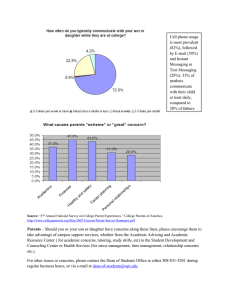
What is a COMPUTER SYSTEM? Computer System - is defined as a digital electronics device that can be programmed to accept some inputs in terms of data, then process this data as per the program instructions and provide the output in the desired format that can be used for some meaningful work. Main Components Computer Hardware - are physical parts/ intangible parts of a computer. Computer Software Liveware - known as programs or applications. is the computer user. Also known as orgware or humanware. The user commands the computer system to execute instructions. Computer Hardware (Mechanical Parts)- hardware refers to the physical, tangible computer equipment and devices, which provide support for major functions such as 1. input, 2. processing (internal storage, computation, and control), 3. output, 4. secondary storage (for data and programs), and 5. communication. Input Devices - are devices used for entering data or instructions to the central processing unit. Are classified according to the method they use to enter data. 1. Keying Devices - are devices used to enter data into the computer using a set of keys Keyboard - Keyboard (similar to a typewriter) is the main input device of a computer Keys: a. Alphanumeric Keys (Typing Keys) - are used to type all alphabets, numbers and special symbols like $, %, @, A etc b. Special Keys (Control Keys) - such as <Shift>, <Ctrl>, <Alt>, <Home>, <Scroll Lock> etc. are used for special functions. c. Function keys - such as <Fl>, <F2>, <F3>, etc. are used to give special commands depending upon the software used d. Cursor Movement (Navigation Keys) - These keys are used for moving around in documents or WebPages and editing text. e. Numeric Keypad - The numeric keypad is handy for entering numbers quickly 2. Pointing Devices - are devices that enter data and instructions into the computer using a pointer that appears on the screen. Mouse - a small device used to point to and select items on your computer screen Buttons: a. Primary Button (Left Button) - the one you will use most often b. Secondary Button (Right Button) c. Scroll wheel - Most mice also include a scroll wheel between the buttons to help you scroll through documents and WebPages more easily. On some mice, the scroll wheel can be pressed to act as a third button. Advanced mice might have additional buttons that can perform other functions. Holding & moving the mouse Mouse Actions a. Single-Clicking - To click an item, point to the item on the screen, and then press and release the primary button (usually the left button). Clicking is most often used to select (mark) an item or open a menu. This is sometimes called single-clicking or left-clicking. b. Double Clicking - To double-click an item, point to the item on the screen, and then click twice quickly. If the two clicks are spaced too far apart, they might be interpreted as two individual clicks rather than as one double-click. Double-clicking is most often used to open items on your desktop. c. Right-clicking - To right-click an item, point to the item on the screen, and then press and release the secondary button (usually the right button). 3. Scanning Devices - are devices that capture an object or a document directly from the source. They are classified according to the technology used to capture data Scanner - Used to capture a source document and convert it into an electronic form. capture an object or a document directly from the source and converts in into an electronic form Types of Scanner 4. Microphone - Used to convert analogue sound waves into a digital form that can be saved and manipulated by the computer. A microphone can also be used to input voice commands but they do not work well in noisy environments. 5. Assistive Technology - Devices that are used by some people with disabilities to access computers. For example, a sip/puff tube can be used by someone with a disability such as a paralysis to control a computer system. Processing Devices Central Processing Unit - is the brain or the heart of a computer. It performs the calculation. Three Units: a. Control Unit (CU) b. Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) c. Main Memory Unit (MMU) The system unit is the core of a computer system. Usually, it's a rectangular box placed on or underneath your desk. Inside this box are many electronic components that process data. The most important of these components is the central processing unit (CPU), or microprocessor, which acts as the "brain" of your computer. Another component is random access memory (RAM), which temporarily stores information that the CPU uses while the computer is on. The information stored in RAM is erased when the computer is turned off. Read-only Memory (ROM) contains the start-up instructions. Almost every other part of your computer connects to the system unit using cables. The cables plug into specific ports (openings), typically on the back of the system unit. Hardware that is not part of the system unit is sometimes called a peripheral device. Peripheral devices can a mouse, keyboard, printer, monitor, or scanner be external such as external Zip drive , The secondary memory system of the computer system and retains data even when the power supply is off (also known as external memory or auxiliary storage) or internal, such as a CD-ROM drive, CD-R drive, or internal modem. Internal peripheral devices are often referred to as integrated peripherals. There are