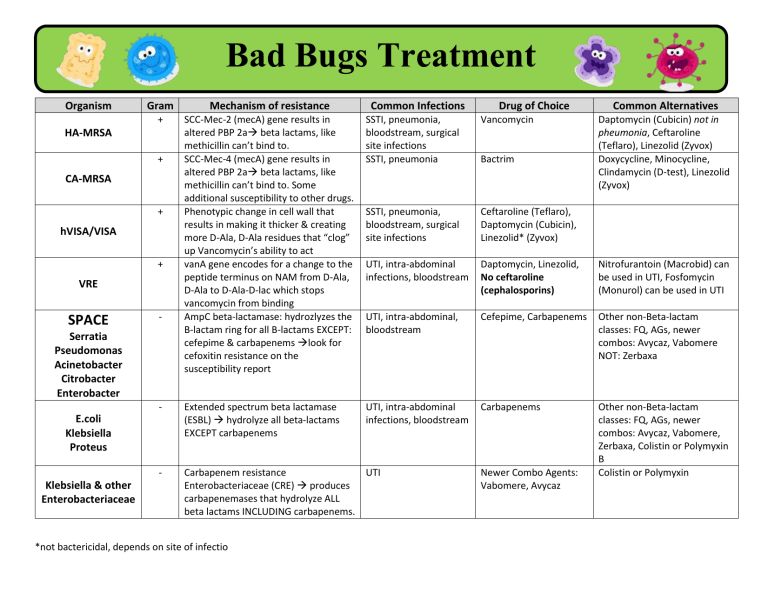
Bad Bugs Treatment Organism Gram Mechanism of resistance + SCC-Mec-2 (mecA) gene results in altered PBP 2a beta lactams, like methicillin can’t bind to. SCC-Mec-4 (mecA) gene results in altered PBP 2a beta lactams, like methicillin can’t bind to. Some additional susceptibility to other drugs. Phenotypic change in cell wall that results in making it thicker & creating more D-Ala, D-Ala residues that “clog” up Vancomycin’s ability to act vanA gene encodes for a change to the peptide terminus on NAM from D-Ala, D-Ala to D-Ala-D-lac which stops vancomycin from binding AmpC beta-lactamase: hydrozlyzes the B-lactam ring for all B-lactams EXCEPT: cefepime & carbapenems look for cefoxitin resistance on the susceptibility report SSTI, pneumonia, bloodstream, surgical site infections SSTI, pneumonia Vancomycin SSTI, pneumonia, bloodstream, surgical site infections Ceftaroline (Teflaro), Daptomycin (Cubicin), Linezolid* (Zyvox) UTI, intra-abdominal infections, bloodstream Daptomycin, Linezolid, No ceftaroline (cephalosporins) Nitrofurantoin (Macrobid) can be used in UTI, Fosfomycin (Monurol) can be used in UTI UTI, intra-abdominal, bloodstream Cefepime, Carbapenems Other non-Beta-lactam classes: FQ, AGs, newer combos: Avycaz, Vabomere NOT: Zerbaxa - Extended spectrum beta lactamase (ESBL) hydrolyze all beta-lactams EXCEPT carbapenems UTI, intra-abdominal infections, bloodstream Carbapenems - Carbapenem resistance UTI Enterobacteriaceae (CRE) produces carbapenemases that hydrolyze ALL beta lactams INCLUDING carbapenems. Other non-Beta-lactam classes: FQ, AGs, newer combos: Avycaz, Vabomere, Zerbaxa, Colistin or Polymyxin B Colistin or Polymyxin HA-MRSA + CA-MRSA + hVISA/VISA + VRE SPACE - Serratia Pseudomonas Acinetobacter Citrobacter Enterobacter E.coli Klebsiella Proteus Klebsiella & other Enterobacteriaceae *not bactericidal, depends on site of infectio Common Infections Drug of Choice Bactrim Newer Combo Agents: Vabomere, Avycaz Common Alternatives Daptomycin (Cubicin) not in pheumonia, Ceftaroline (Teflaro), Linezolid (Zyvox) Doxycycline, Minocycline, Clindamycin (D-test), Linezolid (Zyvox) Parasite Treatment Generic Name Brand Spectrum of Activity Mechanism of Action Pertinent ADEs Other Giardia Tindamax Tinidazole Protozoa including Giardia lamblia Creation of reactive nitrogen radical may be responsible for antiparsitic action. Released nitrates may also damage DNA Better tolerated then Flagyl. Metallic taste. Approved for patients > 3 years Quite toxic- Rarely used anymore Cichonism: tinnitus, HA, nausea abdominal pain, blurred vision. Blindness Alkaloid from the bar of the S. American cinchona tree. Dates back hundreds of years Stereoisomer of quinine Malaria Chlorquine sensitive Malaria Merozoiticide for Plasmodium spp- kills merozoites in the blood Chlorquine sensitive Malaria Merozoiticide for Plasmodium spp 3 Hypothesized mechanisms: 1. DNA intercalation-sticking between DNA base pairs in minor and major grooves 2. Inference with Plasmodium’s ability to digest Hb 3. Inhibition