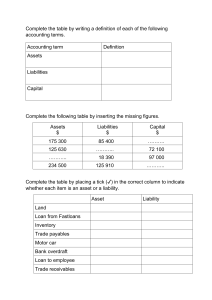
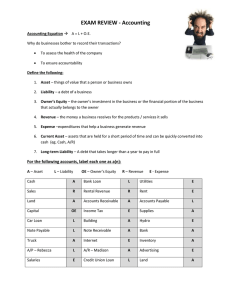
Topic 1: Accounting Equation and Double-entry System In order to understand the concept of accounting, one needs to grasp the concept of accounting equation first. The basic accounting equation is: Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Equity The expanded version is: Assets Current Asset + Non-Current Asset = Liabilities Current Liabilities + Non-Current Liabilities + Owner's Equity Beginning Capital +/Net Income or Net Loss + Additional Investment – Withdrawal This equation is the fundamental of every journal entry, thus, the foundation of the financial statements. The accounting equation is the product of the usage of Double- Entry System which means that in every transaction, there is always two or more accounts affected, and that, there is always at least one account debited and one account credited. Net income is computed as the difference between Income and Expense. In any case, if income is greater than expense, result is net income which is added to equity; if expense is greater than income, result is net loss which is deducted from equity. Elements of Financial Statements 1. Assets – a present economic resource controlled by the entity as a result of past events. These are basically the resources used by company in generating income, paying expenses and settling maturing obligations. These can be classified as either current or noncurrent. ➢ Current Assets- an asset is considered current if it is either of the following: (1) held for the purpose of being traded, or (2) expected to be realized or consumed within 12 months after the end of reporting period or operating cycle which ever is longer. Common examples of current assets are as follows: • Cash • Inventory • Account receivable • Notes receivable • Prepaid expense ➢ Non-current assets- if an asset doesn't meet the definition of current asset, it is considered as non-current assets. Common examples of non-current assets are as follows: • Property, Plant and Equipment • Accumulated Depreciation • Intangible Assets • Long- Term Investments 2. Liabilities- A present obligation of the entity to transfer an economic resource as a result of past events. These are dues the company owe to other parties to provide more fund in the short- term and long- term operation of the company. The se can be classified as either current or noncurrent. ➢ Current Liabilities - A liability is considered current if it is either of the following: (1) held primarily for the purpose of trading, or (2) due within 12 months after the end of the balance sheet date. In other words, they are expected to be paid in the next year. Common examples of current liabilities are as follows: • Accounts Payable • Notes Payable • Accrued Liabilities • Unearned Revenues • Current Portion of Long- Term Debt ➢ Non-current liabilities- if a liability doesn't meet the definition of current liability, it is considered as non-current liability. Common examples of non-current liabilities are as follows: • 3. Expense – Decrease in economic benefit or incurrence of liability that results in decrease of equity other than the withdrawals of owners. Usually incurred to generate an income. Let's break down the words used in the definition • Decrease in economic benefit – decrease in asset • Incurrence of liability – increase in liability • Results in decrease of equity – there must be an adverse or negative effect to the entity • Other than the withdrawals of the owner- the decrease in asset or increase in liability must be a result of outside transactions. The definition of expenses encompasses expenses and losses. Expenses – arises in the course of ordinary activities of the enterprise. There are various classes of expenses but they are generally classified as cost of services rendered or cost of goods sold, distribution or selling expenses, administrative expenses or other operating expenses. Losses – represent other items that meet the definition of expenses and may or may not, arise in the course of ordinary activities of an enterprise. Losses represent decreases in economic benefits and as such are no different in nature from expenses. Typical Account Titles Used Cost of Sales – The cost incurred to purchase or to produce the products sold to customers during the period; also called cost of goods sold. Salaries or Wages Expense – Includes all payments as a result of an employer-employee relationship such as salaries or wages, 13th month pay, cost of living allowance, overtime pay, hazard pay, holiday pay and other benefits. Telecommunications, Electricity, Fuel and Water Expense – expenses related to the use or consumption of telecommunication facilities, electricity, fuel and water. This is also called Utilities Expense Rent Expense – Expense for rentals for space, equipment or other assets used in the business Supplies Expense – Expense of using supplies (e.g. office supplies, store supplies) in the conduct of operations 4. Income- Increase in economic benefit or decrease in liability that results in increase of equity other than the investments of the owners. Usually earned as a result of incurring expenses. Let's break down the words used in the definition • Increase in economic benefit – increase in asset • Results in increase of equity – there must be a positive effect to the entity • Other than the investments of the owners - the increase in asset or decrease in liability must be a result of outside transactions. The definition of income encompasses both revenue and gains: Revenue – arises in the course of the ordinary activities of an enterprise and is referred to by a variety of different names including, sales, fees, etc. Gains – represent other items that meet the definition of income and may, or may not, arise in the course of ordinary activities of an enterprise. Gains represent increases in economic benefits and as such are no different in nature from revenue. Typical Account Titles Used Service Income – Revenues earned by performing services for a customer or client; for example, accounting services by a CPA firm, Haircut services by a Salon, Construction Services by an Engineering Firm. Sales – Revenues earned as a result of sale of merchandise; for example, sale of furniture by firm whose main line is about manufacturing furnitures. 