two types according to shape: tower and desktop. Motherboard (Mainboard, system board, planar board or logic board) - is the main printed circuit board found in computers and other expandable systems. It holds many of the crucial electronic components of the system, such as the central processing unit (CPU) and memory, and provides connectors for other peripherals. Central Unit - Is the center of operations for the computer system, it directs the activities of the computer system. System Unit - It is the core of a computer system which is a rectangular box placed on or underneath your desk and has electronic components that process data. Output Devices - allows data to be transmitted by the computer in a human-friendly form, for example, sound being played through a speaker. a. Monitor - The main output device of a computer. It forms images by converting electrical energy into light in the form of tiny dots on the screen called pixels. The sharpness of the image depends upon the number of pixels. b. Printer - Used to print information on paper. Commonly uses either lasers or inkjets to precisely place ink onto the page to recreate text and high-quality images. c. Speaker - Converts digital signals into audible sound waves. d. Projector - A device that is used to project video output from the computer onto a wall or screen. Computer Software (Programs) - instructions that tell a computer what to do. The software comprises the entire set of programs, procedures, and routines associated with the operation of a computer system. Two types of Computer Software a. System Software - controls a computer’s internal functioning, chiefly through an operating system, and also controls such peripherals as monitors, printers, and storage devices Operating System (OS) – a software that supports a computer’s basic functions such as scheduling tasks, executing applications, and controlling peripherals. b. Application Software - by contrast, directs the computer to execute commands given by the user and may be said to include any program that processes data for a user. c. Liveware - includes software engineers hardware engineers, managers, network engineers, data entry operators. Internet - Original name is International network It is a globally connected network system that uses TCP/IP to transmit data via various types of media. The internet is a network of global exchanges – including private, public, business, academic, and government networks – connected by guided, wireless and fiberoptic technologies. - Internet is a global network which when it is intertwined with other networks produces what is known as the internet. - The internet is the connectivity that makes it possible to provide the software tools and materials through the World Wide Web (WWW) as it supports administrative and learning tasks. Therefore, the interlinked documents which can be sourced via the internet are identified as the World Wide Web. - A global network of billions of computers and other electronic devices connected together - Largest example of WAN (Wide Area Network) Who Invented the Internet? Vinton Cerf and Bob Kahn - - - - Computer scientists called the Fathers of the Internet are credited with inventing the Internet communication protocols we use today and the system referred to as the Internet. Created in 1969 by US defense through ARPA (Advanced Research Project Agency) Cerf and Kahn developed a set of guidelines for data transfer using packet switching in 1980, calling those guidelines TCP/IP, or Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol. The TCP part of the protocol is in charge of packing the data before it moves across the network and unpacking it once it has arrived. The IP component acts as the trip coordinator and maps the movement of information from its start point to its endpoint. While Kleinrock’s experiment proved that a single network between two computer systems as possible, Cerf and Kahn’s TCP/IP provided the backbone for an efficient and large web of interconnected networks—thus the name “Internet.” Though other protocols were developed and used before TCP/IP, such as the file transfer protocol (FTP) and network control protocol (NCP), the Internet as we know it today is built on the basis of Cerf and Kahn’s “network of networks.” Everything you do on the Internet involves packets. For example, every Web page that you receive comes as a series of packets, and every e-mail you send leaves as a series of packets. Networks that ship data around in small packets are called packetswitched networks. What is the brief history of the Internet? - - The first workable prototype of the Internet came in the late 1960s with the creation of ARPANET in 1969, or the Advanced Research Projects Agency Network. Originally funded by the U.S. Department of Defense, ARPANET used packet switching to allow multiple computers to communicate on a single network. Arpanet is used as military information for national defense. The first network before the internet existed. The internet began as ARPANET, an academic research network that was funded by the military's Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA, now DARPA). These standards, known as TCP/IP, became the foundation of the modern internet. ARPANET switched to using TCP/IP on January 1, 1983. - The real Internet, the brain behind the information superhighway, is an intricate set of protocols and rules that someone had to develop before we could get to the World