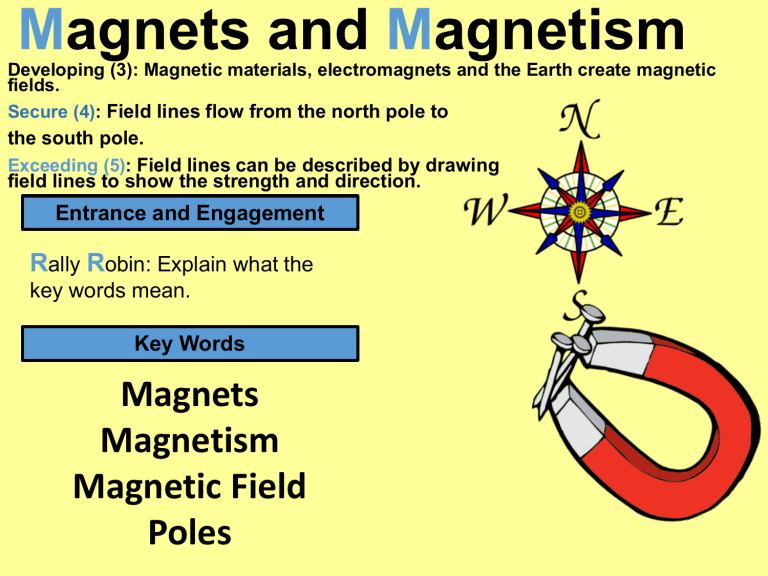
Magnets and Magnetism Developing (3): Magnetic materials, electromagnets and the Earth create magnetic fields. Secure (4): Field lines flow from the north pole to the south pole. Exceeding (5): Field lines can be described by drawing field lines to show the strength and direction. Entrance and Engagement Rally Robin: Explain what the key words mean. Key Words Magnets Magnetism Magnetic Field Poles Engagement Answers Magnet: An object that produces a magnetic field Magnetism: The force produced by magnets Magnetic Field: The area around a magnet where there is a magnetic force Poles: The two opposite ends of a magnet Magnetic Fields • Magnetic fields vary around a magnet. • Magnetic fields force lines are vectors. • Magnetic fields are directed from North to South. • The Earth has a magnetic field, which we can show using a compass. • Note the North pole of Earth is the South pole of a magnet. Practical: Drawing lines of magnetic force • Self Assessment: Check your results. X X X X S X X X N X X X Record your Practical • Method: To complete the practical I … • Results. From the practical I have found that … • WWW • EBI Magnetism Developing (3): Know: How magnets react when placed close together, Same poles and opposite poles. Secure (4): Understand: A compass uses the magnetic field Earth’s magnetic field. Exceeding (5): Apply: How to create and destroy a magnet. Entrance and Engagement Rally Table: Explain what the key words mean. Key Words Compass Magnetise Repel Attract Engagement Answers •Compass: A device with a magnetised needle that points to Earth’s magnetic north pole. •Magnetise: process of making an object magnetic. •Repel: Instance where a force pushes an object away from itself. •Attract: Instance where a force pulls an object towards itself. Using Magnets and Magnetism How could you turn a piece of iron into a magnet? Magnetising metals. Not magnetic, magnetic domains (magnetic fields inside metal)are not uniform To magnetise, rub a magnet along the metal in the same direction. Magnetic, magnetic domains are now uniform S N Demagnetise a magnet. If hit with a hammer the domains will become non uniform. No longer magnetised. Make a compass Make a compass and use it to find Magnetic North pole of earth. Safety: Safety Glasses, be careful with pins, sharp items danger of injury. Step 1: Magnetise the needle Step 2: Float the cork on water. Step 3: Carefully, place the needle on the cork and note the direction the needle turns to. Is it North? Record your Practical • Method: To complete the practical I … • Results. From the practical I have found that … • WWW • EBI Assessment of Learning Peer / Self Marking Answers: 2. The needle will point in the same direction wherever you point it in a room because; we are very far from the north pole, so we cannot see any changes in direction, it is too small. End Of Lesson Activities • Hand back borrowed: • Pens / Rulers / Pencils • Green pens back into pen block • Books open on today’s work • Stand behind your chairs to be dismissed Electromagnets Developing (3): Know: How an electromagnet works and how to create an electromagnet. Secure (4): Understand: An electromagnet uses the principle that a current through a wire causes a magnetic field. Exceeding (5): Apply: Create and increase the strength of an electromagnet. Entrance and Engagement Rally Table: Explain what the key words mean. Key Words Current Coil Engagement Answers •Current: An electric current is a flow of electric charge in electric circuits. • Coil: insulated wire wrapped around a core. Making an Electromagnet You will now make an electromagnet. you must: Know: how to make an electromagnet. Know: how to change the