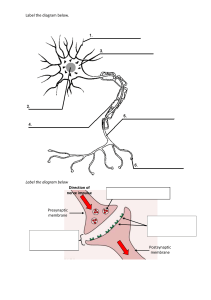
THE DEPARTMENT OF BASIC SCIENCE COPPERBELT UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE PHYSIOLOGY (MBS 210/MBM 220) DEFERRED TEST 1. DATE: FRIDAY SEPTEMBER 25TH TIME:13:00- 13:40 SINGLE BEST OPTION Choose the most appropriate answer The skeletal muscles Contain pacemaker cells Contract when Ca2+ is taken up by the sarcoplasmic reticulum Contraction strength is related to the initial length Contract when actin and myosin filaments shorten The nerve impulse: Maximum conduction is approximately as the speed of light Requires energy Is not delayed at the synapses before transmission Can travel in one direction only Is conducted by the same speed in different axons Myelin sheath Present in the myelinated and unmyelinated nerve fibers. Formed of lipoprotein complex and acts as electric insulator. It is formed of successive wrappings of the membrane of Schwann cells. It is the cause of decreased conduction of nerve impulse. In the motor end plate, all the following is true except: The acetylcholine receptors are similar to those in smooth muscle The nerve ending contains many vesicles and mitochondria Lack of Ca2+ diminishes the release of acetylcholine There is a high concentration of the cholinesterase enzyme There is a delay of neuromuscular transmission of 0.5-0.7 millisecond All of the following are effects of denervation of skeletal muscles except: Muscle fibrillations Hypersensitivity to circulating acetylcholine Atrophy of muscles Muscle fasciculations The absolute refractory period (ARP) of a nerve fibre: Occurs mainly during repolarization Has a duration about 10 msec and is longer than that of cardiac muscle Occurs during the time of increased permeability of the membrane to Na+ Follows the relative refractory period Last throughout the action potential In the action potential, all the following is true except: The firing level is the level at which the spike potential begins The rapid repolarization is due to increased K+ permeability The duration of the isoelectric interval ( latent period) is inversely proportional to the speed of conduction Decreasing the external Na+ concentration reduces the size of the action potential The absolute refractory period is the period from the firing level until repolarization is completed. The Treppe (stair case) phenomenon is characterized by: It is related to the muscle length It does not occur in the cardiac muscle It has no relation to the availability of Ca2+ It is produced by a series of maximal stimuli below the tetanizing frequency Concerning the oxygen debt mechanism: It involves the oxygen consumed during muscular exercise It is used for supply of the basal oxygen consumption Athletes develop a greater O2 debt during a given exercise than sedentary people It is used to remove excess lactic acid and to replenish the ATP and CP stores In skeletal muscles: The initiation of contraction occurs by binding of Ca2+ to tropomyosin Fatigue has no relation to the adequacy of the blood supply The action potential follows the work done Fatigue sets in after fatigue occurs in the nerves The one way conduction at the M.E.P is due to location of the chemical mediator ( acetylcholine) in the nerve terminals In skeletal muscles, the tranverse tubules and adjacent cisterns constitute: A triad A myofibril The sarcolemma The sarcomere A muscle fibre About the types of nerve fibres, all the following is true except: The preganflionic autonomic nerves belong to type B The type A fibres have the largest diameter and most rapid conduction velocity The type A fibres have a spike duration longer than that of type B fibres The type C fibres have the smallest diameter and lowest conduction velocity The postganglionic autonomic nerves belong to type C Decreasing the Na+ concentration around a nerve: Increases the overshoot Decreases the resting potential Increases the chronaxie Decreases the action potential Pale (fast) fiber: contains much blood capillaries. doesn't show fatigue. contains low concentration of myoglobin. depends on aerobic oxidation. The absolute refractory period: Follows the negative afterpotential Is due to hyperpolarization Is prolonged when K+ efflux is delayed Refers to a normal or increased excitability state Is equal in skeletal and cardiac muscles The resting membrane potential in nerve fibres is: A passive process Normally about -10 mV Due to diffusion of intracellular protein to outside the nerve fibres Due to K+ diffusion from outside to inside the nerve fibres None of the options During nerve cell excitation, the peak of K+ efflux occurs: Before the spike Before the peak of Na+ influx Coincide with the peak of Na+ influx After both the spike and peak of Na+ influx In the after-depolarization phase of action potential Unmyelinated nerves differ from myelinated nerves in that they: Are more excitable Conduct impulses by saltatory conduction Have no nodes of Ranvier Are not capable of regeneration Have no neurolemma (Schwann cells) Which of the following occurs in plain muscles but not in skeletal muscles: The sliding mechanism of contraction Cholinergic innervation Action potential Breakdown of ATP Myogenic rhythmicity In skeletal muscles, all the following is true except: Tropomyosin is found in the thin filaments Myosin is found in the thick filaments The lateral sacs of the sarcoplasmic reticulum are rich in Ca2+ Troponin C molecules bind Ca2+ Energy from ATP is not required for muscle relaxation The fast type of muscles is characterized by all of the following except: Innervation by large motor neurons Specialization for posture maintenance High ATPase activity in the mitochondria Absence of myoglobin Rapid fatigue The resting heat production in skeletal muscles: Occurs during contraction Occurs during recovery following exercise Is called the initial heat Is the external manifestation of basal metabolic processes The following characteristics are present in both skeletal and smooth muscles: Both can be affected by hormones and chemicals equally Both contain actin and myosin and show tonic (partial) contractions at rest Both initiate spontaneous rhythmic contractions The myofibrils in both have Z membranes The local response in a single nerve fibre: