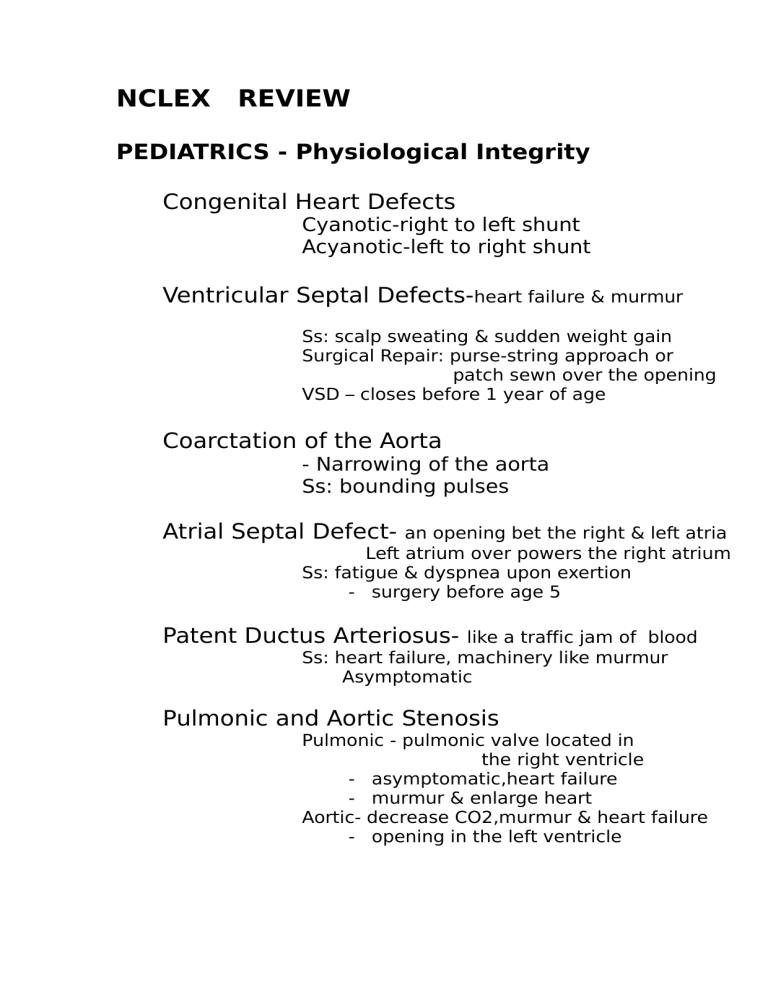
NCLEX REVIEW PEDIATRICS - Physiological Integrity Congenital Heart Defects Cyanotic-right to left shunt Acyanotic-left to right shunt Ventricular Septal Defects-heart failure & murmur Ss: scalp sweating & sudden weight gain Surgical Repair: purse-string approach or patch sewn over the opening VSD – closes before 1 year of age Coarctation of the Aorta - Narrowing of the aorta Ss: bounding pulses Atrial Septal Defect- an opening bet the right & left atria Left atrium over powers the right atrium Ss: fatigue & dyspnea upon exertion - surgery before age 5 Patent Ductus Arteriosus- like a traffic jam of blood Ss: heart failure, machinery like murmur Asymptomatic Pulmonic and Aortic Stenosis Pulmonic - pulmonic valve located in the right ventricle - asymptomatic,heart failure - murmur & enlarge heart Aortic- decrease CO2,murmur & heart failure - opening in the left ventricle Transposition of Great Vessels - pulmonary artery leaves the left ventricle & the aorta exits from the right ventricle. Tetralogy of Fallot - four defects that constitute pulmonary stenosis,overriding aorta right ventricular hypertrophy, vsd PORV Ss: skin bluish in color, heart murmur Rheumatic Fever cause by beta hemolytic strep infection ss: tachycardia,rash,fever,chest pain migratory large joint pain,chorea & skin nodules. *administer penicillin until age 21 - Kawasaki Disease vasculitis infection of the small vessels ss: dry red cracked lips,rashes arms & legs conjunctivitis,strawberry tongue, peeling skin on the palms & soles of feet high fever, unresponsive to antibiotic, impaired swallowing,coronaryaneurysm Gamma Globulin IV 400mg/kg/day x weight in kg Live attenuated vaccine must delayed-polio,MMR - Asthma Ss: chest tightness & dyspnea,distant breath sounds,wheezing episodes,fatigue & wet lungs *theophyllinetoxicitydiarrhea,vomiting,headache Cystic Fibrosis - is hereditary disorder, lung congestion & Infection Ss: positive sweat test, bulky greasy stools, meconium ileus,early chronic dry cough deficient in vits. A,D &K fat soluble vits. Down Syndrome Ss: almond shape eyes,short broad neck protruding tongue,low set ears,broad hands w/ simian crease GERD Ss: frequent or persistent cough,heart burn abdominal pain,recurrent aspiration,anemia Main concern: airway obstruction,fluid and Electrolyte imbalance & apnea Pyloric Stenosis Ss: mild vomiting turned into vomiting that shot across the room,palpable mass RUQ, hungry,crying Hirschprung’s Disease part of bowel there is no nerve cells, no peristalsis in the section of the bowel ss: constipation,foul smelling ribbon like stool abdominal distention - diagnosis established until infant is 6-12 months old - 10x more common in girls than boys - Epilepsy - chronic seizure disorder asso. recurrent unprovoked seizures. w/ Spina Bifida - a congenital malformation of spinal column - many areas of the central nervous system may not develop or function adequately. Ss: club feet,hip dysplexia,latex allergy or sensitivity Scoliosis - affects female 10-13 yrs. Old - brace must be worn 16-23 hrs a day,7 days a week from 6 mos to 2 yrs to correct - after surgery flat position, log rolling ss: assymetrical hemline,unequal leg lengths, morethan 5 degree deviation on scoliometer Cerebral Palsy - abnormal muscle tone & coordination,spastic movement in one or more extremity, and disturbances in gait & abnormal posture. *ORTALENIS- click hip dysplasia,head of femur displaced from acetabulum,unequal leg lenght ss: fluid volume deficit, altered nutrition,ineffective airway Reye’s Syndrome - mild viral infection, ICP Encepalopathy Varicella chicken pox risk to develop Reye’s Ss: viral URTI,severe vomiting,liver dysfunction, fever, cerebral edema & increased ICP,irritability, agitation * Avoid aspirin administration w/ viral infection Bronchiolitis - bronchioles become inflammed - cause by a Respiratory Syncytial Virus RSVRSV- high affinity for respiratory tract mucosa - prevalence in winter & spring *Ribavirin – antiviral used to treat bronchiolitis Caused by RSV VIR meds means antiviral Ss: wheezing in auscultation Intussusception - nephrosis of bowel tissue - commonly occurs in male 3 & 5 yrs. old Ss: vomiting,lethargy,sudden acute abdominal pain, sausage shape abdominal mass,bloody stool or jelly stool Celiac Disease - poor food absorption esp. gliadin - patient unable to digest gliadin a by product of gluten *Serum anti-gliadin antibody- diagnostic test for Celiac disease *Gluten Sensitive Eneteropathy- other name Ss: vomiting,diarrhea pale & watery,abdominal distention,foul smelling stool Diet: No B.R.O.W, iron supplements,vits ADEK in water soluble Cleft