Properties of Matter Practice Questions
advertisement

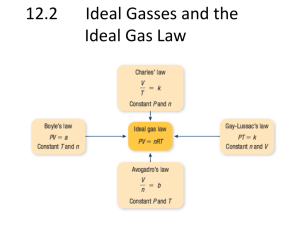
Properties of Matter – Practice Questions 1. Determine the weight of a mass at a location where g = 9.77m/s2 if it weighed 40N at sea level. 2. Determine ϒ if g = 9.81m/s2, V = 10 m3 and ν = 20 m3/kg. 3. If Patm = 100 kPa, the pressure at a point where the gage pressure is 300mmHg is nearest (ɣHg = 13.6ɣwater) 4. 5. 6. 7. A 0.2 m³ container holds oxygen at 70°C and 25 bars. Calculate the amount of oxy- gen in the container if the atmospheric pressure is 1 bar. 8. The temperature of a given gas is -10°C. What are the equivalent Fahrenheit and absolute Kelvin scale readings? 9. If the temperature of the air in a chemistry laboratory is ambient (77°F), what is the equivalent scale in Kelvin? 10 . Calculate the temperature of a fluid when both a Fahrenheit and a Celsius thermometer are immersed in it, under the following conditions: a) the numerical reading is identical in both thermometers and b) the Fahrenheit reading is numerically twice that of the Celsius reading. Express the values in °R and °K 11 Determine the mass and specific volume of argon gas in a vessel at 150 kPa and 20°C. The vessel is spherical and has a radius of 5m. 12 The gauge pressure in an automobile tire when measured during winter at 0°C was 207 kPa. The same tire was used during the summer, and its temperature rose to 100°C. If we assume that the volume of the tire did not change, and no air leaked out between winter and summer, what is the new pressure as measured on the gauge? 13 A pioneer aeronaut is planning the design of a hot-air balloon. What volume of air at 100°C should be used if the balloon is to have a gross lifting power of 200 kg (defined as the mass of displaced air minus the mass of hot air)? The ambient temperature and pressure are 25°C and 1 atm, and the average molecular weight of air is 29 g/mole, whereas that of the hot air is 32 g/mol (due to the presence of some CO2). Properties of Matter – Practice Questions 14 A container having a volume of 2.5 ft³ initially contains oxygen gas at a pressure of 125 psia and a temperature of 75°F. Oxygen then leaks from the container until the pressure drops to 100 psia, while the temperature remains the same. Assuming ideal gas behavior, determine how many pounds of oxygen leaked out of the container. 15 A closed system consists of 0.5kmol of ammonia occupying a volume of 6 m3. Determine (a) the weight of the system in N, and (b) the specific volume, in m3/kmol and m3/kg. 16 If Superman has a mas of 105kg on his birth planet Krypton where the acceleration of gravity is 25m/s2, determine (a) his weight on Krypton, in N, and (b) his mass in kg, and weight, in N, on Earth where g = 9.81m/s2. 17 A town has a 1-million-litre storage capacity water tower. If the density of water is 1000kgm-3 and the local acceleration is 9.81m/s2, what is the force, in N, the structural base must provide to support the water in the tower? 18 A vacuum gage indicates that the pressure of carbon dioxide in a closed tank is -10 kPa. A mercury barometer gives the local atmospheric pressure as 101 kPa. Determine the absolute pressure of the carbon dioxide in kPa. 19 The pressure of the gas contained in a piston cylinder assemble varies with its volume according to the equation p = A + (B/V) where A and B are constants. If pressure is in N/m2 and volume in m3, what are the units of A and B. 20 A cylindrical storage tank having an internal volume of 0.465 m3 contains Helium at 20°C with a pressure of 137 bar. If the tank outlet valve is opened until the pressure in the cylinder is quartered, determine the mass of gas which escapes from the tank assuming the tank temperature remains constant. The molecular formula for Helium is He2. 21 A rigid sealed container holds 2kg of hydrogen at atmospheric pressure (101 kPa) and 30°C. Determine: a) What is the volume of the container? b) How many moles of hydrogen are present? c) What is the molar mass of hydrogen? d) If the container is heated so that the temperature of hydrogen increases by 100°C. What is the change in pressure in the container? 22 23 24 25 Properties of Matter – Practice Questions 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 Find the capillary rise in a tube for water-air-glass interface (Ɵ = 0°) if the tube radius is 1 mm and the temperatre is 20°C. 37 Find the capillary rise in a tube for mercury-air-glass interface (Ɵ = 130°) if the tube radius is 1 mm and the temperatre is 20°C. 38 Properties of Matter – Practice Questions 39 40 41 The glass tube below is used to measure pressure p1 in the water tank. The tube diameter is 1 mm and the water is at 30°C. After correcting for surface tension, what is the true water height in the tube?