of protozoal DHFR leading to decreased production of DNA synthesis Chlorquine sensitive Malaria More effective & safer than the quinine quinidine Weakly basic- accumulates in the acidic lysosome of Plasmodium & stops the organism from being able to digest hemoglobin for protein & binds hemozoin to reduce RBC lysis Lariam Chlorquine-resistant Malaria Schizonticide. Associates with hemozoin inside the erythrocyte. Daraprim Chlorquine resistant Malaria and Toxoplasmosis Malarone Chlorquine resistant Malaria Schizontocide. Inhibits DHFR to reduce tetrahydrofolate production & creation of DNA bases & methionine. 1000xs more selective for Plasmodium DFHR than mammalian DHFR Atovaquone- Inhibits parasite mitochondrial electron transport resulting in decreased ATP synthesis Proguanil-Metabolized to cycloguanil which is DHFR inhibitor for Plasmodium Quinine Quinidine Aralen & Chloroquine Plaquenil phosphate Hydroxychloroquine (Plaquenil) Mefloquine Pyramethamine Atovaquone/ Proguanil Can produce severe hypoglycemia Hypo or hypertension Cardiotoxicity & arrhythmias QTc Pg 154 Contraindicated in epilepsy Very toxic: Neuropsychiatric symp: (Seizures, psychosis) QTc Hematologic toxicity due to MOA- Anemia, leucopenia, thrombocytopenia Abdominal pain and nausea. Up to 20% DOC in many areas without resistance Designed by US Army Very long half life Give with Folinic acid (leucovorin) Can crush tabs for kids Generic Name Brand Spectrum of Activity Mechanism of Action Pertinent ADEs Other Hookworms, Pinworms Albenza Albendazole Pin-X Pyrantel Pamoate Nematodes (Hookworms, Pinworms, Roundworms), Cestodes Nematode (hookworm, roundworm, pinworm) Inhibits microtubule assembly which results in decreased spindle formation during mitosis and inhibits cell division. Microtubules involved in helminth cytoskeleton disruption. More selective for parasitic betatubulin than human. Abdominal pain and nausea, increased LFTs. Well-tolerated Depolarizing neuromuscular blocker of worms by activation of nicotinic receptors resulting in paralysis (analogous to succinylcholine) Pamoate salt makes it NOT absorbed Very safe. GI symptoms Secondary mechanism of action is inhibition of ATP synthesis Resistance occurs with gene mutation. Lice, Scabies Stromectol, Nematodes Mectizan, (Pinworms and Sklice Roundworms), lice, scabies Ivermectin A-200, RID Note: even though used antihelminth and antiectoparasite, focus in this lecture is use in lice and scabies Ectoparasites (scabies and lice) Pyrethryins Permethrin Nix-1 Elimite, Ectoparasites Immobilizes organisms via muscle paralysis from continued depolarization of glutamate gated Cl channel. This channel is only in invertabrates Well-tolerated. Used in vet med and as agriculture From chrysanthemums. Binds to the parasitic sodium channel and results in consistent depolarization leading to paralysis of the organisms. Combined with PBX to decrease degradation Lab synthesized. Increased stability Not used with PBX Human cyp enzymes metabolize these rapidly making them safe. Can be toxic to animals 1% lice, 5% scabies