Lip and Palate - cleft lip repair at 2 months - cleft palate repair at 2 years Sickle Cell Disease - cell halfmoon shape, blood O2 decrease - common to African-Americans - cause of anemia- an imbalance bet. Red cell destruction & production - 12 to 20 days RBC life span - avoid overheating during physical activities Ss: hypoxia, organ dysfunction due to ischemia and infarction,painful episodes Esophageal Atresia & Tracheoesophageal Fistula - infants do not have meconium because saliva cannot enter the stomach ss: 3 C’s – coughing, choking & cyanosis Tonsillitis - inflammation of tonsils, hinders swallowing and breathing ss: sorethroat,bad breath,mouth breathers snores acute – fever chronic – apneic Epiglottiditis Ss: sit upright position lean forward,chin thrust out tongue protruding *Haemophilus Influenza-B Hib- prevention for epiglottiditis ORTHOPEDICS Fracture Ss: swelling,intense pain shortening of extremities and limited mobility Cast Care Traction Skeletal traction- buck’s traction,russel Steinman pin,crutchfield Halo vest,Gardner-wells tongs Skin traction Total Joint Replacement Osteoarthritis Ss: presents w/ Heberden nodes or Bouchard’s nodes experiences loss of ROM,occurs in weight bearing joints - ESR,CBC,C-reactive protein det. Accurate diagnosis - Corticosteroids is not prescribed Rheumatoid Arthritis - auto immune disease,membrane around joints inflamed,smaller joints - cause by virus/bacterial infection - ESR & CBC,C-reactive protein and Rheumatoid factor,ANA & Antibody test - DMARDS-Disease Modifying Anti RheuMatic Drugs-infliximab (Remicade) Etanercept (Enbrel),methotrexate (rheumatrex) Ss: weight loss, morning stiffness,blateral swollen & tender joints Systemic Lupus Erythematosus - auto immune disease that attack diff. organs of the body - lab. to det. high levels of antinuclear anti body & Coomb’s test,high level of C-reactive protein - stress,sunlight exposure,infection can contribute to lupus - NSAIDS,corticosteroids,reduce stress get plenty of rest & exercise are the treatments ss: exacerbation & remissions,mild to extreme fatigue sudden unexplained weight loss, pericarditis, nervous system/mental health problems,hairloss Raynaud’s phenomenon kinds of Lupus - Discoid Lupus- butterfly rash skin Chemically /drug- induced lupus-hydralazine Procainamide Neonatal lupus- newborn Gout - acid crystal build in joints - “TOPI” accumulation of crystals big toe - Over production of uric acid,reduce ability of kidney to get rid of uric acid - Diabetes, obesity & sickle cell anemia increase the risk - May cause join deformity & limited motion - Synovial fluis analysis,joint x-rays, uric Acid elevated Men-6mg/dl women 5mg/dl - diet low in purines,NSAIDS, corticosteroids, clochicine, indomethacin allupurinol,naproxen Ss: pain is throbbing, crushing, excruciating,warmth, tenderness & redness of joints Amputations - elevate on pillow for first 24 hours - prevent hip/knee contractures - limb sock must be worn under the prosthesis Crutch Walking - bear your weight to hands not in armpit - position crutches 4 inches to side & 4 inches to front - Swing-through-gait, three-point-gait, Swing-to-gait are the 3 types of technique - Tripod gait is used when client unable to walk Common drugs for Orthopedics Anti-resorptive agents – ex: Calcitonin Biophosphonates - ex: Fosamax Bone forming agents - ex: Flouritab, androgens NSAIDS - ex: Celebrex, Mobic Antineoplastic agents - ex: Methotrexate MATERNAL & CHILD Physiological Adaptation Psychosocial Adaptation Signs of Pregnancy Family Planning Antepartum hCG – biological marker of pregnancy Alpha Fetoprotein- present when the baby amniocentesis neural tubal defect Maternal Hypertension – most common cause of fetal growth retardation Ectopic Pregnancy - zygote implants outside the cavity - Intra abdominal bleeding is common cause of ectopic pregnancy. Ss: sharp localized pain when the cervix is touched during vaginal exam, sudden acute abdominal pain , Keh’r sign – pts. lie down there is a pain in the tip of shoulder due to accumulation of fluid in the peritoneal cavity,due to rupture of zygote Methotrexate (Trexall) – treatment a folic acid antagonist, inhibits cell growth, allowing the tube to be saved Laparoscopy – small incision into the tube & removal of embryo Hyperemesis Gravidarum - increased BUN & decrease urinary output - ketoacidosis-breakdown of fat stored to make metabolic needs. - high level of hCG & estrogen Hydatidiform Mole - absence of FHTs, grape-like clusters of vesicles, vaginal discharge that may contain vesicles,uterus enlarge to fast. - Asian women at risk 45 yrs and above. - hcg should be measured weekly until normal then