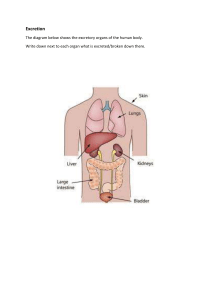
1. Gross Anatomy vs. Microscopic Anatomy a. Gross Anatomy: i. Involves examining fairly large structures. ii. Can be conducted without using a microscope and can involve the study of anatomy by dissecting a cadaver. b. Microscopic Anatomy: i. Deals with structures we cannot see without magnification. ii. The boundaries of microscopic anatomy are set by the limits of the equipment we use. 2. Levels of Organization a. The chemical level i. Atoms are the smallest stable units of matter. They can combine to form molecules with complex shapes. b. The cellular level i. Cells are the smallest living units in the body. Complex molecules can form various types of larger structures called organelles. c. The tissue level i. A tissue is a group of cells working together to perform one or more specific functions. d. The organ level i. Organs are made up of two or more tissues working together to perform specific functions. e. The organism level i. An individual life form is an organism. ii. Chemical-Cellular-Tissue-Organ-Organ System-Organism 3. Functions of each organ system a. Integumentary System i. Major Organs: 1. Hair 2. Skin 3. Nails 4. Sweat Glands ii. Functions: 1. Protects against environmental hazards. 2. Helps regulate body temperature. 3. Provides sensory information. b. Skeletal System i. Major Organs: 1. Bones 2. Cartilage 3. Associated Ligaments 4. Bone Marrow ii. Functions: 1. Provides support and protection for other tissues. 2. Stores calcium and other minerals. 3. Forms blood cells. c. Muscular System i. Major Organs: 1. Skeletal muscle and associated tendons ii. Functions: 1. Provides movement. 2. Provides protection and support for other tissues. 3. Generates heat that maintains body temperature. d. Nervous System i. Major Organs: 1. Brain 2. Spinal Cord 3. Peripheral Nerves 4. Sensory Organs ii. Functions: 1. Directs immediate responses to stimuli. 2. Coordinates or moderates activities of other organ systems. 3. Provides and interprets sensory information about external conditions. e. Endocrine System i. Major Organs: 1. Pituitary gland 2. Thyroid gland 3. Pancreas 4. Adrenal glands 5. Gonads 6. Endocrine tissues in other systems ii. Functions: 1. Directs long-term changes in the activities of other organ systems. 2. Adjusts metabolic activity and energy use by the body. 3. Controls many structural and functional changes during development. f. Cardiovascular System i. Major Organs: 1. Heart 2. Blood 3. Blood Vessels ii. Functions: 1. Distributes blood cells, water, and dissolved materials including nutrients, waste products, oxygen, and carbon dioxide. 2. Distributes heat and assists in control of body temperature. g. Lymphatic System i. Major Organs: 1. Spleen 2. Thymus 3. Lymphatic Vessels 4. Tonsils h. i. j. k. ii. Functions: 1. Defends against infection and disease. 2. Returns tissue fluids to the bloodstream. Respiratory System i. Major Organs: 1. Nasal Cavities 2. Sinuses 3. Larynx 4. Bronchi 5. Lungs 6. Alveoli ii. Functions: 1. Delivers air to alveoli. 2. Provides oxygen to bloodstream. 3. Removes carbon dioxide from bloodstream. 4. Produces sounds for communication. Digestive System i. Major Organs: 1. Teeth 2. Tongue 3. Pharynx 4. Esophagus 5. Stomach 6. Small Intestine 7. Large Intestine 8. Liver 9. Gallbladder 10. Pancreas ii. Functions: 1. Processes and digests food. 2. Absorbs and conserves water. 3. Absorbs nutrients. 4. Stores energy reserves. Urinary System i. Major Organs: 1. Kidneys 2. Ureters 3. Urinary Bladder 4. Urethra ii. Functions: 1. Excretes waster products from the blood. 2. Controls water balance by regulating volume of urine produced. 3. Store urine prior to voluntary elimination. 4. Regulates blood in concentrations and pH. Male Reproductive System i. Major Organs: 1. Testes 2. Epididymis 3. Ductus Deferentia 4. Prostate Gland 5. Penis 6. Scrotum ii. Functions: 1. Produces male sex cells (sperm), seminal fluids, and hormones. 2. Sexual intercourse l. Female Reproductive System i. Major Organs: 1. Ovaries 2. Uterine tubes 3. Uterus 4. Vagina 5. Labia 6. Clitoris 7. Mammary glands ii. Functions: 1. Produces female sex cells (oocytes) and hormones. 2. Supports developing embryo from conception to delivery. 3. Provides milk to nourish newborn infant. 