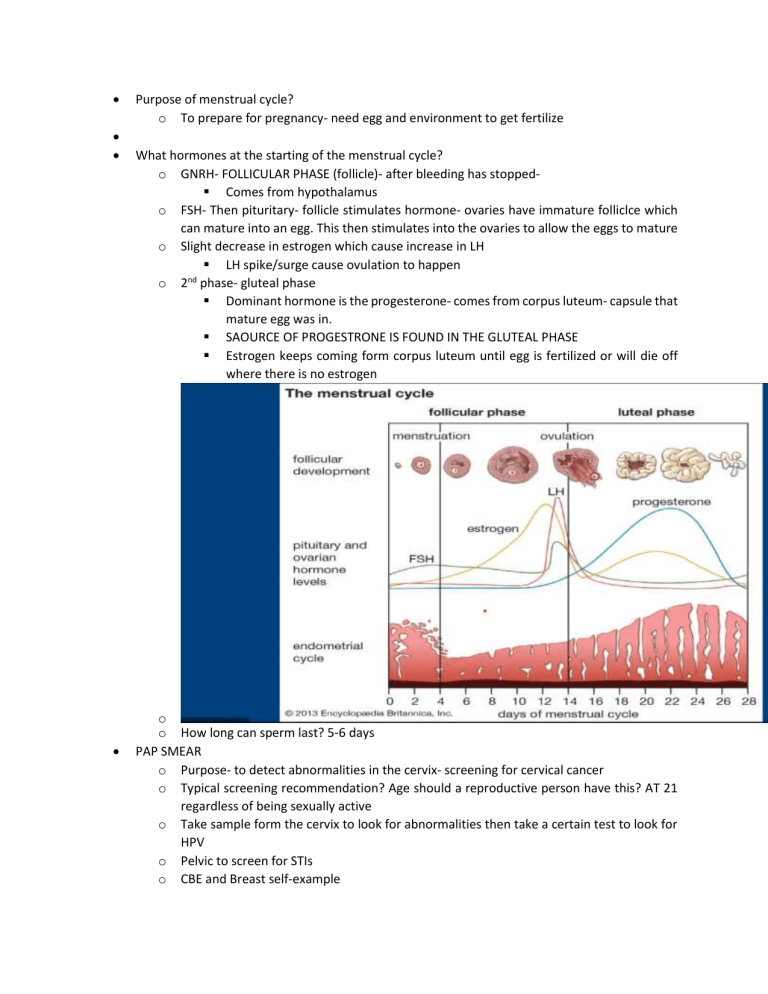
Purpose of menstrual cycle? o To prepare for pregnancy- need egg and environment to get fertilize What hormones at the starting of the menstrual cycle? o GNRH- FOLLICULAR PHASE (follicle)- after bleeding has stopped Comes from hypothalamus o FSH- Then pituritary- follicle stimulates hormone- ovaries have immature folliclce which can mature into an egg. This then stimulates into the ovaries to allow the eggs to mature o Slight decrease in estrogen which cause increase in LH LH spike/surge cause ovulation to happen nd o 2 phase- gluteal phase Dominant hormone is the progesterone- comes from corpus luteum- capsule that mature egg was in. SAOURCE OF PROGESTRONE IS FOUND IN THE GLUTEAL PHASE Estrogen keeps coming form corpus luteum until egg is fertilized or will die off where there is no estrogen o o How long can sperm last? 5-6 days PAP SMEAR o Purpose- to detect abnormalities in the cervix- screening for cervical cancer o Typical screening recommendation? Age should a reproductive person have this? AT 21 regardless of being sexually active o Take sample form the cervix to look for abnormalities then take a certain test to look for HPV o Pelvic to screen for STIs o CBE and Breast self-example Purpose How to conduct- start under the axillary and not take hands off so don’t miss area Mammogram-start getting at 40-45, can be earlier if there’s history Osteoporosis Who is at risk? o Lifestyle changes- weight, increasing vitamin D Anorexia and bulimia o Know the difference between the two o o o Amenorrhea- absence of menses o Primary Someone who hasn’t gotten period by age 15, regardless of sexual characteristics Cause- related to endocrine disorder and treating it o Secondary Someone who has had menses before and all of sudden do not 1st question to ask- is if they’re pregnant? If not/rule out/long term amenorrhea, then look at endocrine issue Gynecological disorders- fibroids, endometriosis, PID, PICO PICO- ovarian syndrome is an ENDOCRINE issue related to Hyperinsulinemia Endometriosis- abnormal growth of then endometrial lining outside of the endometrial wall (intermenstrual bleeding- bleeding in between the cycle)- HAVE EXTRA SPOTTING IN BEWTEEN Fibroid- heavier. Pain bleeding d/t abnormal noncancerous growth in the uterus. Dysmenorrhea- PAINFUL MENSES o Primary Discomfort comes from the release of NO PATHOLOGU Management0- treat whatever discomfort is occurring like aspirin o Secondary o Causes- related to other gynecological problems- may have endometriosis or fibroids to make cramping more painful o Management-0 treat whatever the secondary is Case Study- NOT CANDIDATE FOR IUD o Varies type of IUD o Hormonal Skylar 3yrs Myrana 5yrs Progesterone- cause the thickening of the cervical mucous that makes it harder for sperm to penetrate into uterus to meet the sperm. o Non-hormonal- copper Last for 10 year, How does it prevent pregnancy-copper makes for an environment not conducive for implantation and doesn’t do anything for sperm Copper is the inhibitor for killing sperm o o o o o Multiple partners History of PID, STIs Recommend nexprodone for the arm nuvaring over CAP and IUD can get DEPO Counsel Use it consistently Screening In addition to hormonal IUD, Explain the use of condom consistently Talk about barrier methods- at risk for STI PILL Educate about the pill doesn’t give cancer History of clot- not recommend an estrogen and progesterone type of combo o Case 2- IPV- partner speaking for her, not making eye contact, looking for permission from partner signs of IPV and keeping in mind culture o Ask if they feel safe o Contraception options- any restrictions or contraindications to contraceptive method? On the surface- no issues or