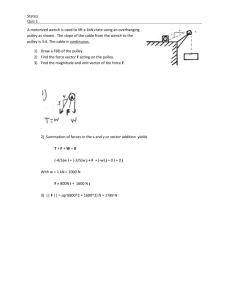
SIMPLE MACHINES __________ ____________ are mechanical devices, with few or no moving parts, that make it easier to carry out _______! They are the elementary __________ _________ of which more complicated (compound) machines are composed. There are ________categories of Simple Machines. This is an example of a ______________. A ________ is a simple machine used to push two objects apart. Two inclined planes placed back to back make a __________. Examples of ___________ include knives, chisels and axes. This is an example of a ____________. A ________ is an ___________ ___________ wrapped around a pole. ________can be used to help lift things, or hold things together. Examples of __________ include swivel chairs, jar lids and screws. This is an example of a _________ & _________. A _________ & _______ uses a wheel, with a rod attached in the middle as an axle, to help lift or move loads. Examples of a ________& _______ include a door knob, a screwdriver, an egg beater and a water wheel. More examples of a wheel and axle: 1. Force applied on the axle: IMA <1: In this type, the force is applied to the axle and transmitted to the wheel, rotating rapidly This is an example of a ________________. A __________ is a type of simple machine consisting of a rope passing over a grooved wheel. The rope fits into the groove and one end of the rope attaches to the __________. The _________ is exerted as a pull on the other end of the rope. _____________ can be used to change the magnitude of a force, or simply to change its direction. There are ________ types of Pulley systems. *A __________ pulley system is when the pulley is usually attached to a ceiling or framework and is ____________ (does not move). This type of pulley changes the ____________ of the force, but not the ___________. Examples include flag poles and window blinds. *The 2nd type of pulley is the ____________ pulley. The pulley is allowed to _______ with the load. The advantage of a movable pulley is that ______ work is required to move the load. However, the movable pulley has its disadvantages as well. In a movable pulley system, the pulley itself must be pushed or pulled up and down, adding its own weight to the existing load. (A zip-line is an example of a movable pulley). *The 3rd type of pulley is a ______________ pulley. A ______________ pulley uses a combination of fixed and movable pulleys. The ________ needed to move a load rigged to a compound pulley system can be less than half of the _______. Examples of ____________ pulleys can be found on large sailboats and at construction sites. This is an example of an _____________ __________. An ____________ __________ makes it easier to move an object to a higher elevation. Ramps and slides are also examples of __________ __________. This is an example of a _____________. A ___________ consists of a beam, or a rigid rod, which can pivot on a fixed hinge, or ____________. Examples of levers include a seesaw, pliers, crowbars, and tweezers. There are _________classes of Levers. Class 1---the ___________ lies between the __________ and the ________. Examples of ___________ are found in a teeter-totter, boat oars, a catapult, scissors and a pair of pliers. Class 2-----the _______ is located between the _______ and the ________. Examples of Class 2 Levers are found in a wheelbarrow, a crowbar and a nutcracker. Class 3----the _______ lies between the _________ and the _______. Examples of Class 3 Levers are found in a stapler, a broom and a hockey stick. Simple machines work in 1 of 3 ways: 1) By ____________ the amount of input force needed. (and increasing the distance over which the force acts). 2) By ____________ the amount of the input force needed. (and decreasing the distance over which the force acts). 3) By changing the ______________ of the input force. Work is a measure of the amount of Energy that is transferred when an object is moved over a distance by an external Force. A simple machine can, however, multiply the force put into a machine (the _________into a larger output force (the______). The ratio of these two forces is known as the ________ ___________. The Actual Mechanical Advantage - takes into account ________loss due to _________, deflection and wear. However, it is usually more difficult to measure - unless, for example, you use a Spring Scale to measure the Force Effort Although less accurate, the Ideal Mechanical Advantage is usually easier to determine, because it uses the ratio of ___________.