rechecked every 2-4 weeks then every 1 to 2 months for 6 months to 1 year Interventions: surgical removal of neoplasm,monitor ring for pre-eclampsia & choriocarcinoma , hysterectomy Incompetent Cervix - cervix dilates prematurely usually occur during 4 mothns of pregnancy - repeated spontaneous & painless second trimester pregnancy. Preeclampsia Ss: suddenweight gain,swollen hands and feet, Headache, and blurred vision, hypertension Proteinuria,anasarca, Severe if diastolic more than 110, Mild 140/90 Weight 2 kilos/week Magnesium sulfate is the drug of choice and should be monitored for toxicity done every 1-2 hrs. - diminishes neuromuscular transmission, promotes maternal vasodilation and has anticonvulsant effect. Diminished deep tendon reflexes sign of Magnesium sulfate toxicity. Placenta Previa - painless vaginal bleeding, implantation of placenta low Placenta Abruptio - sharp sudden abdominal pain - premature placental separation\ - causes, cocaine use, PIH, manual vacuu aspiration, abortion procedure,rapid decompression of the uterus multipara domestic violence Premature Labor can sometimes be stopped by hydrating the mother and by treating vaginal & UTI - Bethamethasone,celestone IM injection to help maturation of the lungs - Labor & Delivery Prolapsed Umbilical Cord - knee-chest position - c-section immediately - cover umbilical cord with saline bandage Post Partum - hydrop’s fetalis a serious hemolytic reaction baby experience severe anemia cardiac decompensation,edema - Rhogam can give to mother w/ Rh+ baby, After spontaneous or induced abortion, Amniocentesis or chronic villi sampling, Bet 28 & 32 weeks of gestation,RH- with Bleeding episodes. - Serum bilirubin normal values .2 to .6 - Golden-colored amniotic fluid is severe Fetal disease asso. w/ Rh factor - Direct Coomb’s test is done w/ the mother to measure the number of antibodies in her blood Indirect Coomb’s test is done on baby it tells if there are any antibodies stuck to the red blood cells. Newborn Care - Ballard scale, a newborn assessment maturating scale - Respiratory Rate 30 to 60 breaths/min with 10 seconds apnea - Red reflex test serious visual defects is performed in small dark room looking at the retina there’s a red reflex equally red to roll-out any defects of cornea. CARDIAC Physiological Integrity Cardiac Rhythms Conduction System ECG Complex ECG Grid Lead Placement Snow over grass- right side Smoke over fire - left side Interpreting Rhythm Strips Normal ECG Concepts Normal Sinus Rhythm Sinus Bradycardia Sinus Tachycardia Supraventricular Tachycardia SVT Atrial Fibrillation Atrial Flutter Premature Ventricular Contractions PVC’s Venticular Tachycardia Ventricular Fibrillation Asystole First Degree Block Type 1 Second Degree AV Block Mobitz 1, Wenckebach Type 2 Second Degree AV Block Mobitz 2 Third Degree AV Block Complete hear block Congestive Heart Failure Left sided Heart Failure Ss: blood tinged frothy sputum dyspnea, cough, crackles pulmonary congestion, irritability, anxiety Right sided Heart Failure Ss: peripheral edema ascites, nocturia, hepatomegally Monitoring/testing: BNP & hemodynamic monitoring - Cardiac marker for CHF Echocardiogram & Chest X-ray Allen’s test Myocardial Infarction Ss: shortness of breath, crushing pain that radiates to his neck and left arm decrease CO2, increase WBC, increase temp. ST segment depression, T wave inversion,Q waves Laboratories/testing: CPK MB, LDH, Troponin q8 hrs Coronary arteriogram & 12 lead EKG MUGA Scan-used to measure heart function by determining the ejection fraction, this is the percentage of blood ejected from the heart w/ each beat Management: MONA- Morphine-Oxygen-Nitroglycerine-ASA Fibrinolytics- are used to dissolved clots & reduced the size of infarction - must administered 6 hrs post MI - before administered insert 2-3 large bore peripheral IV’s - monitor for bleeding, neuro vital signs watch rhythm PTCA- procedures performed on a double vessel disease. Anti-embolism stocking- to prevent venous stasis and thrombophlebitis. Repolarization- ventricles are resting & then fill up with blood Dressleis Syndrome- combination of pericarditis pericardial effusion & constrictive pericarditis. Immune symptoms reaction Angina Pectoris Ss: dull chest pain Treatment: Beta-blockers & calcium channel Blockers ends with pine Ex: Procardia (Nifidipine) Norvasc (Amlodipine) Cardiac Tamponade Ss: tachycardia & distended neck veins Pallor, cardiac rhythm changes Treatment: elevate head of bed 60 degrees Vessel Insufficiency Chronic arterial Insufficiency Chronic venous insufficiency Deep Vein Thrombosis DVT SS: tenderness and warm to touch, increase pain with ambulation,no