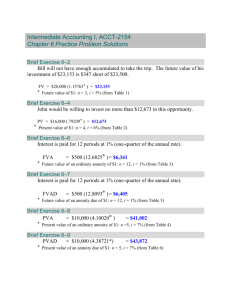
Finance Notes Lecture 1 Four Basic Areas of Finance Corporate finance AKA business finance o Basic theories and ideas of finance Investments o Financial assets such as shares and bonds Financial institutions o Firms dealing in financial matters International Finance o Covers the above areas in a global context What is Business finance? Some questions a business needs to answer: o What equipment to buy? o Will you use your money or someone else’s? o When do you pay suppliers? The answers are provided by the financial manager o Coordinates treasury and accounting activities Goal of Financial Management Aim of the financial manager is to maximize shareholder wealth o Maximization of share price Profit maximization is not an appropriate goal o Not time frame o What measure of profit? Profit measures are dependent on accounting standards Other goals, such as the maximization of sales, are also not appropriate Its all about the cash! Any business needs cash to survive It is important not to confuse accounting income with cash flow o Many non-cash items in profit Operation cash flow and free cash flow o Not in any financial statement Cash from assets = Cash flow to creditors + Cash flow to shareholders What happens if there is insufficient cash? Factors in any financial decision Dollar amount o Dollar amount of the actual cash flow received or paid out Time o When cash flow is received or paid out Time value of money (TVM) Risk o Amount of uncertainty Investors require higher returns for higher risk The relationship between expected return and risk Financial Manager’s responsibilities Investment decision o What assets to buy? Capital Budgeting decision Financing decision o Where does the money come from? Capital Structure decision Working Capital decision o Inventory, Receivables, Accounts Payable o Less potential for value creation The Investment Decision It is the most important decision o Incorrect decisions are costly to reverse How to determine the value of long-term asset Evaluate size, time, and risk of cash flows Select assets that create most shareholder wealth The Financing Decision How to finance an investment? Determine the best mix between o Debt (Loan funds) Contractual claim o Equity (Owner’s funds) Residual claim o Trade-off between return and risk Use of debt is called ‘gearing’ or ‘leverage’ The Working Capital Decision Managing short-term assets and liabilities Forms part of the investment decision o Inventory Management What is the optimal level of inventory? o Receivables Management o Should credit sales be allowed? Accounts Payable Management How long should suppliers have to wait before being paid? Forms of Business Sold Trader/ Proprietorship o Single owner – can employ others o Unlimited liability o Success or failure relies on the owner o Lasts as long as the owner is alive or sells o Equity component limited to sole trader’s wealth o Easy and inexpensive to establish o Minimal reporting requirements Partnership o Similar to sole trader except several individuals o All share in gains and losses o Characterized by a partnership agreement o If one wants to leave, partnership ends Company o Most important form o Separate legal entity o Unlimited life o Many formal and legal requirements o Limited liability for shareholders o Only a small number of companies are listed o Superior form when raising capital Corporate Governance Objectives of management may differ from shareholders Managers may be satisfiers rather than maximizers o Management plays it safe, rather than maximizing the value of the firm Management are agents for the owners Introduces a potential conflict o Agency problem Principal and Agent Law Agency law is part of commercial law It is a contractual relationship between a person (The agent) who is authorized to act on behalf of another (the principal) Agent can create legal relationship with third party Creation of agency o Expressly in writing or verbally o Implied by law As part of a necessity, or by cohabitation, by status (such as a partnership) or working relationships Employer-employee relationships Not all employees are agents for the employer This will depend on the type of work carried out o Salespeople are agents for the employer as they are arranging sales o Managers tend to be agents as they enter into contracts for the employer Agents can be Special, General or Universal Duties of an agent o Follow the principal’s instructions o o o o o Act personally (not delegate to another) Exercise reasonable skill and diligence Act in the principle’s best interest Not to make secret profit Not to divulge confidential information Interaction between firms and financial markets Primary Market The first sale of a security or instrument by a firm Funds are raised by the firm and flow to it Can be debt or equity funding Public or private offering Fund raising between investors and firm Secondary Market Financial securities that are already