8th Grade English Daily Lesson Log: Sentence Structure & Reading
advertisement

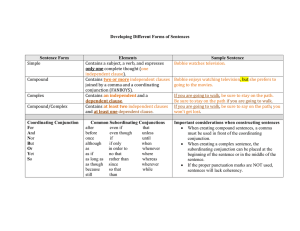
GRADES 1 to 12 DAILY LESSON LOG I. OBJECTIVES A. Content Standards: B. Performance Standards: C. Learning Competencies/Objectives: Write the LC Code for each School: Teacher: Teaching Dates and Time: MONDAY JOSE RIZAL APOC-APOC NHS JOAN QUIAMCO-BEDIORES 7:45-8:45/8:45-9:45 TUESDAY WEDNESDAY Grade Level: Learning Area: Quarter: THURSDAY 8 ENGLISH FIRST FRIDAY Objectives must be meet over the week and connected to the curriculum standards. To meet the objectives, necessary procedures must be followed and if needed, additional lessons, exercises and remedial activities may be done for developing content knowledge and competencies. These are using Formative Assessment strategies. Valuing objectives support the learning of content and competencies and enable children to find significance and joy in learning the lessons. Weekly objectives shall be derived from the curriculum guides. . The learner demonstrates understanding of: African literature as a means of exploring forces that human beings conntend with; variuos reading styles vis – à-vis purposes of reading; prosodic features that serve as carriers of meaning; ways by which information may be organized, related, and delivered orally; and parallel structures and cohesive devices in presenting information. The learner transfers learning by composing and delivering a persuasive speech based on a specific topic of interest keeping in mind the proper and effective use of parallel structures and cohesive devices and appropriate prosodic features, stance, and behavior. EN8LC-If-5.2: Note the changes in volume, projection, pitch, stress, intonation, juncture, and rate of speech that affect meaning. EN8OL-If-5: Use appropriate prosodic features of speech when delivering lines EN8G-If-7: Use parallel structures Know about conjuction. Identify conjunctions in a sentence Differentiate coordinating conjunction from subordinating conjunction Constuct sentences using coordinating conjuctions. EN8V-Ie-4: Use appropriate strategies in unlocking the meaning of unfamiliar words EN8RC-If-7: Use the appropriate reading style (scanning, skimming, speed reading, intensive reading etc.) for one’s purpose EN8G-If-7: Use parallel structures. Differentiate Simple sentence, coumpound sentence, complex sentence, and compoundcomplex sentences. Construct sentences. Content is what the lesson is all about. It pertains to the subject matter that the teacher aims to teach. In the CG, the content can be tackled in a week or two. II. CONTENT III. LEARNING RESOURCES A. References 1. Teacher’s Guide Pages 2. Learner’s Materials Pages 3. Textbook Pages 4. Additional Materials from Learning Resource (LR) portal B. Other Learning Resources Sentence stress Conjunction Vocabulary Mapping Characteristic of Indian Literature Kinds of sentences according to Simple sentence, coumpound sentence, complex sentence, and compound-complex sentences. Lists the materials to be used in different days. Varied sources of materials sustain children’s interest in the lesson and in learning. Ensure that there is a mix of concrete and manipulative materials as well as paper-based materials. Hands-on learning promotes concept development. 71-73 77 74-75 78-81 76-79 82-85 87 95 WEDNESDAY THURSDAY Writer’s Choice: grammar and composition MONDAY TUESDAY FRIDAY IV. PROCEDURES These steps should be done across the week. Spread out the activities appropriately so that students will learn well. Always be guided by demonstration of learning by the students which you can infer from formative assessment activities. Sustain learning systematically by providing students with multiple ways to learn new things, practice their learning, question their learning processes, and draw conclusions about what they learned in relation to their life experiences and previous knowledge. Indicate the time allotment for each step. A. Reviewing Previous Lesson or Presenting the New Lesson Review about the traditional dances ofAfro- Asian people Take a look from the lines taken from the excerp of “The Prophet” Read the selection about Indian Literature Define sentence. B. Establishing a Purpose for the Lesson How can you better understand your identity as an Asian? Identify words used to connect the ideas in the sentence What is the parts of sentences C. Presenting Examples/Instances of the Lesson Read the passage about Indian culture. Focus on giving emphasis on words in the message. Students will listen carefully. Discuss about Sentence stress. Connect clauses or phrases using conjunction. Give the meaning of the italicized word using the vocabulary mapping procedure Follow the process for vocabulary mapping Explain the key points about coordinating and subordinating conjunction Give the definition of skimming and its importance in getting information from a reading text. Discuss the four kinds of sentences according to structure. Allow students to identify the stressed and unstressed word in the selection. Do activity 2.:practice makes perfect. Allow students to connect word or group of words using conjunction. Instruct students to do activity 5. Ask students to construct their own sentence using each structure. Sentence stress refers to the emphasis or prominence given to a syllable of certain words in a sentence. A. Coordinating conjunctions tie together words and wordgroups which have the same grammatical construction. List of coordinating conjuntions: F – for A – and N – nor B – but O – or B. Subordinating Conjunctions D. Discussing New Concepts and Practicing New Skills #1 Differentiate content words from function words. Allow student to read the sentences posted on the board. E. Discussing New Concepts and Practicing New Skills #2 F. Developing Mastery (Leads to Formative Assessment 3) G. Finding Practical Applications of Concepts and Skills in Daily Living H. Making Generalizations and Abstractions about the Lesson Have you experienced finding serenity in nature when you have a problem? Subordinators are function words that join dependent clauses to main clauses; they are of two types: those that pattern like because and form that pattern like who, whom, Skimming is one skill which can help you get a quick overview of the material you are reading. To skim is to get the gist or the general understanding of a reading material. Kinds of Sentences According to Structure A. Simple sentence – is a sentence with one independent clause and no subordinate clause. It may contain two or more verbs or two or more subjects connected by subordinators, but this does not alter the fact that only one thought is expressed. Compound Sentence – is a sentence composed of two or more independent clauses but no subordinate clauses. The whose, which and that. These words not only introduce the subordinate clause but link it to the main clause. Their chief function is to make clear what the relation between the two clauses is. The chief relations they show are time, place, cause, result, exception, condition, and alternative. I. Evaluating Learning J. Additional Activities for Application or Remediation V. Activity: Retrieval chart clauses of a compound sentence may be separated by semi-colons or commas followed by coordinating conjunctions; or semi-colons followed by sentence connectors. You may separate the two main clauses of a compound sentence into two simple sentences Complex Sentence - is a sentence containing one independent clause and at least one subordinate clause. Compound-Complex Sentence – contains two or more independent clauses and at least one subordinate clause. Activity 10: Sentence Structure Test Do activity 3: Connect me if I’m right Construct sentences using coordinating and subordinating conjunction. Read the story Mahabharata and Ramayana. Try to get information through skimming. Write your reflection about nutrition month celebration using the kinds of sentences. REMARKS VI. REFLECTION Reflect on your teaching and assess yourself as a teacher. Think about your student’s progress this week. What works? What else needs to be done to help the students learn? Identify what help your instructional supervisors can provide for you so when you meet them, you can ask them relevant questions. A. No. of learners who earned 80% in the evaluation B. No. of learners who require additional activities for remediation C. Did the remedial lessons work? No. of learners who have caught up with the lesson D. No. of learners who continue to require remediation E. Which of my teaching strategies work well? Why did these work? F. What difficulties did I encounter which my principal or supervisor can help me solve? G. What innovations or localized materials did I used/discover which I wish to share with other teachers? Checked by: MARIVIC T. DELGADO Principal 1