pulse to the affected extremity, dull ache in calf, one side swelling, heavy sensation Causes of DVT: CHF,MI,obesity,fractures,sepsis Hematological disorder,pregnancy,malignancies, Immobilization Treatment: Doppler of the lower extremities, Venography- due to any clog artery Hypertension Buerger’s Disease SS: numbness & tingling sensation of the toes pale finger tips, weak peripheral pulses,ischemic ulcerations, intermittent claudication Tx & Mngmt: smoking cessation, promotion of Isometric exercises. Raynaud’s Phenomenon SS: hand & fingers turning white Causes: smoking & stress Precautions: over the counter cold remedies such As Sudafed,clonidine,migraine, meds Contain ergot alkaloids Endocarditis Ss: fever, clubbing of fingers, malaise, cardiac murmurs, anorexia Tx: prophylaxis,antibiotics,oxygen,anticoagulants, antipyretics Types of Shock 1. Hypovolemic- volume reduction ex: bleeding, burns 2. Cardiogenic – unable to circulate ex: dysrythmias, MI, CHF 3. Neurogenic – loss of vasomotor tone ex: spinal cord Injury, spinal anesthesia 4. Septic –dilation of blood vessels ex:gram negative infection 5. Anaphylactic- antigen-antibody reaction ex: transfusion Reaction,allergies, insect bites. RESPIRATORY Physiological Adaptation Thoracentesis - removal of fluid from pleural space 50cc H2O Procedure: take chest x-ray & vital signs position the client sitting up over bedside table or lying on unaffected side with HOB at 45 degree tell client not to cough,breathe deeply or move during the procedure Chest Tubes - reestablish a negative pressure done when there is a fluid build-up in lung lung cllapse spontaneous collapse Fluctuation will occur when the suction is working properly - bubbling becomes continous,vigorous or excessive it means there is an air leak in the system - inserted at 2nd ICS at the midclavicular line Tension Hemothorax- complete collapse of the lung - an be fatal as the accumulating pressure compresses vessels decrease venous return and decrease cardiac output Hemothorax – is a collection of blood in the pleural cavity Pneumothorax – is a collection of air/gas in the pleural cavity Fracture of Sternum/Ribs Flail Chest – tachycardia,assymetrical, multiple fracture End expiration – the vent exerts a pressure into the lungs to to keep alveoli open Ventilator – improves gas exchange and decreases work of breathing PEEP Positive in Expiratory Pressure – expands the thorax and realign the ribs, denotes amount of pressure in the end of expiratory pressure. BIPAP Bi level Positive airway Pressure - is used often with pulmonary edema but may be done prior to Intubation. CIPAP Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Lung sounds PEEP,CIPAP,ventilator - nursing assessment for Pulmonary Embolism Ss: shortness of breath, cough & increase heartrate, Hypoxemia, chest pain,hemoptysis, angina - it can occur when a clients become dehydrated - clients who have venous stasis - women who take birth control pills Laboratories/Test: D-dimer – a lab. work detects presence of high fibrin clot, thrombus VQ Scan – ventilation perfusion scan, inject isotope to measure ABG TX: oxygen, heparin or Coumadin thrombolytics Surgically placed filter in vena cava. warfarin, Chronic Obstructive Airway Disease Ss: cough & sputum production Lab/Test: chest x-ray, chest CT, pulmonary function Tests, ABG Blue- patients suffering from chronic bronchitis Pink – patients suffering from emphysema Tx: bronchodilators,theophylline,inhaled/intravenous/ oral steroids, & antibiotic. Emphysema - it destroys alveoli - it narrows & collapses small airways - it causes the lungs to lose elasticity Tx: high in carbohydrates, increase fluid intake As alveolar wall dies, there is less surface for gas exchange Asthma Types of asthma: 1. Emotional – cause by person 2. Extrinsic – caused by dust,mold,pets 3. Intrinsic – common cold, allergens 4. Mediated Pneumonia Tuberculosis Endotracheal Tube Goal: to position the end of ETT 2 cm above the bifurca-tion of the lungs or the carina Special Double Lumen ETT – have been developed for lung -and other intrathoracic surgery -this tubes allow one lung ventilation while the -other lung can be collapsed to make surgery -easier. -ETT with a suction port are proven to decrease - the amount of bacteria which could possibly -grow in the secretions Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome -alveolar spaces are filled with fluid -prone position, it makes more alveoli accessible -ABG indicators if ARDS is improving. NEUROLOGY – Physiological Integrity Neurological Assessment Frontal Lobe- damage, changes in behavior Neurological assessment: Mental Status- most important indicator