Wide Web. - Before the current iteration of the Internet, long-distance networking between computers was first accomplished in a 1969 experiment by two research teams at UCLA and Stanford. - Though the system crashed during the initial attempt to log in to the neighboring computer, the researchers, led by Leonard Kleinrock, succeeded in creating the first two-node network. - The experiment was also the first test of “packet switching,” a method of transferring data between two computer systems. - A packet is a small block of data that is transmitted from one computer to another. - Packet switching separates information into smaller “packets” of data that are then transported across multiple different channels and reassembled at their destination. - The packet-switching method is still the basis of data transfer today. When you send an email to someone, instead of needing to establish a connection with the recipient before you send, the email is broken up into packets and can be read once all of the packets have been reassembled and received. It is to transfer the file faster. Internet Protocol (IP): - internet’s primary component and communications backbone. A sequence of numbers that uniquely identifies the location of each computer or device connected to the internet the internet is comprised of hardware and software layers, the IP communication standard is used to address schemes and identify unique connected devices. Prominent IP versions used for communications include Internet Protocol version 4 (IPv4) and Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6). Router – a device that allows the computers to communicate with the internet Server – a place where websites are stored and works a lot like your computer’s hard drive Bandwidth – the transmission capacity of computer network and how wide the internet highway Bitrate – the number of bits that can be transferred per second. There are eight (8) bits in one byte Latency – The time it takes for a bit to travel from one computer to another Communications: The internet is the most cost-effective communications method in the world, in which the following services are instantly available: ● Email ● Web-enabled audio/video conferencing services ● Online movies and gaming ● Data transfer/file-sharing, often through File Transfer Protocol (FTP) ● Instant messaging ● Internet forums ● Social networking ● Online shopping ● Financial services WORLD WIDE WEB An information system on the internet that allows documents to be connected to other documents by hypertext links, enabling the user to search for information by moving from one document to another. The World Wide Web is the key to the development of the Information Age and is the principal tool that billions of people today use to interact on the internet. The leading information retrieval service of the Internet. Tim Berners-Lee, a British computer scientist who was born in London and his parents were early computer scientists. He invented the www in 1989. After graduating from Oxford University, Berners-Lee became a software engineer at CERN, the large particle physics laboratory near Geneva, Switzerland. Scientists come from all over the world to use its accelerators, but Sir Tim noticed that they were having difficulty sharing information. Tim thought he saw a way to solve this problem – one that he could see could also have much broader applications. Already, millions of computers were being connected together through the fastdeveloping internet and Berners-Lee realized they could share information by exploiting an emerging technology called hypertext. In March 1989, Tim laid out his vision for what would become the web in a document called “Information Management: A Proposal”. Believe it or not, Tim’s initial proposal was not immediately accepted. In fact, his boss at the time, Mike Sendall, noted the words “Vague but exciting” on the cover. The web was never an official CERN project, but Mike managed to give Tim time to work on it in September 1990. He began work using a NeXT computer, one of Steve Jobs’ early products. By October of 1990, Tim had written the three fundamental technologies that remain the foundation of today’s web (and which you may have seen appear on parts of your web browser): HTML - HyperText Markup Language. The markup (formatting) language that most web pages are written in. URI - Uniform Resource Identifier. A kind of “address” that is unique and used to identify to each resource on the web. It is also commonly called a URL. URL – a unique web address for every page on the internet, an address for a single file on the internet HTTP - Hypertext Transfer Protocol. Allows for the retrieval of linked resources from across the web. Tim moved from CERN to the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in 1994 to found the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), an international community devoted to developing open web standards. He remains the Director of W3C to this day. What's the difference between the World Wide Web and the internet? ❑ the internet is bigger and much bigger. It's actually a network of networks, connecting millions of computers around the globe. Any of these computers can communicate with one another, so long as each machine is connected to the Internet. ❑ The World Wide Web, however, is a system we use to tap into that internet. The World Wide Web uses Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) - a language used to