issued are bought and sold Way of transferring ownership An example of a secondary market o Securities exchange Investor-to-Investor trading No additional funds are raised by the firm Balance Sheet Market Values and Book Values Income Statement Lecture 2 (The Time Value of Money 1) Time value of money (TVM) The financial manager makes decisions about proposals with cash flows over long period of time TVM is based on the principle that a certain amount of money received today is worth more than that same amount of money received in the future Two important considerations: o $100,000 received today o $100,000 received in five years’ time Which of the following cash flows would you prefer to receive? o $100,000 received today o $150,000 received in five years’ time Example 1 You invest $1,000 in a bank today for a period of one year The bank will pay interest at a rate of 5% pa. How much will you have in the bank at the end of one year? Three known variables: o Dollar amount invested today (present value) $1,000 o Interest rate paid by the bank 5% o The period the money is invested for 1 year o One unknown variable: The dollar amount at the end of the period (future value) $? Step 1: Calculate the interest o 1000 *5% or (0.05) = 50 Step 2: Add the interest to the original investment o $1000 + $50 = $1,050 Terminology Time Value of Money has its own language: o PV = present value or principle o i = interest rate, later we use ‘r’ o n = number of periods, later we use ‘t’ o FV = future value o PMT = periodic payment (next week) This week, we learn about applications that require three variables to then determine a fourth Timeline Simple Interest Calculated on the original present value o Takes no account of changes in principle o Sometimes called flat rate interest Used in the valuation of short-term financial instruments traded in the money market o Term is under 12 months o Bills of exchange Future value with simple interest Step 1: INT = PV *I *N o i = simple interest rate per year o n = number of years Step 2: FV = PV + INT o FV = future value at the end of term o PV = principal value at beginning o INT = interest rate amount over the time period FV = PV + (PV * i * n) Simplified: FV = PV (1 + i * n) Example 2 Compound interest Interest is added to the principal each period o Interest on interest o Called compounding The compounding period can be any designated length of time o Yearly, Half yearly, monthly Simple interest is calculated only on the original amount Future value Example 3 Example 4 Present Value Example 5 Frequency of Compounding Example 6 Example 7 Example 8 Lecture 3 (The Time Value of Money 2) Understand the principles of annuities and perpetuities Be able to calculate o The future value of an annuity o The present value of an annuity and perpetuity o An annuity payment Annuity Annuities are a special case of multiple cash flows An annuity is a number of equal cash flows occurring at equal time intervals An ordinary annuity assumes all cash flows occur at the end of each period Both the future value and the present value of an annuity can be calculated using the formulas introduced last week In the above future value calculation: o First payment receives interest for two periods o Second payment receives interest for only one period o Third payment receives no interest Example 1 Future value of an annuity Example 1 (solution) Example 2 Example 3 Present value of annuity Example 4 Example 5 Example 6 Example 7 Perpetuity A perpetuity is a special type of annuity with an infinite number of payments o It is a perpetual annuity The present value of a perpetuity is: o PV = PMT / i There is no future value Example 8 Example 9 Lecture 4 (The Time Value of Money 3) Saving Examples of saving Retirement planning (super) Saving for an expense in the future Investments Example 1 You are required to analyze the investment potential of a forestry plantation. The cost to invest is $6,000 in 2019. Projected returns from this investment are o $3,000 in 2022 and o $7,500 in 2027 The interest rate is 15%. Is it worth investing in this project? Example 2 Bert and Beryl want to establish a fund that will pay $10,000 to each of their two grandchildren, Peter, and Mary, when they turn 21. Mary turns 21 in ten years’ time and Peter turns 21 in twelve-and-a-half years’ time. If the fund’s interest rate is 8% pa. compounded half-yearly, what amount should Bert and Beryl deposit today? Example 3 Examples 4 Effective annual Rates (EAR) Example 5 The “Rule of 72” Borrowing Examples of Borrowing Loans Mortgages Example 6 Example 7 Amortization Schedule Lecture 5 (Debt) What is debt? Distinguishing Features of debt? Why lenders protect against loss Short Term Debt Bills of Exchange Legal Definition of a bill Features of a Bill Long Term Debt Features of a Bond Valuation of Debt Valuing Bills Example 1 Example 2 Bond Valuation Question Example 3 Example 4 Example 5 Bond values and yields Yield to maturity Example 6 Example 7