Can produce an action potential if the membrane potential reaches -55 mV Is associated with increased K+ permeability Is not dependent on the intensity of stimulus Is produced by a cathodal current of the threshold intensity About the action potential, all of the following is true except: It is initiated by reduction of the membrane potential to a critical value It is the result of a transient increase in Na+ permeability followed by a prolonged increase in K+ permeability It is associated with reduction of the electrical resistance of the nerve membrane It has varying amplitudes when produced by stimuli of varying intensities Which of the following statements is wrong? The Na+/K+ pump requires energy from ATP and is essential to keep the normal distribution of ions around the nerve fibre. The electrogenic pump couples Na+ and K+ pump with a ratio of 1:1 The resting membrane potential is the potential difference between the inside and outside of the resting membrane During the nerve action potential, the firing level is reached when the membrane potential reaches -55 mV The nerve cell membrane: Is highly permeable to K+ ions Is moderately permeable to Na+ Maintains a potential difference across it. Has excitability properties that vary in different conditions All options are correct During muscle contraction: The H zones become wider The Z lines move further apart The I bands are elongated The A bands remain constant The tropomyosin molecules remain in place During muscle contraction, all the following is true except: The transverse tubules become filled with intracellular fluid The binding sites at the actin filaments are activated by Ca2+ The walk along theory of the contraction assumes that sliding of actin continues as long as Ca2+is attached to troponin C The detachment of myosin heads from actin needs binding of an ATP molecule A series of stimuli that cause summations of contractions leads to: Rigor Contracture Tonus Tetanus Spasm Continuous conduction: is relatively slow 0.5-2.0 meter / second. occurs by jumping of charges from one node of Ranvier to another. occurs in the neuro-muscular junction. occurs in myelinated nerve fibers. Saltatory conduction: occurs in unmyelinated nerve fibers. occurs by jumping from one neuron to another. may reach up to 120 meter / second. decreases gradually with distance till it disappears. In the nerve, the action potential: Has a magnitude dependent on the stimulus strength Is accompanied by hyperpolarization of the membrane Travels in one direction only Has a velocity that is reduced with demyelination Has a velocity that increases with decreased fibre diameter The chronaxie Is the time needed to excite a nerve by a current strength equal to the rheobase Is the threshold stimulus Can be used as a measure of excitability Is twice the rheobase The all or none law states that a threshold stimulus produces an impulse which: Is not different from that produced by a stronger stimulus Is weaker than that produced by a stronger stimulus Is propagated only partially along the cell membrane Does not need any energy Among the steps of skeletal muscle relaxation: Inward spread of the depolarization wave along the transverse tubules Release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum Binding of Ca2+ to troponin C Pumping of Ca2+ back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum About electrotonus, all the following are true except: It results from stimulation of the nerve by a subthreshold galvanic current Catelectrotonus is accompanied by increased excitability of the nerve A strong catelectrotonus can cause nerve block Catelectrotonus may be followed by the local response Both catelectrotonus and anelectrotonus are passive changes in the nerve membrane In plain muscles (e.g. in the intestine) Catecholamines cause muscle contraction Ca2+ is involved in the initiation of contraction Epinephrine decreases the membrane potential and increases the frequency of spikes The resting potential is high The contraction is dependent on the nerve supply In all or non rule: A minimal stimulus produces a maximal response. The nerve trunk either respond maximally or not respond at all. The response in a single nerve fiber increases with increase intensity of stimulus. Minimal stimulus produces minimal response. Concerning the sodium pump, it: Is independent of K+ influx Is pumping of sodium ions from outside to inside the cell Is independent of the intracellular Na+ concentration Requires high energy phosphate bonds Is explained by facilitated diffusion About nerve impulses, all the following is true except: They can travel in both directions when axon is stimulated at its middle. They travel in one direction only across a synapse and in the M.E.P They have a duration which corresponds approximately to the ARP of the nerve They are conducted at a faster rate in type C nerve fibres than in type B fibres Page 2 of 3 Back Next Never submit passwords through Google Forms. This form was created inside of Kampala International University. Report Abuse Forms THE DEPARTMENT OF BASIC SCIENCE COPPERBELT UNIVERSITY SCHOOL OF MEDICINE PHYSIOLOGY (MBS 210/MBM 220) DEFERRED TEST 1. DATE: FRIDAY SEPTEMBER 25TH TIME:13:00- 13:40 TRUE OR FALSE INDICATE IF THE STATEMENTS BELOW ARE EITHER TRUE OF FALSE Prolonged stimulation of a motor nerve is likely to cause True Slowing of conduction of the action potential along the nerve Diminished acetylcholine secretion in the motor end plate Diminution of transmission at the neuromuscular junction Fatigue of the nerve fibres with impaired conduction False During activation of the nerve cell membrane True False Sodium flows inward Potassium flows inward The membrane potential is reversed Magnesium flows outward During muscle contraction, marked changes occur in the: True H zones I bands A bands Sarcomeres False Troponin C True False Is the binding site for the myosin cross bridges Interacts with tropomyosin Is a Ca2+ binding protein Inhibits the ATPase enzyme The ions that are actively transported out of neurons include: True False Cl- Na+ Ca2+ K+ Page 3 of 3 Back Submit Never submit passwords through Google Forms. This form was created inside of Kampala International University. Report Abuse Forms