Uploaded by
shbudandeniya
Atmospheric Pressure, Energy & Thermal Effects Lecture Notes
advertisement

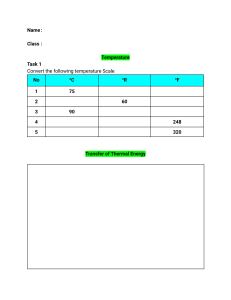
Atmospheric Pressure The pressure due to air particles in the atmosphere is called the atmospheric pressure. The atmospheric pressure acts in all the directions. Pressure becomes less then you move further away from the sea level to measure the atmospheric pressure can use a barrow meter. A barrow meter contains the liquid metal, mercury which is pushed up through the tube due to the atmospheric pressure and the vacuum at the top. Consider the 2 points A and B which are at the same pressure at A is equal to pressure at B where pressure at B equal to 10g. This helps us to find the atmospheric pressure ( pressure at A ) using the height of the liquid column inside the tube therefore the atmospheric pressure through barrow meter is equal height. Question 1. At sea level the atmospheric pressure will support a mercury column at a height of 760mm. Calculate the standard atmospheric pressure at sea level if the density of mercury is 13590 kg/m3 and the value of g is 10N/kg. 1.03*10 power 5 2. Use the above atmospheric pressure and calculate the length of a column of water (1000kg/m3) Which can be supported by the atmosphere at the sea level? Mano Meter A manometer measures a pressure given by a gas can be measured by using a manometer. Question A manometer was connected to a gas container in order to find the pressure given by the gas. Draw the liquid levels in the arms if gas pressure is lesser than the pressure given by the atmosphere. Derive an expression for the pressure given by the gas using the atmospheric pressure and the pressure given by the liquid column. Text book questions in notebook. Gas pressure and volume A fixed mass of a gas pressure, volume and temperature are inter related. That means the change in one of these factors will always change in one of these factors will always produce a change in the other. Voyle's law Here we are dealing with pressure and volume of gases + For a fixed mass of a gas at constant temperature, the pressure is inversely proportional to the volume. +If the pressure of a gas changes from P1 to P2 while the volume of the gas changes from V1 to V2 at constant temperature without changing the mass. Question Explain why the change in pressure occurs when it changes the volume of a gas using the kinetic theory of particles. Text book pg. 75 1,2,3 pg. 77 1,2 Work done and energy When a force acts upon an object it causes a displacement of the object in the direction of the force. This is called the work done. Question A 100N of force is applied to move a 5 kg of mass of a horizontal distance of 5m. a) What is the work done by the force of 100N. 100*5=500Nm b)What is the work done by the gravity? 252 Energy that means now much of work that can be done is the measure of energy. The Si unit of energy is Joules. There are different types of energy we can categories them into 2 groups depending on their nature. They are kinetic energy forms of energy which arise due to the movement of object or particles. Potential energy types of stored energy. Kinetic examples; mechanical energy electrical energy sound energy thermal energy Potential examples; gravitational potential energy elastic energy chemical energy nuclear energy Law of conservation of energy Energy cannot be created/destroyed but it can be changed from one form to another. + Consider a ball thrown upward through air Kinetic energy is maximum at the ground level where the potential energy is 0. The potential energy is maximum at max. height where the kinetic energy is 0 at that position. Calculating Gravitational Potential Energy and Kinetic Energy Kinetic energy Question An object of mass 10kg is released at a height of 6m from the graph. Calculate the following, 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Potential energy of the object before it is released. 120J Potential energy of the object that it has travelled exactly half way. 2*10*3 = 62 Kinetic energy of the object at this position. 60 = v2 Speed of the object at this position. 7.75m/s Kinetic energy of the object where it hits the ground. 103J Speed of the object when it hits the ground. 10.95 Fission and fusion Power Power is the rate of change of energy. We can calculate power using the equation given below, pg. 83 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 10/2/2021 Thermal Effect Temperature Temperature is a physical quantity which measures a hotness or coldness of a substance. Temperature depends on the average kinetic energy of the particles in a substance. If the particles are in motion in any substance it is said that they have kinetic energy, if the temperature is higher the particles can move with a greater kinetic energy. If a hot object is placed in contact with a cold object there is a transfer of thermal energy from the hot object to the cold object. Arrangement of particles in the main three states of matter Transfer of thermal energy There 3 main ways of transferring thermal energy in materials, they are Conduction Convection Radiation Conduction Thermal energy is transferred from one end to another using the vibration of particles this is called the process conduction. The rate of transfer of thermal energy can be depend on the following circumstance, 1. The rate of conduction is greater when the temperature difference is higher at the end. 2. If the length between the ends are shorter the rate of conduction is greater 3. When the cross-sectional area is bigger the rate of conduction is greater. Thermal conductors and insulators Materials which allow thermal energy to pass through them are called conductors. All the metals are considered to be very good conductors. Materials which do not allow thermal energy to pass through them are called insulators. e.g.