4. Sexual intercourse 4. Homeostasis a. Refers to the existence of a stable internal environment. b. Homeostatic Regulation: The adjustment of physiological systems to preserve homeostasis. i. Involves two general mechanisms: 1. Autoregulation: A process that occurs when a cell, tissue, organ, or organ system adjusts in response to some environmental change. a. Example: When the oxygen level decreases in a tissue, the cells release chemical that widen, or dilate, blood vessels. This dilation increases the blood flow and provides more oxygen to the region. 2. Extrinsic Regulation: A process that results from the activities of the nervous system or endocrine system. a. Example: When you exercise, your nervous system issues commands that increase your heart rate so that blood will circulate faster. Your nervous system also causes blood flow to be reduced to less active organs, such as the digestive tract. The oxygen in circulating blood is then available to active muscles, which need it most. c. Negative Feedback i. An effector activated by the control center opposes, or negates, the original stimulus. Tends to minimize change. d. Positive Feedback 5. 6. 7. 8. i. Tends to enhance or increase the change that triggered it. e. Negative feedback examples: i. Body temperature ii. Blood pressure f. Positive feedback examples: i. Blood clotting after massive blood loss ii. Childbirth Anatomical Position, Prone, and Supine a. Anatomical Position: When the body is in this position, the hands are at the sides with the palms facing forward, and feet are together. b. Supine: When a person is lying down, face up. c. Prone: When a person is lying down, face down. Directional Terms a. Superior: Above; at a higher level (toward the head). i. Example: The head is superior to the chest. b. Proximal: Toward the point of attachment of a limb to the trunk. i. Example: The shoulder is proximal to the wrist. c. Lateral: Away from the midline. d. Medial: Toward the midline. e. Distal: Away from the point of attachment of a limb to the trunk. i. Example: The fingers are distal to the wrist. f. Superficial: At, near, or relatively close to the body surface. i. Example: The skin is superficial to underlying structures. g. Deep: Toward the interior of the body; farther from the surface. i. Example: The bone of the thigh is deep to the surrounding skeletal muscles. h. Inferior: Below; at a lower level; toward the feet. i. Example: The knee is inferior to the hip. i. Cranial or Cephalic: Toward the head. j. Caudal: Toward the tail. Planes of the body a. Frontal plane (Coronal): A vertical plane that divides the body or organ into anterior and posterior portions. b. Sagittal plane: A vertical plane that divides the body into left and right portions. i. Midsagittal plane: Lies in the middle. ii. Parasagittal plane: Offset from the middle. c. Transverse plane: Divides the body into superior and inferior portions. Organs in the thoracic cavity vs. organs of abdominal and pelvic cavities a. Thoracic cavity contains: i. Lungs 1. Divided into right and left pleural cavities ii. Heart iii. Associated organs of the respiratory, cardiovascular, and lymphatic system. iv. Inferior portions of the esophagus. v. Thymus vi. Lungs are separated by the mediastinum 1. Mediastinum also contains the pericardial cavity, which is a small chamber that surrounds the heart. b. Abdominal cavity contains (Abdominal Pelvic Cavity): i. Liver ii. Stomach iii. Spleen iv. Small intestine v. Most of the large intestine vi. Kidneys vii. Pancreas 1. Kidneys and pancreas are retroperitoneal, which means they sit behind the peritoneal cavity. c. Pelvic cavity contains (Abdominal Pelvic Cavity): i. Urinary bladder ii. Various reproductive organs 1. Male Reproductive Organs a. Prostate gland b. Seminal glands (seminal vesicles) 2. Female Reproductive Organs a. Ovaries b. Uterine tubes c. Uterus iii. Distal portion of the large intestine. 9. Ventral Body Cavity vs. Dorsal Body Cavity a. Ventral (Anterior) i. The front surface 1. Example: The navel is on the anterior surface of the trunk. b. Dorsal (Posterior) i. The back surface 1. Example: The scapula is located posterior to the rib cage. 10. 4 Tissue Categories a. Epithelial tissue b. Connective tissue c. Muscle tissue d. Nervous tissue 11.