QSAR: Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationship Explained
advertisement

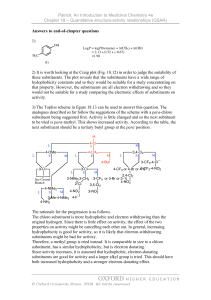
What is QSAR ?? A mathematical relation ships: measurable molecular properties correlates in terms of an equation Some biological activity Steps involved in QSAR * *:Virtual Screening, Molecular Docking and QSAR Studies in Drug Discovery and Development Programme, M. Rudrapal, D. Chetia, Published 2020, Journal of Drug Delivery and Therapeutics Step 2: Molecular Modeling Forms a model of the real word dealing with the model not with the real word It is valid as long as it reproduces the real word Study molecular properties Rationalize, interpret experimental result Make prediction for unstudied systems Molecular modeling is a fast, accurate, cheap way to Design new molecules Step 3: Molecular Descriptors Numerical values associated with the structural features of chemical compounds Geometrical descriptors Electronic descriptors principal moments of inertia. molecular volume. solvent-accessible surface area. Molecular Surface area. dipole moment, Quadrupole moment, polarizibility Molar Refractivity Descriptors falls in 4 classes Topological descriptors Hybrid and 3D Descriptors Atom and Bond Counts substructure counts molecular connectivity Indices Molecular Symmetry spatial autocorrelation vectors pharmacophore fingerprints Eva Descriptors Descriptors of Molecular Field Hydrophobicity Crucial to how easily drug crosses cell membrane and also in receptor interaction Relative distribution is known as partition coefficient (p) ≠ substituents on lead compounds concentration of drug in oil phase P = cocentration of drug in aqeous phase ≠ hydrophobicity and ≠ p values Log (1/C) A straight line would be obtained with equation: Log (1/c) = k1log p + k2 Increasing hydrophobicity increases the biological activity: • Cross hydrophobic barriers to reach the target • Interact with the target P Hydrophobicity Hydrophobicity does not increase biological activity to infinity: • Drug may become poorly soluble in aqueous phase • Drug may trap in fat deposit and never reach the site of action • Suspected to metabolism and elimination. Curve : changes from straight line to parabolic Small value the equation is dominated by first part of the reaction Large value the equation is dominated by second part of the reaction Hydrophobicity ≠ substituents have ≠ hydrophobicity Measure theoretically the relative hydrophobicity (∏) for substituents w.r.t. hydrogen ∏X : Hydrophobicity constant for substituent x PX : Partition coefficient for standard compound with substituent PH :Partition coefficient for standard compound Electronic effect Electronic effect of substituent influences the drug ionization and polarity how easily a drug passes through a cell membrane Affects how strongly it interacts with binding site For substituents on aromatic rings: Hammett’s substituent constant Measure of electron withdrawing or donating ability of substituents at meta and para position measuring dissociation of substituted benzoic acid and comparing to benzoic acid itself Limitations: • Only few drugs (aromatic system) • Ortho position is not considered Electronic effect Aliphatic electronic substituent constants: measuring rates of hydrolysis for a series of ester Methyl ethanoate (parent ester) Rate of hydrolysis varies with substituent X. (Depending on the electronic effect at site of action). Electronic effect is purely inductive and denoted as σ1. Electron-donating group reduces the rate (σ1<0) Electron-withdrawing group increases the rate (σ1 > 0) Steric factor Size and shape of drug influence how easily a drug can approach and interact with binding site Bulky substituent acts like a shield and hinders interaction Steric factor 1: Taft’s steric factor (Es) comparing rates of hydrolysis of substituted aliphatic esters with standard ester under acidic condition. Steric factors Es = log kx – log k0 X=H, F < CH3 Faster rate (KX > k0) KX: rate of hydrolysis of aliphatic ester bearing substituent X. K0 : rate of hydrolysis of reference ester X > CH3 Reduces the rate (KX < k0) Steric Factor Steric factors 2: Molar refractivity (MR) Steric factors 3: Verloop steric parameters volume occupied by an atom or group of atoms n = index of refraction MW = molecular weight d = density MR is particularly significant with substituents having π electrons or lone pair of electrons Involves computer program called Sterimol calculates steric substituent values from: • bond angles • van der Waals radii • bond lengths • possible conformation for substituent. Hansch equation Biological activity of most drugs Is related to combination of physical properties (log p, π, σ, or a steric factor) If hydrophobicity values limited to small range: linear equation spread over a large range: parabolic equation Craig plot Shows values for 2 different physiochemical properties for various substituents Validation Step Validation methods are needed to establish the predictiveness of a model * *: Molecular docking and QSAR analysis of a few Gama amino butyric acid aminotransferase inhibitors,usman abdulfatai, adamu azairu, sani uba, Egyptian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, Volume 5, Issue 1, March 2018, Pages 41-53 Advantage Vs Limitation • Modifying the structure of lead compound to retain or to inforce the desired pharmacological effect. • Helps in understanding the interaction between molecule of many functional groups with their target. • False correlation in case of experimental error. • If dataset is not large enough QSAR results cant predict the compound of best reactivity.