transmit data - to access information that lives on different networks. If you're reading this blog post on a browser Chrome, Firefox, Internet Explorer - you're accessing the internet via the World Wide Web. Internet Access INTERNET - is a physical network. It is made up of wires, cables, satellites, and rules for exchanging information between computers connected to the network. It connects millions of computers together globally by connecting to this network which is referred to as online. WEB - is a multimedia interface to the resources available on the Internet. It is a part of the internet and a network of interconnected Web pages of information stored on Web servers using a consistent page layout and formatting language. NETWORK - a group of two or more computer systems linked together connect and share data with another computer COMMON USES OF INTERNET & WEB Common Uses The most common uses of the Internet and Web include: ❑ Communication – the most popular Internet activity ❑ Shopping – one of the fastest-growing Internet activities ❑ Searching – access libraries and local, national, and international news. ❑ Education – e-learning or taking online courses. ❑ Entertainment – music, movies, magazines, and computer games. The following are used to access the Web: PROVIDERS - The most common way to access the Internet is through an Internet service provider (ISP). - ISP is connected to the internet, providing a path for individuals to access the Internet. - Connection technologies include DSL (Digital subscriber line), cable, and wireless modems. BROWSERS - access the Web allowing you to surf or explore. The web also utilizes browsers to access Web documents called Web pages that are linked to each other via hyperlinks. WEB PAGE - electronic document on the web, which can contain text, graphics, animation, audio, and video. It accessed through a web browser URL – a unique web address for every page on the internet. An address for a single file on the internet All URLs have at least two (2) basic parts: Protocols - these are rules for exchanging data between computers. The protocol HTTPS is used for Web traffic and is one (1) of the most widely used internet protocols. - https:// is a secure protocol that transfers web pages on the internet over SSL (Secure Socket Layer) Domain name - It indicates the specific address where the resource is located. - Registered name of the website - A text version of an IP address of a server - A sequence that represents only country domains br, fr, ar, us, uk, pt EXAMPLE In the URL https://www.facebook .com, the protocol is the HTTPS and the domain name is identified as www.facebook.com. The last part of the domain name following the dot (.) is the top-level domain or Web suffix, it typically identifies the type of organization. For example, .com indicates a commercial site. Traditional top-level domains Domain Type .com Commercial Businesses .edu Educational .gov Government .mil U.S. military .net Network .org Organization (Non-profit org that promote their work and acquire donations) Communication COMMON USES OF THE INTERNET 1. COMMUNICATION -The most popular internet activity. - Types of internet communication are email, messaging, social networking, blogs, microblogs, webcasts, podcasts, and wikis Email or electronic mail is the transmission of electronic messages. The ff. are the different types of Internet communication systems: E-mail - it is the transmission of electronic messages. There are two basic types of e-mail. First introduce in 1972 by Ray Tomlinson Two basic types of e-mail 1. Client-based e-mail systems - these require a special program known as two basic types or an E-mail client to be installed on a computer. An e-mail client communicates with the e-mail service provider. Two (2) of the most widely used e-mail clients are Apple’s Mail and Microsoft’s Outlook. - User is e-mail clients installed on your computer 2. Web-based e-mail system - these are browser-based e-mail systems. When a computer’s browser connects to an e-mail service provider, a special program called a webmail client is run on the e-mail provider’s computer and then you begin e-mailing. This is known as webmail. - Use webmail clients located on the e-mail provider’s computer. This is known as webmail. Three free webmail service providers are: ❑ Google’s Gmail ❑ Microsoft’s Hotmail ❑ Yahoo!’s Yahoo! Mail Messaging - there are two (2) messaging systems: text messaging and instant messaging. 1. Test messaging – texting or SMS (short message service) is the process of sending a short electronic message using a wireless network to another person. Text messaging was originally limited to characters, but a variation of SMS known as MMS (multimedia messaging service) can send images, video, and sound. 2. Instant messaging (IM) – this sends messages over the Internet immediately. Instant messaging requires users to register for instant messaging services such as Facebook or Google+. Most instant messaging programs also include video conferencing features, file sharing, and remote assistance. Examples, are Google Talk, WhatsApp, Yahoo Messenger, WeChat. 