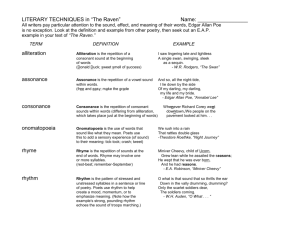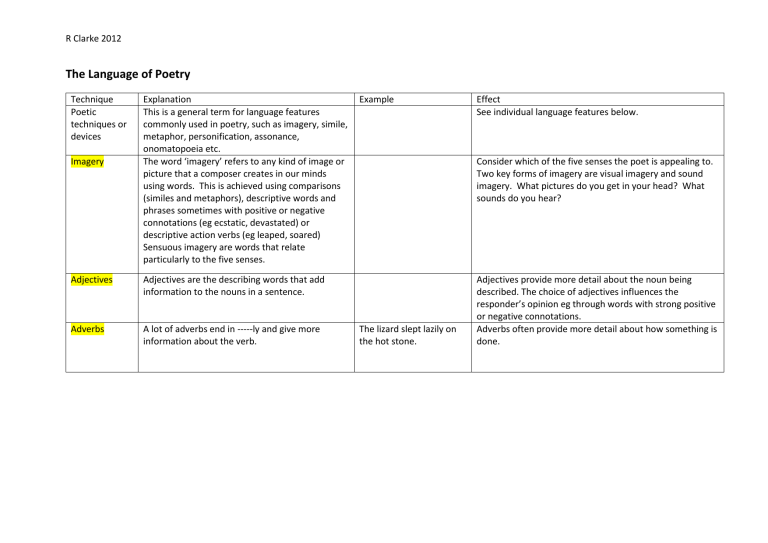
R Clarke 2012 The Language of Poetry Technique Poetic techniques or devices Imagery Explanation This is a general term for language features commonly used in poetry, such as imagery, simile, metaphor, personification, assonance, onomatopoeia etc. The word ‘imagery’ refers to any kind of image or picture that a composer creates in our minds using words. This is achieved using comparisons (similes and metaphors), descriptive words and phrases sometimes with positive or negative connotations (eg ecstatic, devastated) or descriptive action verbs (eg leaped, soared) Sensuous imagery are words that relate particularly to the five senses. Adjectives Adjectives are the describing words that add information to the nouns in a sentence. Adverbs A lot of adverbs end in -----ly and give more information about the verb. Example Effect See individual language features below. Consider which of the five senses the poet is appealing to. Two key forms of imagery are visual imagery and sound imagery. What pictures do you get in your head? What sounds do you hear? The lizard slept lazily on the hot stone. Adjectives provide more detail about the noun being described. The choice of adjectives influences the responder’s opinion eg through words with strong positive or negative connotations. Adverbs often provide more detail about how something is done. R Clarke 2012 Rhythm Rhyme The rhythm of a poem is created by its pattern of stressed and unstressed syllables. Humpty Dumpty sat on the wall ‘Hump’, ‘Dump’ ‘sat’, and ‘wall’ are stressed. They receive more stress than the other syllables, which are unstressed. Rhyme is produced when the last syllables of the words at the end of a line have matching sounds. Rhyme is regular when it creates a pattern. It is irregular when there is some rhyme but no real pattern. Use lower case letters to describe the rhyming pattern eg aa bb cc or a b c a b c Free verse is poetry in which the line lengths and patterns of rhyme and rhythm are all irregular. Goodness gracious me a There’s a snail on my knee aa Rhyming couplets Rhyming couplets are a pair of lines that rhyme. In the room the women come and go Talking of Michelangelo Technique Explanation Example Free verse Rhythm adds to the musicality of the poem and so influences how much we enjoy it. It affects the pace and contributes to the mood and tone. Comment on whether the rhythm is regular or irregular. A regular rhythm gives a pleasing quality since the beat of the poem falls in a regular, predictable pace. Rhythm of often mimics the mood ie sad, slow rhythm or surging rhythm rising to a faster pace that is urgent or stressed. Rhyme serves to group lines together so creating unity. It contributes to the musicality of a poem. Free verse allows the expression of ideas in a less rigid way than traditional poetry. Rhyming couplets add to the cohesion of a poem because of the regular rhyming pattern. They also make the poem enjoyable and memorable by adding to the musicality of the poem. The main purpose is to make a poignant point that leaves a lasting impression with the responder. Effect R Clarke 2012 Couplet See the word couple in "couplet?" That is at least part of what a couplet is: a couple of lines. However, to the untrained eye, distinguishing a couplet from merely a couple of lines can be difficult. The couplet form is a popular device in poetry. The main purpose is to make a poignant point that leaves a lasting impression with the responder. It is the use of rhyme and rhythm in the couplets that generally achieves this effect. Sometimes each couplet represents a verse. By the poet constantly changing stanzas the flow of the poem and the ideas conveyed will be interrupted and this will draw our attention to each new idea. Couplets generally appear in poetry, and quite frequently they rhyme and have the same meter. The two lines often belong together, and share some sort of similar idea. Onomatopoeia Onomatopoeia refers to words that imitate sounds. Dripping, flop, smash, clap, growl, bang, splash, moan etc Onomatopoeia communicates a sound by creating or using a word whose pronunciation sounds similar to the noise it is describing. Alliteration Alliteration is the repetition of the same consonant sounds at the beginning of words close to each other. Flashing fire and flying feathers Blues boys fire first Technique Explanation Example Use of alliteration attracts the reader’s attention