Point of View (Journal Entry of Accounts) 1. Accounts Receivable (D) Sales (C) 2. Sales Returns and Allowances (D) Accounts Receivable (C) 3. Cash (D) Sales Discount (D) [If there are any / if it is still applicable] Accounts Receivable (C) [Less Sales Returns and Allowances if there are any] 4. Transportation Out (D) Cash (C) Perpetual System (Normal Balance) DEBIT CREDIT Inventory Accounts Receivable Transportation – Out Sales Discount Sales Returns and Allowances (If allowances only are made) Cost of Sales Accounts Payable Sales Cash When is Inventory Debited/Credited? Inventory is DEBITED when the following accounts used in the “Periodic System” is converted into the Perpetual System, such as: 1. Purchases 2. Transportation In 3. Sales Returns Inventory is CREDITED when the following accounts used in the “Periodic System” is converted into the Perpetual System, such as: 1. Purchase Discount 2. Purchases Returns and Allowances OR, when Cost of Sales is journalized When is Cost of Sales journalized? Cost of Sales is JOURNALIZED only when there are sales made, or when there are returns done by the buyers. To compute for the Cost of Sales, you must reduce the amount of item being SOLD from the items that are recorded in the Inventory. Item sold * Original Amount when it was purchased = Cost of Sales For example: Sold (120 items which are originally bought for 2,500) 120 * 2,500 = 300,000 (The amount to be entered or journalized as a debited Cost of Sales is 300,000 worth of merchandise to be reduced from inventory) Normally, Cost of Sales is DEBITED when sales are made. However, if SALES RETURNS occur, Cost of Sales must be credited. Buyer’s Point of View (Journal Entry of Accounts) [Please refer to the Periodic System journal entries for reference of conversion] 1. Inventory (D) [Less trade discount/volume discount if there are any] Accounts Payable (C) 2. Accounts Payable (D) Inventory (C) 3. Accounts Payable (D) [Less Purchase Returns and Allowances if there are any] Inventory (C) [If there are any / if it is still applicable] Cash (C) 4. Inventory (D) Cash (C) Seller’s Point of View (Journal Entry of Accounts) 1. Accounts Receivable (D) Sales (C) 2. Sales Returns and Allowances (D) [If Allowances are only made] Accounts Receivable (C) 3. Cash (D) Sales Discount (D) [If there are any / if it is still applicable] Accounts Receivable (C) [Less Sales Returns and Allowances if there are any] Cost of Sales (D) Inventory (C) 4. Transportation Out (D) Cash (C) 5. Inventory (D) [If Sales return occurred] Cost of Sales (C)