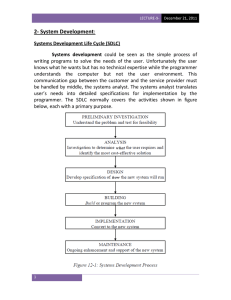
DATE: 24 January 2022 TOPIC: System development life cycle Systems Analysis is investigating the current system to determine is problems, requirements and the best way of solving the problems. System: A groups of elements working together to achieve a common goal. Systems are of two types: Physical system: refers to tangible systems like schools, firm, shop, etc Conceptual systems: these exist in mind or paper and cannot be touched. They just represent a physical system. This chapter is concerned with the development and maintenance of system like stock control, patient monitoring, banking and payroll which are part of physical systems. The systems analyst This is a person who identifies problems of the existing system and recommends the best solution to such a problem. The duties of a systems analyst are: Identifies the problems of the current system. Liaises with system users and determine their requirements. Finds out facts important to the design of the new system. Determines the human and computer procedures that will make up the system. Participates in the process of system implementation. By performing such duties, the systems analyst acts as: i. A consultant: can be called or hired to identify problems in a system ii. A supporting expert: draws together professional expertise concerning computer hardware and software and their uses in business. iii. An agent of change: bring new ideas into the organisation Qualities of a systems analyst Must have good oral and written communication skills for all managerial levels of an organisation. Must be able to work as a team. Must be well educated, with at least a degree. Must be well experienced in computers and at top managerial levels. Must have good managerial skills. Must be a problem solver and see problems as challenges. Must be self-motivated. Must be well disciplined. Must be able to work under pressure and meet deadlines. Initiation (Origination) Of Systems Analysis Changes to a system can be triggered by many factors, some of which are: i. System users: they may be dissatisfied with the current system since they are the ones who operate it. They will the sent requests to have a new system or some modification to the existing one. ii. Top management: they may issue directives in order to meet new organisational objectives. It can also be due to change in management (new manager), new requirements, etc. iii. The need for improved operating efficiency: Errors in the existing systems may be intolerable, especially to customers. iv. Changes in technology: new hardware and software may force organisations to change their ways of operation. v. Change of government policies: new government laws and policies can force organisations to change their systems vi. The user can change his mind Systems Development Life Cycle (SDLC) This refers to the stages through which a system develops from ‘birth’ to ‘death’, i.e. from the moment the system is incepted until it is modified or replaced with a new one. Can also be referred to as the Waterfall Model The stages, in their order, include: Problem identification, Fact Finding feasibility study, analysis, design, Development and testing Documentation and user training implementation, Evaluation/review/maintenance. Below is a diagram that indicates the SDLC stages Problem Identification Evaluation Fact Finding Implementation Feasibility Study Documentation & User Training Analysis Development & Testing Design