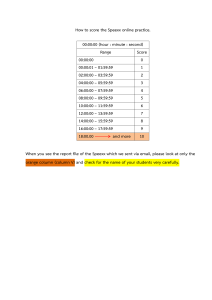
Gas/Liquid Chromatography Presented by: Eman Jawad The Structure How it works Very small quantities of the sample in injected in the machine using a small syringe. Temperature of thw injector is set such that the molecules have enough energy to move with the gas phase One of the three things might happen to a particular molecule in the mixture injected into the column. It may condense on the stationary phase A compound with a boiling point higher than the temperature of the column will obviously tend to condense at the start of the column. It may dissolve in the liquid on the surface of the stationary phase A component that absorbs most strongly to the stationary phase will spend more time in the column (will be retained in the column for the longest time) and will, therefore, have the longest retention time. It will emerge from the gas phase chromatograph last. It may remain in the gas phase A component that absorbs the least strongly to the stationary phase will spend the least time in the column (will be retained in the column for the shortest time), and will, therefore, have the shortest retention time. It will emerge from the chromatography first. Partition The process where a substance divides itself into two immiscible solvents because it is more soluble in one than the other is known as partition. The detector sends a signal to the recorder which results in a peak on the chart paper. Each peak repreasents the compound in the mixture. RETENTION TIME This time is measured from the time at which the sample is injected to the point at which it shows a maximum peak height for that compound. 1.Boiling point The factors that affect 2.The solubility in the liquid phase the retention time are 3.The temperature of the column Determination of the percentage composition of a mixture by GLC The important thing here to note is The area under a peak is proportional to the amount of a compound present. The peaks are triangular in shape so their area is 1/2 x base x height If the peaks are very narrow or have similar base widths, then peak height may be used instead of peak area. FOR EXAMPLE, FOR A MIXTURE OF THREE ESTERS A,B AND C. FIND THE AMOUNT OF A PRESENT IN THE MIXTURE ? Carboxylic acid - Most polar Ketone - Between J and L Alkene - Most non-polar 18/46+18+28= 19.6% 2 1 3 Thank you!