Osteoarthritis: Active Learning Template for Nursing Students
advertisement
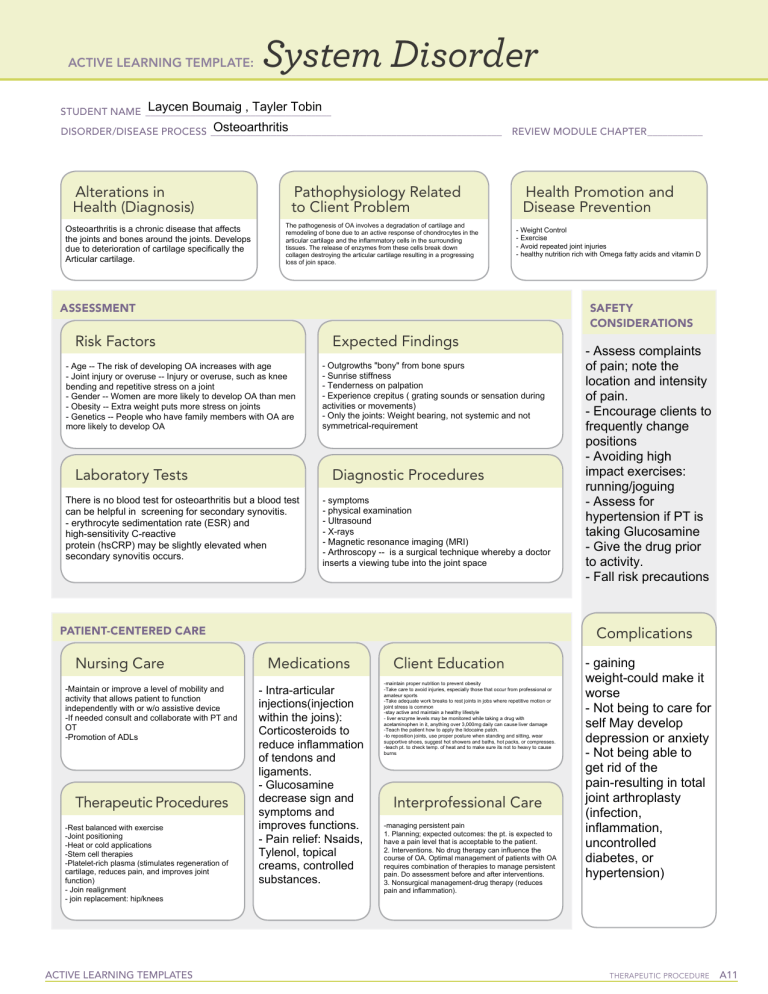
ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATE: System Disorder Laycen Boumaig , Tayler Tobin STUDENT NAME______________________________________ Osteoarthritis DISORDER/DISEASE PROCESS___________________________________________________________ Alterations in Health (Diagnosis) Osteoarthritis is a chronic disease that affects the joints and bones around the joints. Develops due to deterioration of cartilage specifically the Articular cartilage. Pathophysiology Related to Client Problem The pathogenesis of OA involves a degradation of cartilage and remodeling of bone due to an active response of chondrocytes in the articular cartilage and the inflammatory cells in the surrounding tissues. The release of enzymes from these cells break down collagen destroying the articular cartilage resulting in a progressing loss of join space. REVIEW MODULE CHAPTER____________ Health Promotion and Disease Prevention - Weight Control - Exercise - Avoid repeated joint injuries - healthy nutrition rich with Omega fatty acids and vitamin D ASSESSMENT SAFETY CONSIDERATIONS Risk Factors Expected Findings - Age -- The risk of developing OA increases with age - Joint injury or overuse -- Injury or overuse, such as knee bending and repetitive stress on a joint - Gender -- Women are more likely to develop OA than men - Obesity -- Extra weight puts more stress on joints - Genetics -- People who have family members with OA are more likely to develop OA Laboratory Tests - Outgrowths "bony" from bone spurs - Sunrise stiffness - Tenderness on palpation - Experience crepitus ( grating sounds or sensation during activities or movements) - Only the joints: Weight bearing, not systemic and not symmetrical-requirement Diagnostic Procedures There is no blood test for osteoarthritis but a blood test can be helpful in screening for secondary synovitis. - erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) may be slightly elevated when secondary synovitis occurs. - symptoms - physical examination - Ultrasound - X-rays - Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - Arthroscopy -- is a surgical technique whereby a doctor inserts a viewing tube into the joint space PATIENT-CENTERED CARE Nursing Care -Maintain or improve a level of mobility and activity that allows patient to function independently with or w/o assistive device -If needed consult and collaborate with PT and OT -Promotion of ADLs Therapeutic Procedures -Rest balanced with exercise -Joint positioning -Heat or cold applications -Stem cell therapies -Platelet-rich plasma (stimulates regeneration of cartilage, reduces pain, and improves joint function) - Join realignment - join replacement: hip/knees ACTIVE LEARNING TEMPLATES - Assess complaints of pain; note the location and intensity of pain. - Encourage clients to frequently change positions - Avoiding high impact exercises: running/joguing - Assess for hypertension if PT is taking Glucosamine - Give the drug prior to activity. - Fall risk precautions Complications Medications - Intra-articular injections(injection within the joins): Corticosteroids to reduce inflammation of tendons and ligaments. - Glucosamine decrease sign and symptoms and improves functions. - Pain relief: Nsaids, Tylenol, topical creams, controlled substances. Client Education -maintain proper nutrition to prevent obesity -Take care to avoid injuries, especially those that occur from professional or amateur sports -Take adequate work breaks to rest joints in jobs where repetitive motion or joint stress is common -stay active and maintain a healthy lifestyle - liver enzyme levels may be monitored while taking a drug with acetaminophen in it, anything over 3,000mg daily can cause liver damage -Teach the patient how to apply the lidocaine patch. -to reposition joints, use proper posture when standing and sitting, wear supportive shoes, suggest hot showers and baths, hot packs, or compresses. -teach pt. to check temp. of heat and to make sure its not to heavy to cause burns Interprofessional Care -managing persistent pain 1. Planning; expected outcomes: the pt. is expected to have a pain level that is acceptable to the patient. 2. Interventions. No drug therapy can influence the course of OA. Optimal management of patients with OA requires combination of therapies to manage persistent pain. Do assessment before and after interventions. 3. Nonsurgical management-drug therapy (reduces pain and inflammation). - gaining weight-could make it worse - Not being to care for self May develop depression or anxiety - Not being able to get rid of the pain-resulting in total joint arthroplasty (infection, inflammation, uncontrolled diabetes, or hypertension) Therapeutic Procedure A11