Pupillary changes- 2-6mm normal pupil Motor strength & coordination Corneal assessment Vital Signs- widening pulse pressure when there is Increase ICP Movement- is the lowest move, speech is the highest level of brain neuro function Noxious Stimuli Reaction- the client will pull away from pain Stimuli used: sternal rub,supraorbital pressure,nailbed pressure, trapezius squeeze Oculocephalic Reflex test (doll’s eye reflex) & Oculovestibular Reflex test (Ice waterCaloric test)– performed assessing Brain Stem Function Babinski Reflex – stroked on the lateral part of foot of an infant under 1 year old + is ok, - is bad over 1 year old + is bad, - is ok Negative- curled down Positive – curled up Reflex table – 0 = absent 1+ = present,diminished 2+ = normal 3+ = increase but pathologic 4+ = hyperactive not necessarily Computed Tomography CT Scan - identify certain lesions - takes pictures in slices - he will need to take his head still - consent due to the dye Magnetic Resonance Imaging MRI - identifies abnormalities in soft tissue - using a magnet last to 1hour - client must void prior to exam - clients w/ claustrophobia cannot receive this exam - clients can talk & hear during the scan - client will hear a thumping sound Cerebral Angiography - catheter inserted w/ a dye to the brain consent due to the dye metallic taste in mouth warm sensation during the procedure clients well hydrated during the procedure. Complications: - risk of embolus - check for pulse, hematoma & change in LOC - 12-24 hours of bed rest Myelogram - is an x-ray of spinal & sub arachnoid space - air & water base - NPO 8-12 hours - Does not require a heavy sedative - Dye is injected to sub arachnoid space - Trendelenburg position for Air - 30 to 50 degrees for water - Must be flat in 6-8 hrs. After procedure observe for the Signs: Stiff neck & chills Brudzinski’s sign- when neck is flexed your knee & hips is also flexed. Kernig’s sign- flex the knee the opposite leg cannot extend Photophobia & headache Electroencephalogram EEG - diagnose seizure disorder records the electrical activity of the brain helps in screening for a coma 3 flat EEG reading indicate brain death Nursing care: - put patient in dim light & quiet room - no caffeine alter the results - no sedatives 2-3days prior alter the result hold sedatives Pre-procedures: - medicated w/ a mild sedative - may have not caffeine - eat a light breakfast - we may flashlights in the face Lumbar Puncture - performed when patient is on unexplained fever and elevated WBC - invasive procedure - punctured site is 3rd & 4th lumbar subarachnoid space - knee chest position, fetal position lie on right side - 4-8 hours flat on bed to prevent spinal Headache, post procedure - Fluid &blood patch- pull out blood use it & inject at pain area - Normal CSF- clear, no RBC - Abnormal CSF- cloudy, increase protein, & WBC Performed when: check for blood, measure pressures,admi-nister drugs intrathecally. Brain Herniation - cause a sudden decrease of ICP - the brain tissue is pulled down through the foramen magnum Epidural Hematoma - arterial bleed - gain & lost of consciousness for minutes - pts. See stars Tx: burr holes,remove the clot and control ICP Subdural Hematoma - venous bleed Acute & fast – s/s bet. 24 to 72 hours after slow bleed, nonacute bleed Tx: remove clot to control ICP Sub-acute - s/s bet 72 to 2 weeks w/ rapid Chronic Scalp Laceration- infections is the problem Skull Injury - may or may not damage the brain ss: Battle sign-bleeding over the mastoid Racoon eyes-peiorbital bruising Cerebrospinal rhinorrhea Basal skull fracture- bleeding from eyes, ears, nose, throat fracture at the base of the skull Open fracture – dura is torn Depressed fracture – is usually require surgery Concussion Ss: headache, dizziness, seeing spots diff. waking up or speaking, confusion, severe headache & vomitting Contusion - the brain is bruised w/ a possible surface hemorrhage Alzheimers - progressive disease, irreversible, loss of cerebral function due to cornical atrophy - begins 40 to 65 y.o. , 8 to 10 years onset to death Early stage- memory loss, subtles personality,diff abstract thinking Middle stage- language is impaired, difficulty w/ motor activity Final Stage- complete loss of language Rohin’s stage- loss of bowel & bladder control Ss: progressive decline in recent & remote, aphasia, agnosia cannot recognized memory, cannot learn new things, recall, recognized information Nsg. Management: promote clients independence Promote contact with reality Establish a routine J- impaired judgement, inappropriate O- orientation confused C- confabulation, inventing stories, defense mechanism A- affect M- mentally