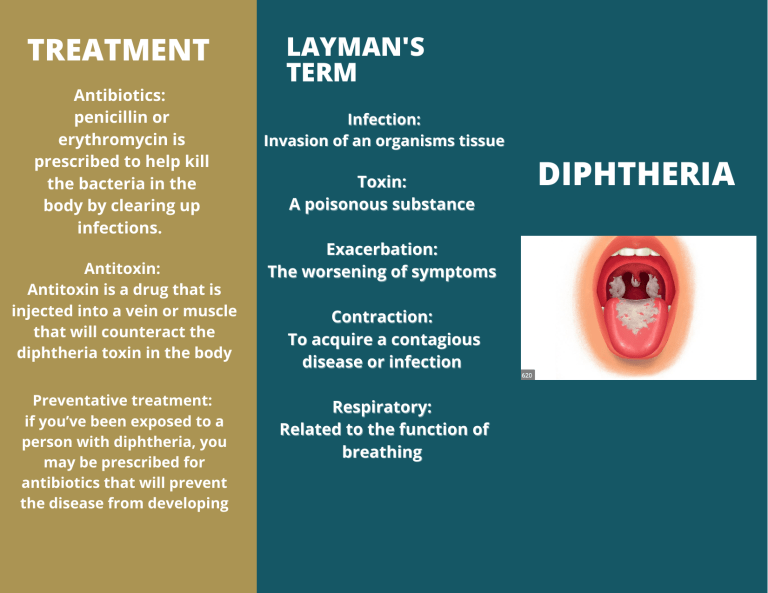
TREATMENT Antibiotics: penicillin or erythromycin is prescribed to help kill the bacteria in the body by clearing up infections. Antitoxin: Antitoxin is a drug that is injected into a vein or muscle that will counteract the diphtheria toxin in the body Preventative treatment: if you’ve been exposed to a person with diphtheria, you may be prescribed for antibiotics that will prevent the disease from developing LAYMAN'S TERM Infection: Invasion of an organisms tissue Toxin: A poisonous substance Exacerbation: The worsening of symptoms Contraction: To acquire a contagious disease or infection Respiratory: Related to the function of breathing DIPHTHERIA CAUSES Bacteria: Diphtheria is caused by strains of bacteria called Corynebacterium Diphtheria that make a toxin. SYMPTOMS: -Sore throat and hoarseness TESTS Swab test: Doctors swab the back of the throat or nose and test it for bacteria that causes diphtheria. -Difficulty breathing or rapid breathing A doctor can also take a sample from an open sore or ulcer and grow the bacteria -Fever and chills Contaminated people of household items: Diphtheria can be contracted from handling an infected person items that could be contaminated with bacteria Airborne droplets: when an infected persons sneeze or cough people may inhale the bacteria -Swollen glands -Sore throat and hoarseness -Nasal discharge -Tiredness