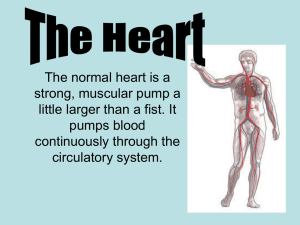
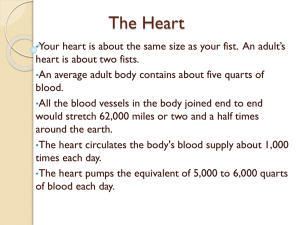
Francisco Leon Key Terms for VNRS 164 Body Structures and Function 05-19-2021 Professor Macready Chapter 16 Anatomy of the Heart 1. Aortic valve ( 314) – semilunar valve located between the left ventricle and aorta. 2. Atrioventricular valves (313) – cuspid valves located between the atria and ventricles; includes the tricuspid and bicuspid valves ( mitral). 3. Atrial conducting fibers (318) – The specialized conducting fibers that transmit the cardiac impulse (action potential) from the SV node in the right atrium to the left atrium. 4. Atrium ( 312) – Upper chamber of the heart that receives blood from veins. 5. Automaticity (319) – The ability of the cardiac cells to generate its own electrical signals independently of stimulation from the CNS. 6. AV node (318)- a part of the cardia conduction system that acts as a relay station for the electrical signal coming from the SA node in the right atrium into the ventricles; the AV node slows the signal. 7. Bicuspid valve (314) – the atrioventricular valve between the left atrium and left ventricle; also called the mitral valve. 8. Cardiology (308) – the study of the heart. 9. Chordae tendineae (313) – tough fibrous bands of connective tissue that 10. Conduction ( 315) loss of heat energy as it is transferred from the warm body to a cooler object, such as a cooling blanket. 11. Coronary arteries (315) – right and left coronary arteries deliver oxygenated blood to the heart muscle. 12. Electrocardiogram (ECG) – graphic recording of the electrical events that occur during the cardiac cycle. 13. Endocardium (310) – inner lining of the heart wall. 1 14. Epicardium (310) – outer layer of the heart; forms part of the pericardium. 15. Great vessels (313) – the large blood vessels that bring blood to and away from the heart; aorta, superior and inferior venae cavae, pulmonary trunk, and pulmonary veins. 16. Heart (308) – The hollow muscular pump that pumps blood to the lungs for oxygenation and then to the rest of the body for the distribution of oxygen, nutrients, and hormones; the heart also picks up and delivers wastes to the organs of excretion. 17. His-Purkinje system (319) – a path of specialized conducting cells within the ventricles of the heart; allows the electrical signals to spread throughout the ventricles rapidly, thereby initiating myocardial contraction (systole). 18. Interatrial septum (312) –the septum between the right and left atria of the heart. 19. Interventricular septum (312) -the septum between the right and left ventricles of the heart. 20. Mitral valve (314) - see bicuspid valve. 21. Myocardium (310) – heart muscle 22. Pacemaker (318) – specialized conduction tissue located in the upper right atrium; its rate of depolarization determines heart rate. 23. Pericardium (310) – sling-like serous membrane that partially encloses the heart; supports the weight of the heart. 24. Precordium (309) – area of the anterior chest that overlies the heart. 25. Purkinje fibers (318) – fast conducting fibers located in the ventricle walls; conduct the electrical impulses from the bundle of His to the ventricular myocardium. 26. Rhythmicity (319) – regularity in tempo, as in the rhythmic beating of the heart. 27. SA node (318) – see pacemaker 28. Semilunar valves (313) – valve shaped like a half moon located between the ventricles and their attached vessels; pulmonic valve and aortic valve. 29. Tricuspid valve (314) – Atrioventricular valve found between the right atrium and right ventricle. 2 30. Ventricle (312) - cavity in an organ, such as the ventricles in the heart and brain. Chapter 17 Function of the Heart 1. Afterload (331) -the force against whch the heart contracts, such as blood pressure. 2. Cardiac cycle (325) - events that occur in the heart during one heartbeat. 3. Cardiac output (228) – amount of blood pumped by the heart in 1 minute (about 500ml/min) ; determined by heart rate and stroke volume. 4. Cardiac reserve (330) – the potential increase in heart output above resting cardiac output. 5. Chronotropic effect (332) – a change in the heart rate (HR). a positive chronotropic event is an increase in heart rate, whereas a negative chronotropic event is a decrease in HR. 6. Diastole (325) – relaxation phase of the cardiac cycle. 7. Dromotropic effect (332) - a change of the speed of the action potential (electrical signals) as it moves from the SA node through the His-Purkinje system. 8. Ejection fraction (331) – the percent of the ventricular volume that is pumped or ejected during ventricular systole (contraction). 9. End-diastolic volume (EDV) p.330 - the volume blood in the ventricle at the end of its resting phase (diastole); also called preload. 10. Heart failure (327) – The inability of the heart to pump blood in sufficient quantities to meet the requirements of the body; characterized by a low ejection fraction and signs of organ congestion, such as pulmonary edema. 11. Inotropic effect (329) - a change in the strength or force of myocardial contraction that does not involve stretching the myocardial fibers. 12. Preload (331) – the degree of ventricular myocardial stretch; end-diastolic volume. 13. Pulmonary edema (PE) p.333 – abnormal collection of fluid in the lungs causing difficulty in the oxygenation of hemglobin. 14. Starling’s law of the heart (329) – Refers to the relationship between myocardial stretch and strength of myocardial contraction. 3 15. Stroke volume (329) – amount of blood that the ventricle pumps in one heartbeat. 16. Sympathomimetic (328) – a drug action that resembles the firing of the sympathetic nervous system. 17. Systole (325) – contraction of the myocardium. 18. Vagolytic (328) - any action or drug that blocks the action of the vagus nerve. 19. Vagomimetic (328) – any action or drug that resembles the action of the vagus nerve. 20. Venous return (328) - the rate of blood flow back to the heart. 4