impaired Parkinson’s Disease - decreased production of dopamine ss: mask-like facial expression, fatigue, stiffness, rigidity & diff. rising from sitting position TRAP- tremors,rigidity,akinesia,poor balance Lab/test: EEG,MRI,CT Scan of Tx: levodopa, anticholinergics (akineton), antihistamines -lessened rigidity & tremor Laminectomy - excision of vertebral arc, herniated disc - nurse must assess for circulation & motor sensory checks, dressing, bowel & bladder function Cervical Laminectomy- level of consciousness Lumbar laminectomy- circulation, motor, 5 p’s, pulse,pallor Amyoptrophic Lateral Sclerosis LOU GEHRIG’S Disease - the brain is fine but the body deteriorates - is a degeneration of upper & lower neurons ss: mildly clumsy, weakness of upper & lower extremities atrophy of the muscle & extremities, trunk Tx: muscle relaxants for spasticity, speech theraphy Multiple Sclerosis 3rd leading causes of death in the US - Destruction of myelin sheath of the brain - Demyelination of white matter throughout the brain and spinal cord - Motor- weakness, paralysis,spasticity, gait disturbances Cranial nerve – blurred vision,dysphagia, diplopia, facial Numbness Cerebellar – dysarthria, tremor, incoordination, ataxia, vertigo Sensory – paresthesias,decrease proprioception Cognitive – decrease ST memory, difficulty w/ new information word finding difficulty, short attention span Tx: lumbar puncture, MRI, evoked potentials or response ACTH Adrenocorticotrophic hormone, physical the raphy , occupational theraphy, encourage exerci -se Glasgow Coma Scale - measures level of consciousness - involves 3 responses, eye opening, verbal response, best motor response Coma – is defined as, not opening eyes, not obeying commands, not uttering un derstandable words Coma clients is 90% less than or equal 8 8 is the critical score 8 at 6 hours, 50% die > 9 not in coma 9-11 moderate severity > 12 is a minor injury Cerebrovascular Accident Stroke Risk Factor: uncontrolled hypertension Smoking & obesity Increased blood cholesterol Chronic atrial fibrillation African-american males over 65 y.o. Transient ischemic attack- double vision, left side of the body paralyzed 2 types of stroke: Hemorrhagic stroke – blood vessel rupture with bleeding into the brain, hypertensive & older patients Ischemic stroke – slower onset, caused by cerebral embolism,atherosclesrosis Subarachnoid hemorrhage- cause by a rupture of intraCranial aneurysm Epidural bleed- artery is involved Subdural bleed – vein I sinvolved Guillain Barre Syndrome Ss: last for 6 months need mechanical ventilation require intubation recovery period for few weeks or few years rubbery legs, weakness progressive upward over a period of two days, arms & facial muscles have been affected Myasthenia Gravis - problem in neurotransmitter, myelin sheath is intact, but decrease acetylcholine production ss: drooping of eyelid, speech and swallowing disorder, blurred vision, sensation remained intact Head Injury Intracranial Pressure ICP Spinal Cord Injury PSYCHIATRY – Psychosocial Integrity Depression Anxiety Mania Post Traumatic Stress Disorder Schizoprenia Suicide Paranoia Panic Disorder Phobia Hallucinations Personality Disorder Obssesive-Compulsive Disorder Dissociative Disorders Alcoholism Anorexia Bulimia Electro-Convulsive Therapy ECT Antidepressants Antipsychotics Anticonvulsants ENDOCRINE Hyperthyroid Graves Disease Hypothyroid Myxedema Parathyroid Problems Cushing’s Disease Diabetes ONCOLOGY Lung Cancer Laryngeal Cancer Bladder Cancer Stomach Cancer Cervical Cancer Uterine Cancer Breast cancer Colorectal cancer Prostate cancer Branchytherapy Internal Radiation Teletheraphy & Beam Radiation External Radiati Chemotherapy GASTROINTESTINAL – Physiological Adaptation Pancreatitis Ss: abdomen,bruising severe abdominal pain RUQ, rigid around umbilical or flank area, ascitis, abdominal distention -worsen after eating & lying flat -decrease hemoglobin & hematocrit -alcohol consumption is the number one cause -no morphine can cause spasm of odi spinchter -give calcium supplements Fecal occult blood- blue litmus paper signs of bleeding Medicines: Zantac – decrease acid productions,H2 antagonist Antacids – counteracts stomach acidity Protonix – decrease gastric acids,privacid nexium Carafate- barriers of acid Cirrhosis -liver cells necrotic, destroyed & replaced by scar tissue -increase ammonia level, fiteb breath, bleeding tendencies, -risk for esophageal varices & portal hypertension -increase bilirubin in urine & increase SGOT & SGPT -decrease serum albumin & cholesterol -impaired aldosterone metabolism results to edema -providing thiamine & B12 -bleeding precautions, avoid