5. Owner’s Equity- Also known as net assets or equity, capital refers to what is left to the owners after all liabilities are settled. Capital – This account is used to record the original and additional investments of the owner of the business entity. It is increased by the amount of profit earned during the year or is decreased by loss. Cash or other assets that the owner may withdraw from the business ultimately reduce it. This account title bears the name of the owner. Withdrawals – When the owner of a business entity withdraws cash or other assets, such are recorded in the drawing or withdrawal account rather than directly reducing the owner’s equity account. Income Summary – It is a temporary account used at the end of the accounting period to close income and expenses. This account shows the profit or loss for the period before closing to the capital account. THE ACCOUNT The basic summary device of accounting is the account. A separate account maintained for each element that appears in the balance sheet (assets, liabilities and equity) and in the income statement (income and expense). Thus, an account may be defined as a detailed record of the increases, decreases and balance of each element that appears in an entity’s financial statements. The simplest form of the account is known as “T-account” because of its similarity to the letter “T”. ACCOUNT TITLE Left Debit side Dr. side or Right side or Credit side Cr. Exercises: Accounting Equation and Double-entry System Choose the best answer. 1. Which of the following accounting equations is correct? 1. Non-current assets + Current assets = Non-current liabilities – Current liabilities + Capital 2. Assets – Liabilities = Capital + Revenue – Expenses 3. Capital + Non-current liabilities = Non-current assets + Working capital a. (1) and (2) only b. (1) and (3) only c. (2) and (3) only d. (1), (2) and (3) 2. Which of the following is correct under the double- entry system? a. Asset amount must be equal to liability account b. The change in asset must be compensated by a change in liability c. The change in a debit-side entry must be compensated by a change in credit-side entry d. An increase in asset must be compensated by a decrease in asset 3. Which of the following statements is correct? 1. The total amount of liabilities can be greater than the total amount of capital 2. Asset = Capital + Liabilities 3. The total amount of asset can be greater than the sum of liabilities and capital a. (1) and (2) only b. (1) and (3) only c. (2) and (3) only d. (1), (2) and (3) 4. Which of the following statements regarding the double-entry system is incorrect? a. An increase in asset means a credit entry in assets account b. A decrease in liability means a debit entry in liabilities account c. An increase in drawings means a debit entry in capital account d. A decrease in non-current asset means a credit entry in assets account 5. Which of the following is correct if the sole proprietor of an entity borrows P30,000 in the name of the entity and deposits it into the entity’s bank account? a. assets of the entity increase by P30,000 b. The liabilities of the entity decrease by P30,000 c. The capital of the entity increases by P30,000 d. The drawings of the entity increase by P30,000 6. Which of the following transactions affects the total value of liabilities of a firm? a.) goods purchased from suppliers by cash b.) Interest received from a bank c.) office equipment bought on credit d.) goods sold to customers on credit 7. On May 1,2021, Chia Ohab sets up a business and brings office equipment of P50,000 and inventory of P30,000 to the business. Chia puts up P80,000 into the firm’s cash box and P100,000 into the firm’s bank account. Meanwhile, the firm lends P50,000 cash to BCD Company and borrows P200,000 from You Do Note bank to acquire a piece of premises. What is the amount of total assets on May 1,2021? a. P510,000 b. P210,000 c. P260,000 d. P460,000 8. If during the accounting period the assets decreased by P10,000, and equity increased by P2,000, then how did liabilities change? a.) Increased by P12,000 b.) Increased by P8,000 c.) Decreased by P12,000 d.) Decreased by P8,000 9. If during the accounting period the assets increased by P14,000, and equity increased by P4,000, then how did liabilities change? a.) Increased by P10,000 b.) Increased by P4,000 c.) Decreased by P4,000 d.) Decreased by P10,000 10.If during the accounting period the assets increased by 30,000 and Liabilities decreased by P8,000, then how did equity change? a.) Increased by P22,000 b.) Increased by P38,000 c.) Decreased by P22,000 d.) Decreased by P38,000 11. Which of the following statements is incorrect? a. The settlement of a liability requires cash payment b. Liabilities can result from accepted trade practices or business commitments. c. An estimated amount may be assigned to a liability when it is presented in the balance sheet. d. Liabilities represent present economic obligations that would future settlement 12.Which of the following statements is incorrect? a. The term income encompasses both realized and unrealized gains. b. The term income encompasses both revenues and gains. c. Recognition of income is generally accompanied by a simultaneous recognition of an asset. d. Income is recognized only when cash is collected from the client or customer 13.Which of the following transactions will increase the total assets of the business? a. a customer’s payment, to apply on his open balance b. Bought an equipment, on cash basis c. Bought an equipment, on account basis d. Paid utilities expense incurred. 14. An account has the following uses, except a. Sorting device that is used to be able to group the business transactions by accounting elements. b. Sorting device that is used to summarize the net effect of the transactions one each accounting element. c. Source of the balances that are reported in the financial statements. d. Accounting device used to detect errors committed 15.Which of the following statements is incorrect? a. The owner’s equity represents the claim of the owner over the assets of the business. b. The owner’s equity increases as a result of additional investments and net income of the business. c. The income and expenses of the business enterprise affect the owner’s equity. d. Debit means increase, and credit means decrease