3. Social Networking – this is one (1) of the fastest-growing and most significant Web 2.0 applications. Social networking sites focus on connecting people and organizations that share a common interest or activity. Some of the best-known social networking sites are Facebook, Google+, Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn. Blogs, Webcasts, and Wikis - these help people communicate across the Web. These communications alternatives offer greater flexibility and security. ● Blogs (web logs) & Microblogs - ● Webcast and Podcast - ● are online journals that support chronological postings like blogs that often contain detailed postings, microblogs publish short, concise sentences. Twitter is the most popular microblogging site. And for Blogs are Blogger and WordPress. Deliver audio, video, and other media content over the internet. Unlike podcast, webcast use streaming technology. For example, the website Youtube.com, as well as other sites, routinely webcast live movie premiers or sporting events. Wiki - Website that is designed to allow visitors to use their browsers to add, edit, delete the site’s content. Often used to support collaborative writing in which there is a community of interested contributors. Wikipedia is one of the most popular wikis created and edited by Web users. Web Utilities - Web utilities are specialized utility programs that make using the Internet and the Web easier and safer. The following are types of Web utilities that can be installed or used in browsers: ❑ Plug-ins - these are programs that are automatically started and operate as part of the browser. These add functionality or specific features to the browser. Many websites require plug-ins to fully experience the content of the Website. The following are some widely used plug-ins: Acrobat Reader from Adobe – for viewing and printing a variety of standards forms and other documents saved in a special format called PDF. Flash Player from Adobe – for viewing videos, animations, and other media. QuickTime from Apple – for playing audio and video files. Windows Media Player from Microsoft - for playing audio files and video files. ❑ Filters - these block access to selected Websites. These programs are used by parents and organizations to block out selected sites and set time limits. Filters are designed to protect children from dangerous and inappropriate Website materials. The best-known filters Filter Site Net Nanny www.netnanny.com Qustodio Parental Control www.qustodio.com AVG Family Safety familysafety.avg.com Norton Online Family Norton.com McAfee Family Protection www.mcafeefamilyprotection.com ❑ File Transfer Utilities - file transfer utility software are used to copy files from specialty configured servers to your computer. This called downloading. These programs are also used to copy files from one (1) computer to another computer on the Internet. This is called uploading. Popular types of a file transfer 1. File transfer protocol (FTP) and secure file transfer protocol (SFTP) – these are used to efficiently copy files to and from one computer across the Internet and are used for uploading changes to a Website hosted by an Internet service provider. ❑ The browser or a file explorer is used to access an FTP site using the address that starts with ftp://. ❑ There are also available FTP applications, such as FileZilla ( ) and WinSCP (www.winscp.net). 2. Web-based file transfer services – these are Web browsers to upload and download files. These eliminate the need for any custom software to be installed. A popular Web-based file transfer service is Dropbox.com and Googledrive.com 3. BitTorrent– this is a method of downloading files using a distributed peerto-peer file sharing system. This distributes file transfer across several computers for more efficient downloads, unlike other transfer technologies whereby a file is copied from one computer on the Internet to another. ❑ Internet Security Suites - file transfer utility software is used to copy files from specialty configured servers to your computer. This is called downloading. These programs are also used to copy files from one (1) computer to another computer on the Internet. This is called uploading. Two best-known Internet security suites are: ❑ McAfee’s Internet Security ❑ Symantec’s Norton Internet Security 2. SEARCH TOOLS SEARCH SERVICES- Maintain huge databases relating to website content. SEARCH ENGINES - Specialized programs to locate information. Also use, enter a keyword or phase and a list of hints or links to references is displayed. Search Tools ❑ ❑ Search Services - operate a website that helps users to locate the information they need. These maintain huge databases relating to information provided on the Web and the Internet. The information stored in these databases includes address, content descriptions or classifications, and keywords appearing on Web pages. - these are search engines’ special programs that continually look to new information and update the search service’s databases. Programs “crawls” around the internet to find websites. Spiders - Search services provide special programs called search engines that the users can use to locate specific information on the Web. ❑ Search Engines - are specialized programs that assist users in locating information on the Web and Internet. To find information, the users go to the search service’s website and use its engine. List of commonly used search engines 1. www.bing.com 2. www.duckduckgo.com 3. www.google .com 4. www.yahoo.com ❑ Specialized Search Engines - focus on the subject-specific website. Specialized sites can potentially save time by narrowing the search. For example, you are searching a paper about history. You could go to a search engine that specializes specifically in history, such as www.historynet.com.