because of the repetition. The repetition also emphasises the words alliterated and helps us to remember them. It makes the phrase catchy and often humorous. Alliteration is often used in poetry to communicate a particular feeling. For example the repetition of the slow ‘l’ sounds in the phrase “their languid, lazy lives” helps to give the feeling of unhurried relaxation whereas the repetition of the sharp ‘t’ sounds in the phrase the “tap-tapping of twenty toes” suggests two people dancing energetically. Effect R Clarke 2012 Assonance Assonance is similar to alliteration but refers to the repetition of the same vowel sound in words close to each other. Atmosphere or mood This refers to the general mood or feeling created by the text. It is often created by the description or visual images of the setting. This is the feeling or mood communicated by a text. Tone The never ending exercise. the cool soothing tune Like alliteration, assonance helps to communicate certain feelings. For example the repetition of the long /u/ sound in the phrase “the cool soothing tune” helps to communicate a feeling of calm relaxation. The language used by the poet creates feelings in the responder and so creates the mood. With his head between his paws He lies on the sandy shores So quiet, so quiet, he scarcely snores. “with his clashing teeth and shaggy jaws” Contrasts with “so quiet, so quiet, he scarcely snores.” (from The Sea by James Reeves) Identify the tone by thinking about the feeling you get when reading the text. In the example the tone is calm and serene. The dog seems peaceful so we think the sea is very calm. Contrast Contrast is used to focus on differences. Layout Layout refers to the arrangement of the written elements in a text. Metaphor A metaphor is a comparison that omits the words ‘like’, ‘as’ or ‘than’ that are used in similes. The responder is expected to recognise that the metaphor is not a statement of fact but a comparison. Her eyes were stars. The river was a silver ribbon in the moonlight. Simile A simile compares two different things using ‘like’, ‘as’ or ‘than’. She swims like a fish. Identify the difference (s) that the author is trying to focus on by looking at the objects being contrasted. Identify where the contrast appears in the poem. The layout communicates meaning by drawing the responder’s attention to particular features, especially line length and stanza breaks in poetry (the creation of white space). Metaphors are very effective in making the responder look at familiar objects and experiences in unexpected and refreshing ways. To explain a metaphor, explore what aspects are the same in the first and second items. A simile draws the reader’s attention to a particular quality of the first item. It connects the first term with other terms that have similar images associated with them. R Clarke 2012 Pace Pace is another word for speed. A fast pace can indicate a speaker is excited or nervous. A slow pace suggests that the speaker is choosing his or her words carefully, or is saying something important. Because there are so many words to describe human characteristics and the way behave it brings the object being personified to life and so gives us a more interesting image of it. Personification Personification is the technique of giving human qualities or characteristics to inanimate objects, as when a house or car is made the narrator of a story. Slowly the fog, Hunch-shouldered with a grey face, Arms wide, advances, Quotations The use of the exact words from the text. Use quotation marks: “ “ when quoting. Repetition Repetition refers to the idea that words or sounds are repeated. Rhetorical question Sarcasm A rhetorical question is a question asked for effect but with no answer expected. Sarcasm is a kind of humour that makes fun of something or someone in a cutting, unkind way and so is often intended to be hurtful. “Seventy summers are Quotations (quotes) the reader to illustrate an idea hived in him like old presented in the text. honey.” (from South of My Days by Judith Wright) Buy! Buy! Repetition emphasises the words or sounds and draws our attention to what the composer is trying to say. So it helps us to remember the words or phrases. Do you need new jeans? The effect is to engage the responder by making us think Sale on now! about the answer to the question. I just love that gorgeous The person to whom the remark is addressed may feel dress! (The speaker is upset and belittled. actually thinking the opposite.)