Im injections & aspirin -measure abdominal girth -do not give narcotics -diet must be low in protein & sodium LV Shunt- remove fluids in peritoneal cavity Ss: abdominal pain, jaundice, anemia, ascitis, clay colored stool, splenomegally, chronic dyspepsia, firm & nodular liver Diverticulitis -small inflamed protruding sacs in the colon that have ruptured -causes impacted stools, history of constipation, Low fiber & high carbohydrates ss: left lower quadrant pain,chills,fever,nausea and vomiting Hepatic Coma -is diagnosed by examining the serum ammonia level -prescribed lactulose (Cephulac) & Neomycin SO4 -decrease protein in the diet,monitor serum ammonia level -recommend cleansing enema Ss: confusion & delusion,motor changes,difficult to Awake,asterixis flapping tremor,fetor hepaticus Musty odor, increase ammonia level Bleeding Esophageal Varices -liver is damage and that collateral circulation has formed into 2 of 3 places are rectum,stomach & esophagus -portal hypertension, increase blood in the liver -coughing & straining can cause rupture of the Varices -Sandostatin-works to lower the BP in the liver -Sengstaken Blakemore tube in the bed side -administer oxygen Ss: black tarry stools,paleness,lightheadedness Ulcerative Colitis -inflammation of ascending colon & rectum -condition affecting the large intestine -low fiber diet to limit motility -avoid meals that are cold -steroids to decrease the inflammation Ss: rectal bleeding,diarrhea,bloody or mucosy stool fever & loss of appetite,constipation,weight loss anemia,rebound tenderness test: colonoscopy,barium enema,sigmoidoscopy CBC Schilling Test- to test Vit. B 12 in urine Koch’s pouch- ileostomy, there is internal reservoir (stoma & bag) Colostomy- permanent stoma is red/pink - irrigate sametime everyday after meal Ileostomy - temporary don’t irrigate as much - no raw vegestables,nuts,grains & peas Chron’s Disease -iflammation or ulceration of digestive tract,chronic & relapsing ss: blood in stool,rebound tenderness,cramping & dehydration,anemia,diarrhea w/ steatorrhea, cramping after meals,abdominal pain,vomiting & fever Partial Bowel Resection – to allow the intestine to rest and heal Transvers- semi-soft stool Descending – formed stool Ascending – liquid stool Appendicitis -associated w/ diet low in fiber -elevate head of bed after any abdominal surgery Ss: increased WBC,sharp pain on right side,nausea & Vomiting,rebound tenderness Ulcers -pain that is worsenes w/ food -pain & burning worsend at night & lying down -mainly found in males -can be found in the stomach,esophagus,duodenum -avoid spicy foods & caffeine,stop smoking -avoid extreme temp hot or cold Gastric ulcer-pain 30 mis. to 1 hour after eating meal when vomit the pain subsides. Duodenal ulcers- pain 2 to 3 hrs. after eating as long there is food in stomach theres no pain Gastrectomy- give vit B12 for life Billroth I – portion of stomach connect to duodenum Billroth II – large potion of stomach connect to duodenum Peritonitis -board like abdomen,low urine output,,nausea & vomiting Dumping Syndrome -increase circulation of stomach -give complex carbohydrate,avoid simple carbohydrates, high fiber -is more common in Billroth II -recumbent position, drink bet meals -lie left side after meals,eat high fat & protein -decrease stress Ss: cramping,diarrhea,weakness Hiatal Hernia -the hole in the diaphragm is too large,the stomach moves up into the thoracic cavity -small protrusion close to the navel -causes, congenital abnormality,trauma,surgery -small frequent meals,elevate head of bed,take small bites,avoid spicy foods Ss: abdominal mass soft can be palpate w/ out pain, fullness after eating & regurgitation Hyperalimentation TPN -need to change the tubing with each bag every 24 hours -can be hung for 24 hours -taper off TPN when discontinuing -needs to be check by 2 nurses before each bag is hung -put in pump -other medications cannot be infused, only insulin, Lipids, K+ -can be mixed daily -IV bag should never be covered -infection can be frequent complication Laboratory values to be monitored: Blood glucose,ketones,BMP,magnesium Dobhoff Tube -a small bore NG feeding tube not attached to suction -more comfortable & less complications -can remain place for weeks Central Line -have client in trendelenburg -rolled towel to middle of back -air from getting in the line,clamp it off -cap the end of tubing,cover the end w/ syringe -position the patient on the left side in case air will get into the line -post insertion chest xray performed to ensure proper placement -10ml syringe use in central line Diagnostic Tests Barium Enema -drink clear liquids -take laxatives or enemas until