- wood, plastic. rubber Convection This occurs in liquids and gases due to the change in density when the liquid and gas is heated. Questions How do the metals conduct thermal energy? Close energy vibrate and thermal energy goes from one end to the other end. What is meant by a convection current? Convection current is when particles of a fluid is heated in a beaker and change in a circle. Why do we place air conditioners near the roof and the heaters on the floor of a room? Air conditioners give out cold air which is denser whereas the heaters gives out hot air which is less denser and also air conditioners grab the hot air particles and reduce the temperature. Heaters grab the cold air particles from the room and warm them up. Radiation Transferring thermal energy from a hot object in the form of an electro magnetic waves is called radiation. Thermal radiations mainly occur in the form of infrared waves, thermal radiations can travel through the vacuums. +Rate of radiation depends on the following features, 1. Temperature of the object - higher the temperature of the object higher the rate of radiation. 2. Surface area of the object - 3. Type of the surface - black and rough surfaces are good absorbers and good emitters of thermal energy so they are said to be poor reflectors. Shiny and smooth surfaces are poor absorbers as well as poor emitters of thermal energy. They said to be good reflectors. Question How does thermo flask prevent heat loss by all 3 methods? Specific heat capacity The temperature of a material can be increased by supplying thermal energy . + The energy that is required to increase the temperature of a substance the energy that is required to increase the temperature of a substance of 1kg by 1 degree c (l kelvin). +Temperature is called specific heat capacity. +The capacity of absorbing thermal energy is different from material to material so the energy that must be transferred to an object to increase it's temperature can be calculated by using the following equation, pg. 121 1, 2,3 1. cooling Latent heat When we heat supplying heat to a solid it increases the temperature while experiencing some state changes. + For an example consider supplying heat to minus 15 degree ice cube as shown below. When a substance change its state it absorbs thermal energy without changing the temperature. The energy that is absorbed is called latent heat. Latent heat of fusion The energy absorbed when a substance melts is called latent heat of fusion. Specific latent heat of fusion The amount of energy needed to convert a solid into 1kg of liquid without changing its temperature is called specific latent heat of fusion. Latent heat of vaporization The energy absorbed when a liquid boils is called latent heat of vaporization. Specific latent heat of vaporization. The amount of thermal energy needed to convert 1kg of liquid of liquid into gas without changing its temperature is called specific latent heat of vaporization. The energy transferred when a substance melts or boils can be calculated by using the equation given below. Textbook pg. 123 1, 2, 3 Melting point and Boiling point of the substance The temperature at which the solid converts into a liquid is called the melting point. The temperature at which a liquid converts into a gas is called as boiling point. Questions Energy needed to change .... Heating curve of water Cooling curve for water Evaporation The process at which the liquids convert into gases below the boiling point is called evaporation. Evaporation can occur at any temperature and pressure and it happens due to the particles with high energy escaping from the liquid forming into gaseous form near the surface level. + Evaporation of a liquid depends on the following, 1. 2. 3. 4. temperature - higher the temperature higher the rate of evaporation surface area - greater the surface area higher the rate of evaporation blowing wind - if blowing wind is greater it increases the rate of evaporation humidity - is a measure regarding the amount of vapor in the atmosphere. When the humidity is less the rate of evaporation is higher. Cooling effect of evaporation If particles with high energy escape from the liquid the remaining particles are with low energy. Sot the temperature of the liquid is lesser than before this is known as cooling effect of evaporation. Question Compare and contrast evaporation and boiling. Boiling Evaporation