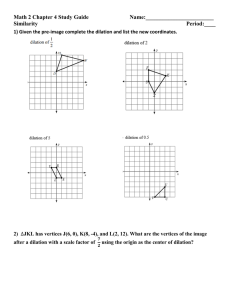
Math 8_Pre Algebra Vocabulary to Support ELL Learning Real numbers Natural numbers Whole number Integer Rational number Irrational number s Terminating and Non-terminating decimal Imperfect squares Perfect squares Can you name the first 15 without looking? Right Triangle hypotenuse Leg Pythagorean theorem Converse of the pythagorean theorem Coordinate grid Ordered pair (4,3) Horizontal Line Vertical Line Quadrants on the grid II I I: 1 II: 2 III: 3 III IV IV: 4 Translation One of four transformations: A slide left or right, up or down, OR Both. Original figure ABC The image is a result of a translation 9 left and 8 down ( x - 9, y - 8) Rotation Reflection clockwise Counter-Clockwise 12 Congruent Orientation When naming the figure can you still name it going in the same direction, or has it’s orientation changed? Dilation What is a dilation in geometry? A dilation (similarity transformation) is a transformation that changes the size of a figure. It requires a center point and a scale factor. The value of the scale factor determines whether the dilation is an enlargement or a reduction. Simply put, dilations always produce similar figures. Enlargement Reduction Scale factor Corresponding side Corresponding Angle similar proportional Examples: Scale factor that is Greater than 1 If the scale factor (number you multiply by) used is greater than 1, the dilation is an ENLARGEMENT. ● ● ● ● x 1.5 x2 x 2.5 x3 Scale factor that is Less than 1 Examples: If the scale factor (number you multiply by) is less than 1, then the dilation is a REDUCTION. ● ● ● ● x ½ or .5 x ¼ or .25 x ⅕ or .2 x ⅓ or .333333… 2 x ½ = 1 (see how 2 multiplied by ½ got smaller?) Parallel Lines Line p and line m are parallel lines: line b below are NOT parallel lines. Line a and a p m b Yes, parallel! NOT parallel!!! Supplementary Angle pairs (sum=180°) Complementary Angle pairs (sum= 90°) Vertical Angles Transversal line This transversal crosses two non-parallel lines. The transversal is the yellow line because it crosses or intersects another line or lines. The white lines are parallel in this case. Function Proportional Mapping a Function Rate of change Similar triangles on a Grid Rise over run per Unit rate Slope y-intercept Vertical change horizontal change Undefined slope m= y₂-y₁ x₂-x₁