clear -ensure post procedure bowel movement Liver Biopsy -PT/INR,PTT prior to procedure -position pt supine w/ hand behind head -have client lie on affected side for 8 hours post procedure Paracentecis -have pt. sit in high fowlers position -have pt. empty his bladder prior to procedure -the fluid removed will be yellow -monitored for signs of shock GENITOURINARY – Physiological Adaptation Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia -frequent waking at night to urinate -urination -serum PSA & urinalysis -PSA secreted by pituitary gland Medicines: Prazosin (minipress) – helps the urination urgency Doxazosin (Cardura) – helps the symptoms of BPH Prostatectomy- normal to pass urine in blood tinged & blood clots & tissue debris Percutaneous Renal Biopsy -instruct the pt to restrict food & fluids for 8 hrs before the test -administer mild sedatives 30 to 1 hour before procedure -check vital & inform pt. to void before procedure -place pt in prone position -observe for bleeding & hypotension Nephrotic Syndrome -leaking of the protein into the urine -perform U/A,glucose tolerance,serum protein, Serum albumin,renal biopsy -edema,swelling around eyes,extremities & abdomen -circulating blood volume decrease causing kidney to activate its Renin Angiotensin cascade,aldosterone is produce to retain sodium & H2O -Corticosteroids,prednisone & Diuretics drug of choice Acute Glomerulonephritis -sorethroat,headache & lower back pain -protein in the urine,increase BUN & creatinine, hematuria & hypertension -strep infection is the main cause -common bet age 6 to 7 yrs. old -antibiotics,bedrest & increase carbohydrates in diet -decrease protein & sodium in the diet and dialysis -reddish brown urine Renal Failure -sudden loss of kidney function resulting in electrolyte imbalance 7 retention of nitrogenous substance -during oliguric phase the patient is in a fluid volume excess -diet should be in high carbohydrates -low protein,sodium,potassium & phosphorous Urinary Tract Infection -fluids morethan 3,000 ml, acid ash diet -avoid coffee & tea -Medicines: Ofloxacin (Floxin) Nitrofurantoin (Macrodantin), Pyridium Cotrimoxazole (Bactrim) Hemodialysis -access route are: External AV shunt,fistula,femoral/ Subclavian cannulation -fistula access 3 months to mature -must be done 3-4 times a week -during treatment period monitor for: depression, suicidal tendencies,electrolytes & BP -bruit & thrill must be assessed before accessing hemodialysis access ports -cathflo must be used if pt allergic to heparin -decrease protein, sodium & potassium in the diet -pt. w/ unstable cardiovascular system cant tolerate hemodialysis Peritoneal Dialysis -ambulatory -dialysate is warm to increase blood flow -patients who get peritoneal dialysis cannot tolerate hemodialysis -possible complications are: peritonitis,respi. Diff. protein loss -cloudy drainage,there is an infection, it should be pink tinged color -if the fluid does not come out, turn the pt side to side Intravenous Pyelogram -NPO 8 hrs before the test -sitting straight up during procedure -after procedure, increase fluids,apply warm soaks if hematoma develops Cystoscopy -involves a lighted scope which is used to visualize the bladder -consent, anesthesia, a sedative and enema can be used -used to diagnosed & evaluate urinary tract disorder, enlarged prostate,recurrent bladder infection -notify doctor if there is still blood in the urine after 3 days -expect burning on urination Ultrafiltration -only pulls off water -has the same principles applied as hemodialysis -may be utilized w/ peritoneal dialysis or hemodialysis Kidney Stones Renal Calculi -KUB & IVP -increase fluid intake and modify his diet,avoid high contain of calcium & oxalate -strain his urine Calcium Oxalate: beer,rhubarb and wheat germ, spinach chocolate Calcium Phosphate: milk & milk products, foods high in calcium, meats, grains & cranberry Uric Acid: avoid Vit C supplements, corn & lentils EXtracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy (ESWL) Pelvic Inflammatory Disease -history of menses,sexual habits, contraceptives Used -look for signs of hypovolemia,hypotension & fever -Medicines: Quinolones,cephalosporins & tetra-cyclines, penicillins Continous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis CAPD -increase protein & fiber in the diet -ambulatory walking around w/ peritoneal dialysis going on -complications: hernia, peritonitis, low back pain, nausea Continous Renal Replacement Therapy CRRT -little bit longer than hemodialysis -is less aggressive -has only 80ml of blood in the machine at any given time Hemoglobin: male 13-18 Hematocrit: 42-52% Urine Specific gravity: 1.005-1.029