strength of an electromagnet. Make a compass Make a compass and use it to find Magnetic North pole of earth. Safety: Safety glasses, be careful with wire sharp items danger of injury. Equipment: Iron nail, copper wire, battery, connectors, paper clips. Step 1: wrap the wire around the nail to make a coil. Step 2: Connect the coil to a battery. Step 3: Check how many paper clips you can pick up. Step 4: Investigate how you could increase the strength of the magnet. Will number of coils change field strength? Will increasing current change field strength? Using Magnets Developing (3): Know: Where are magnets used? Secure (4): Understand: How eelectromagnets and permanent magnets are used in various everyday devices. Exceeding (5): Apply: Describe how magnetic devices function. Entrance and Engagement Watch the video. Discuss with your partner, the use of magnets for this purpose. Magnetic Carousel Positioned around the laboratory are a selection of devices that use magnetism to function. For each, discuss with your team, as a group describe how they work and their purpose. Record your solutions on your feedback sheet. A: Electric bell B: Micro Switch C: Speaker D: Microphone E: Screwdriver F: Circuit Breaker Magnetic Carousel • Electric Bell The circuit is open (not connected). When the manual switch is pressed the circuit is complete and starts the electromagnet. The magnetic field makes the arm move to strike the bell. As it moves it breaks the circuit. A spring pulls the arm back, this re-connects the electromagnet, making the arm strike the bell again. This repeats making the bell ring until the manual switch is open. • Micro Switch. When the manual switch it pressed (closed), an electromagnet is activated connecting the circuit. When the switch is open, the electromagnet disconnects the circuit. Magnetic Carousel • Speaker When a current is present in the circuit, an electromagnet causes the centre cone of the speaker to vibrate. This produces sound that can be heard. • Microphone. Sound causes the cone /diaphragm to vibrate. This causes a magnet to move in a coil, producing an electric current. This is used by devices to record or amplify sound. Magnetic Carousel • Screwdriver. The screwdriver has a permanent magnetic tip. When it is in contact with a screw it sticks to the screw, if the screw falls it will stick to the magnetic tip to stop it falling into inaccessible places. • Circuit Breaker (RCD Switch). Electrical current passes through the circuit breaker, which has an electromagnet connected. If the current is below a safe set level, the magnetic field is too small to make the core of the electromagnet move. If the current passes above the set (safe) level, the electromagnetic core will move, breaking the circuit. Assessment of Learning Electromagnets Describe: How this electromagnet works. • Describe how the electromagnet works. • Pass your book to your partner. • Partner to Add, edit or correct the other persons work. Book Review Title Topics covered so far: D S 1. Magnetism 2. Magnetic fields 3. Electromagnets 4. Circuit breakers 5. Electric bell 6. Device selection in everyday life. Keyword accumulator: Look for any spelling errors and write them correctly below: E Science Intervention Tasks: 1. Identify the three elements that can be magnetised. 2. Identify the direction of force for a magnet. 3. Draw a diagram of Earth and associated magnetic fields. 4. Draw the magnetic field for an bar magnet. 5. Draw the magnetic field for an electromagnet. 6. Identify three things that affect the strength of an electromagnet. 7. Draw a circuit for an electromagnet circuit breaker. 8. Describe three considerations when deciding to use a permanent magnet or electromagnet.