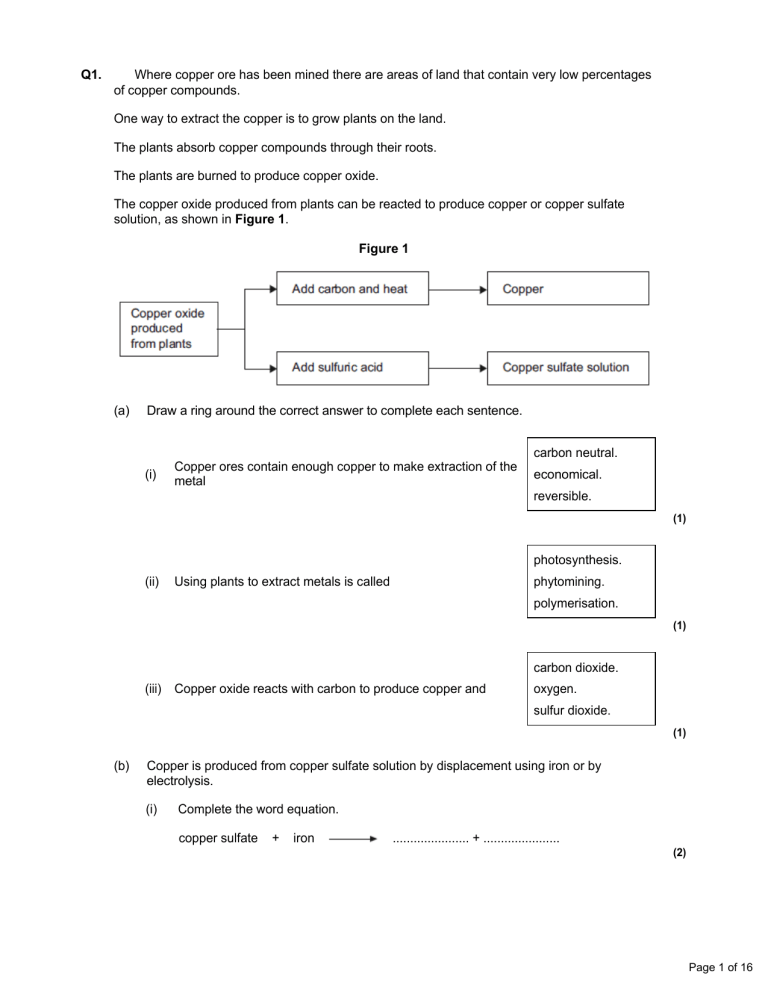
Q1. Where copper ore has been mined there are areas of land that contain very low percentages of copper compounds. One way to extract the copper is to grow plants on the land. The plants absorb copper compounds through their roots. The plants are burned to produce copper oxide. The copper oxide produced from plants can be reacted to produce copper or copper sulfate solution, as shown in Figure 1. Figure 1 (a) Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete each sentence. carbon neutral. (i) Copper ores contain enough copper to make extraction of the metal economical. reversible. (1) photosynthesis. (ii) Using plants to extract metals is called phytomining. polymerisation. (1) carbon dioxide. (iii) Copper oxide reacts with carbon to produce copper and oxygen. sulfur dioxide. (1) (b) Copper is produced from copper sulfate solution by displacement using iron or by electrolysis. (i) Complete the word equation. copper sulfate + iron ...................... + ...................... (2) Page 1 of 16 (ii) Figure 2 shows the electrolysis of copper sulfate solution. Figure 2 Why do copper ions go to the negative electrode? ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (1) (c) Suggest two reasons why copper should not be disposed of in landfill sites. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (2) (Total 8 marks) Q2. The Sun is mainly hydrogen and helium. The diagrams show an atom of hydrogen and an atom of helium. Hydrogen (a) Helium Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete each sentence. molecule. (i) The centre of each atom is called the nucleus. shell. (1) Page 2 of 16 a bond. (ii) The circle (labelled R) around the centre of each atom is called an electrical charge. an energy level (shell). (1) (b) Use the diagrams in part (a) to help you to answer these questions. Draw one line from each question to its correct answer. Question Answer 1 How many protons are there in the hydrogen atom? 2 How many electrons are there in the helium atom? 3 What is the mass number of the helium atom? 4 (3) (c) The Sun is 73% hydrogen and 25% helium. The rest is other elements. What is the percentage of other elements in the Sun? .............................. % (1) (d) One of the other elements in the Sun is neon. Neon is in the same group of the periodic table as helium. Use the Chemistry Data Sheet to help you to answer these questions. (i) How many protons are there in a neon atom? ............................................................................................................... (1) (ii) Which group of the periodic table are helium and neon in? ............................................................................................................... (1) (Total 8 marks) Page 3 of 16 Q3. The iron produced from iron ore in a blast furnace is called cast iron. Cast iron is converted into steel in a furnace. Iron ore contains iron oxide. Coke contains carbon. (a) Quarrying iron ore will have an impact on everything near to the quarry. (i) Describe one positive impact and one negative impact of quarrying iron ore. positive impact ...................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... negative impact .................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence. carbon neutral. Ores contain enough metal to make extraction of the metal economical. reversible. (1) (b) Many chemical reactions take place in a blast furnace. Use the flow diagram to help you to answer this question. Suggest how the blast furnace is heated. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (1) (c) A chemical reaction for the extraction of iron is: Fe2O3 (i) + 3CO → 2Fe + 3CO2 Complete the word equation for this chemical reaction. ................................. + carbon monoxide → iron + ................................. (2) Page 4 of 16 (ii) Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence. decomposition. Iron is extracted from its ore by oxidation. reduction. (1) (d) Cast iron contains about 4% carbon. Cast iron is converted into low-carbon steels. (i) Low-carbon steel is produced by blowing oxygen into molten cast iron. Suggest how oxygen removes most of the carbon. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Draw a ring around the correct answer to complete the sentence. corrode easily. Metals, such as nickel, are added to low-carbon steels to make the steel easy to shape. much harder. (1) (e) Recycling steel uses less energy than producing steel from iron ore. Tick ( ) one advantage and Tick ( Statement ) one disadvantage of recycling steel. Advantage Tick ( ) Disadvantage Tick ( ) Iron is the second most common metal in the Earth’s crust. Less carbon dioxide is produced. More iron ore needs to be mined. There are different types of steel which must be sorted. (2) (Total 12 marks) Page 5 of 16 Q4. Crude oil is a mixture of a very large number of compounds. Figure 1 shows a laboratory experiment to separate crude oil. Figure 1 (a) Complete the sentence. The name for compounds that contain only hydrogen and carbon is ...................................................................... . (1) (b) Use the correct word from the box to complete each sentence. condensation decomposition distillation evaporation reduction (i) The process of separating crude oil is fractional ........................... . (1) (ii) The process taking place at A is ............................................... . (1) (iii) The process taking place at B is .............................................. . (1) (c) One of the compounds in crude oil is hexane. The displayed structure of hexane is shown in Figure 2. Figure 2 Complete the sentences. (i) Each line between the atoms in hexane represents a covalent ............................... . (1) Page 6 of 16 (ii) Complete the chemical formula for hexane. CH 6 ............ (1) (iii) Hexane can be broken down into smaller molecules by a process called ................................ . (1) (d) Small molecules, called alkenes, are used to make polymers. (i) Name the polymer made from butene. ............................................................................................................ . (1) (ii) Incinerators are used to burn waste polymers, such as plastic bags. Tick (✓) one advantage and tick (✓) one disadvantage of burning plastic bags. Advantage Tick (✓ ✓) Disadvantage Tick (✓ ✓) Energy is released. More recycling is needed. Carbon dioxide is produced. (2) (Total 10 marks) Page 7 of 16 Q5. The hip joint sometimes has to be replaced. Early replacement hip joints were made from stainless steel. Stainless steel is an alloy of iron, chromium and nickel. The diagram below represents the particles in stainless steel. Paticle diagram of stainless steal (a) Use the diagram to complete the percentages of metals in this stainless steel. The first one has been done for you. Element Percentage (%) Iron, Fe 72 Chromium, Cr Nickel, Ni (2) (b) Pure iron is a soft, metallic element. (i) Why is iron described as an element? ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (1) Page 8 of 16 (ii) Pure iron would not be suitable for a replacement hip joint. Suggest why. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (1) (iii) The three metals in stainless steel have different sized atoms. Stainless steel is harder than pure iron. Explain why. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (Total 6 marks) Q6. Carbon dioxide is produced when copper carbonate is heated. A student investigated heating copper carbonate. The student used the apparatus to measure how long it took for carbon dioxide to be produced. The student also noted what happened during each minute for three minutes. (a) The student used changes to the limewater to measure how long it took for carbon dioxide to be produced. Describe how. ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ ........................................................................................................................ (2) Page 9 of 16 (b) The student wrote down her observations. Time interval in minutes (i) Observations Between 0 and 1 A slow release of gas bubbles. The limewater did not change. The solid in the test tube was green. Between 1 and 2 A fast release of gas bubbles. The limewater changed at 1 minute 10 seconds. Between 2 and 3 No release of gas bubbles. The solid in the test tube was black. Suggest the reason for the student’s observations between 0 and 1 minute. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (ii) Explain the student’s observations between 1 and 2 minutes. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) (iii) Explain the student’s observations between 2 and 3 minutes. ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... ............................................................................................................... (2) Page 10 of 16 M1. (a) (i) economical 1 (ii) phytomining 1 (iii) carbon dioxide 1 (b) (i) copper / Cu 1 iron sulfate / FeSO4 1 (ii) copper / ions have a positive charge it = copper ions allow copper ions have a different charge accept copper / ions are free to move accept to gain electrons accept copper / ions are attracted to the negative electrode or opposite charges attract 1 (c) any two from: ignore not biodegradable or does not decay • • • • • • copper ores are limited / running out allow copper is running out copper can be recycled copper can be reused copper is expensive landfill sites are filling up copper compounds are toxic allow copper is toxic 2 [8] M2. (a) (i) nucleus 1 (ii) an energy level (shell) 1 (b) 3 Page 11 of 16 (c) 2 / two(%) 1 (d) (i) 10 / ten 1 (ii) (group) 0 accept noble gases ignore (group) 8 1 [8] M3. (a) (i) Positive impact any one from: • provides employment or • improves local economy • improved transport - new roads are built, new rail links • after use the quarry could provide recreation facilities 1 Negative impact any one from: • destruction of animal habitats • fewer plants and trees to absorb carbon dioxide • visual pollution or noise pollution or atmospheric / air pollution allow dust pollution • more traffic • uses non-renewable resources allow pollutants from burning diesel 1 (ii) economical 1 (b) carbon / coke burns (in oxygen / air) accept carbon / coke reacts with oxygen / air 1 (c) (i) iron oxide (reactant) must be words 1 carbon dioxide (product) 1 Page 12 of 16 (ii) reduction 1 (d) (i) oxygen reacts with carbon 1 or oxygen and carbon produce carbon dioxide / carbon monoxide carbon dioxide / carbon monoxide is a gas or the carbon is removed as a gas 1 (ii) much harder 1 (e) Advantage: less carbon dioxide is produced 1 Disadvantage: there are different types of steel which must be sorted 1 [12] M4. (a) hydrocarbons or hydrocarbon 1 (b) (i) distillation 1 (ii) evaporation 1 (iii) condensation 1 (c) (i) bond 1 (ii) (C6H)14 1 (iii) cracking 1 (d) (i) poly(butene) allow with or without brackets 1 Page 13 of 16 (ii) Advantage = energy is released do not accept more than one tick in the advantage column 1 Disadvantage = carbon dioxide is produced do not accept more than one tick in the disadvantage column 1 [10] M5. (a) (Chromium =) 20 in correct order 1 (Nickel =) 8 accept Chromium = 8 and Nickel = 20 for 1 mark 1 (b) (i) (because iron is made up of only) one type of atom 1 (ii) not strong allow too soft or too flexible accept it rusts / corrodes or that it could wear away accept could change shape / bend accept layers / atoms could slide (over each other) 1 (iii) structure is different / distorted / disrupted accept not in layers or not regular 1 so it is difficult for layers / atoms / particles to slip / slide (over each other) accept layers cannot slip / slide 1 [6] M6. (a) time from when the heating is started until 1 the limewater turns cloudy / milky 1 (b) (i) the temperature was not high enough accept the copper carbonate had not started to decompose / react accept it takes time to heat up the copper carbonate 1 the bubbles of gas were air accept no carbon dioxide produced 1 Page 14 of 16 (ii) the copper carbonate was decomposing / reacting accept the temperature was high enough to cause decomposition / a reaction 1 so carbon dioxide was produced allow correct word / symbol equation 1 (iii) copper oxide was produced allow correct word / symbol equation 1 because the copper carbonate had completely decomposed / reacted ignore all of the carbon dioxide had been given off 1 [8] Page 15 of 16 Page 16 of 16