contraindicated based on health issue-assess more info IUD may not be the best option o STI screening- NO- NOT SEXUALLY ACTIVE BEFORE. Doesn’t need a PAP ASK about Gardasil (11-13 age) can be given up aging 26 in someone not sexually active o EX- chose to use the PATCH o CASE 3 o o o o o o Place it anywhere on the body and change it 3 weeks at the time AVOID BREAST AREA, 4th week is the patch free week then have withdrawl bleed and start over Herpes simplex virus 2- gift that keeps on giving Get tested if there’s an outbreak- DORMANT NO CURE FOR HERPES- treating the outbreak Most contagious time w/ former partner- 3-4 days before the outbreak happens Feelings of tingling Woman in vaginal area- fatigue, flu-like symptoms would be most contagious time If there’s an active outbreak there’s still contagious and ow virus has ruptured, and pain is at the highest and see lesions that are painful Screening (others too)- for chlamydia, gonorrhea- can be asymptomatic- may have these and not know it What screening have you had beside STI screening? PAP smear, when and what was it? Past 21yrs. Normal PAP is every 2-3years TX- provide comfort NOT A CURE o CASE 4 o What do you suspect? STI-Trichomonas- “frothy” foul smelly discharge and green/yellow o Treatment- flaggel 2g by PO (drugs and dosages be on the exam)- once screened o Contraception options Still use condoms, STI to worry about Doesn’t have contraindication- TRICK is not contra for IUD or anything inserted in the virgin When do you plan to conceive, long acting? Oral? Injectable? o CASE 5 o Know if screen appropriately? PAP SMEAR history- every 2-3 years? Did they screen for HPV pap smear? Mammogram? Could be entering perimenopause- where periods are irregular- can be lighter, heavier, spaced out, vasomotor-hot flashes, night sweats o Normal PAP looking for abnormal cells o Menopause- absence of menses/no bleed or spotting for one year consecutively Increase risk for osteoporosis- estrogen helps with bone reabsorptions o CASE 6 o Talk about syphilis- stages? o How long with partner? Rash or lesions? o Lesions Stage 1- PAINLESS, Tainker?-site of injury of Syphilis infection Why it may be missed, and overtime will heel itself Stage 2- wart, flat against perineum against the anus Rash on soles of feet, palm, hives but not itchy Stage 3 Resolved but infection is festering Stage 4 Neurological issue o Treatment- PENICILLIN (DRUG OF CHOICE) o Screening for CHLAMYDIA AND GONORRHEA are partners in crime Screen for other STIs o Negative for syphilis but positive for Gono and chlamydia Treatment for Gono- IM injection- rosephline (both brand and generic name) Treatment for chlamydia- doxycycline or azithromycin Should be treated together o o Doxycycline 100ml and azithromycin 1g o Herpes-penicillin o Trich- Flagel 2g CASE 6 Options for permanent contraception o Tube ligation or vasectomy o IUD- 10yrs o Natural family planning If using contraception, then using this to know when they’re fertile time is No barrier method Awareness of when fertile time is, using body’s natural cycle to determine when to engage in intercourse Methods- calendar, temp increase= ovulation, changes in cervical mucus CONCEICE- HAVE INTERCOURSE DURING FERTILE TIME o C- swelling in legs, no DVT o A- after each menses o C- how early to insert diaphragm prior to intercourse? 6hrs. Stay in 6hrs after intercourse. Douches increase the chance of an infection, throws the PH balance off o C- pill doesn’t protect STI o D-If on oral then watch out for DVT and smoking increases risk o B- warts related to syphilis-flat against cervix. Wart caused by HPV- clustered gray like warts. D(trich), curdy is yeast infection o A- virus, and others are bacteria o B- cervical cancer o