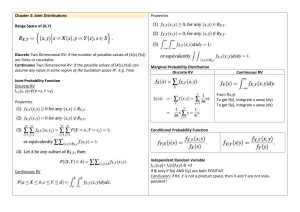
If a and b are constants, then E(aX + b) = aE(X) + b. E(aX) = aE(X) E(b) = b …Expected value of a constant is always a constant For random variables X and Y , E(X + Y ) = E(X) + E(Y ). Also, E(aX + bY ) = aE(X) + bE(Y ). ….basically take the constants out Variance when X is Discreet Variance when X is Random ….basically Variance of a Constant it zero Bernoulli’s Distribution E(X) = p Var(X) = p(1-p) Var (X) = p(1 - p) Binomial Distribution (n independent trials ) X _ Binomial (n; p) Bernoulli distribution is a special case of the binomial distribution with n = 1 If X _ Binomial (n; p), then E(X) = np